Archaeologists Discovered An Ancient City Buried 30 Miles Outside Rome Without Ever Digging It Up
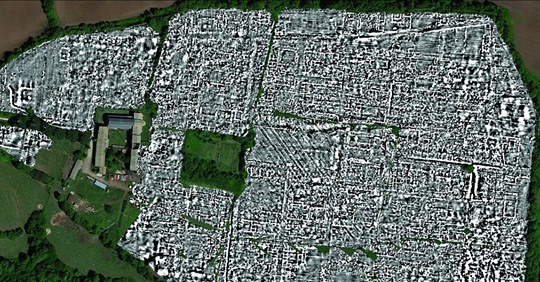
To figure out what they look like, archaeologists no longer have to excavate submerged villages. The entire ancient city of Falerii Novi, some 30 miles outside Rome, has recently been mapped by a group of Belgian and UK researchers, using radar technology that scans beneath the soil.
As the electromagnetic waves of a radar enter an underground structure, they bounce back as a measurement that can be used to produce a 3D image.
The researchers were able to recognise new buildings for the first time, such as an elegant bathhouse and a large public monument that had never been seen before. They were also able to determine how the city was organized compared to other Roman towns.
Though Falerii Novi wasn’t nearly as grand as Pompeii — a wealthy city buried under volcanic ash in