Never before seen strange 5,000-year-old clay figurine with a tattooed face and bone mask
In Russia, a macabre was found it is a 5000-year-old mass grave containing the bodies of five decapitated individuals. Archaeologists suspect the ancient Odinov culture in Siberia were head cultists.
Professor Vyacheslav Molodin said that the graveyard of Ust-Tartas 2 in the city of Novosibirsk comprises three decapitated adults and two teenagers. It is assumed that their heads were cut after death – and then kept for worship.
‘Odinov people definitely had a head or skull cult,’ said the archaeologist.
‘It is a characteristic feature of this culture that they had graves with cut off heads. They were perhaps put into a sanctuary, or buried separately in a different way.’
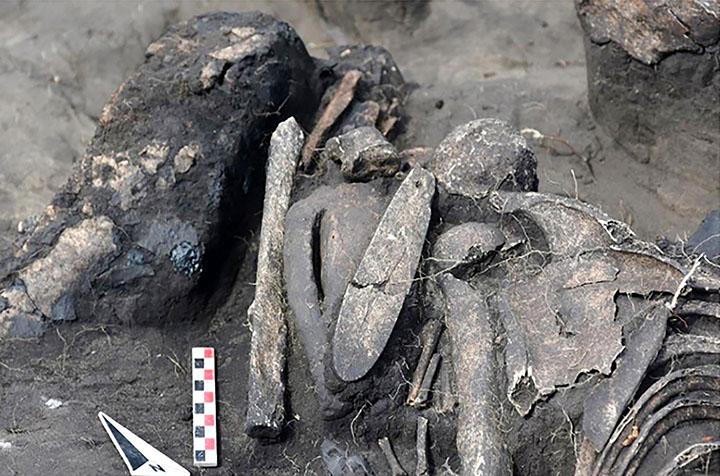
In another grave on the same site, an astonishing figurine has been found on the shoulder of an ancient woman who was laid to rest with her head on a man’s abdomen.
The skeletons of the ancient presumed lovers were cocooned together under a birch bark blanket for five millennia, but in this case, their heads were not severed.
The man lay on his back, she on her front, facing him in a timeless embrace. Perched on the female’s shoulder was a palm-sized clay figurine with a tattooed face.
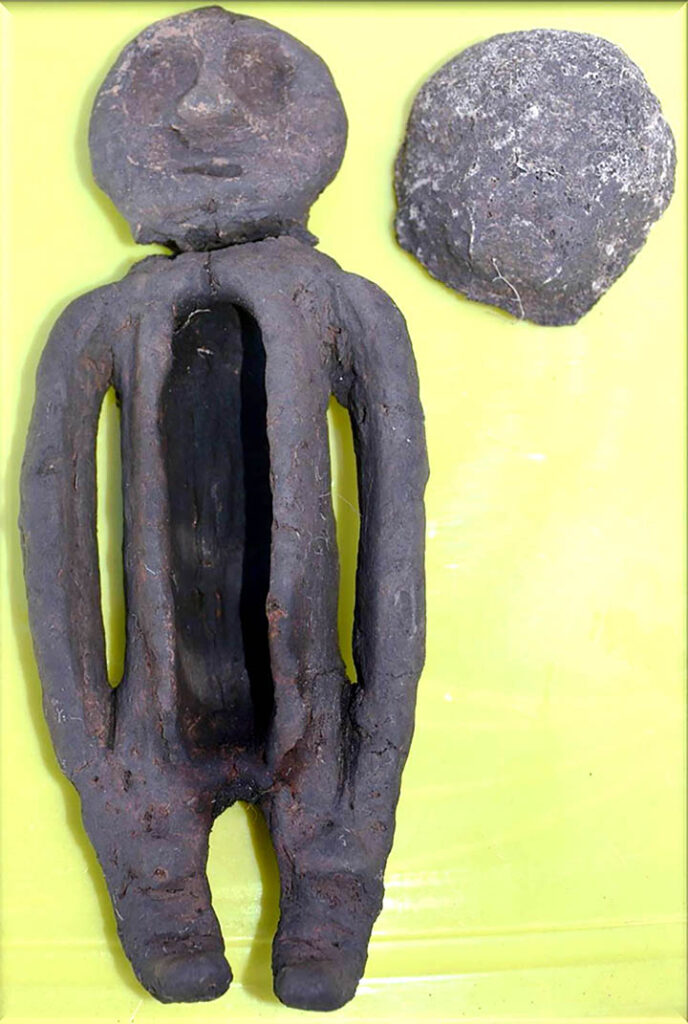
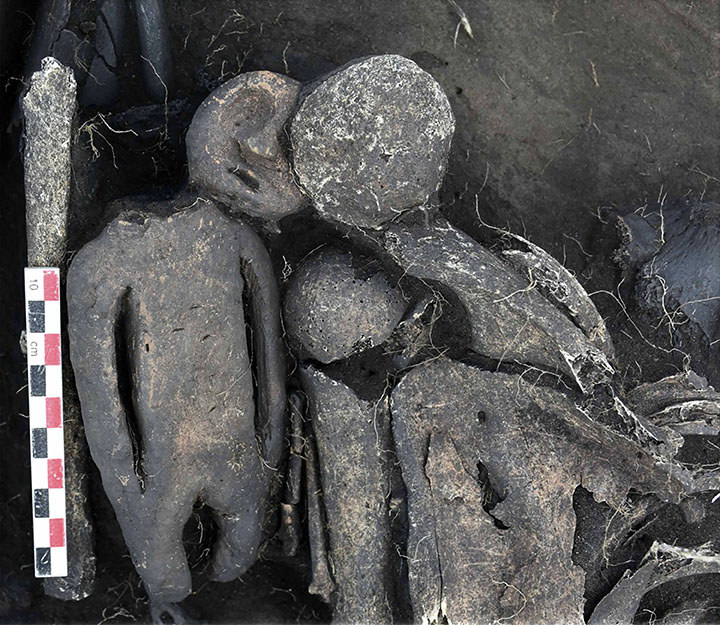


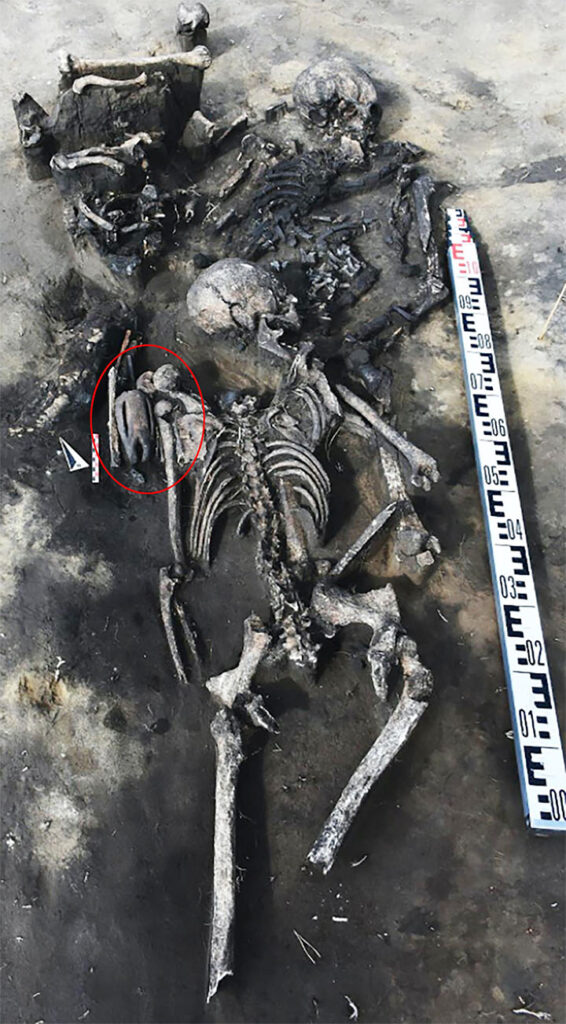
It has a mask made of bone – horse vertebrae – decorated with what appears to be an image of a bear’s muzzle, say scientists. Inside the grave, it had been placed on its front and had its head broken off.
It was then turned upside down so that it ‘looked up’ towards its owner in a bizarre ritual – something ‘yet unseen’ by Novosibirsk archaeologists.
One side of the middle of the statuette also has a long narrow hole, which had a bronze plate and also some organic substance inside it. Chemical tests are needed to establish more about what was placed inside that opening.
Dr Molodin said the discovery was unique.
‘We’ve never come across anything like this, despite our extensive knowledge of the Odinov culture’s burial rites,’ he said to the Siberian Times.
‘The woman must have been an unusual person to have such a figurine “escorting” her to the afterlife.’
Dr Molodin, a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS), called the Bronze Age figurine discovery the ‘most astonishing find’ of the summer archaeological season.
While the Odinov cattle-breeding people were Mongoloids, the face of the figurine ‘has obviously Caucasian features’ with ‘big eyes and a snub nose’, he said.
This was a tiered grave that had two more people buried beneath the loving couple that were facing each other.






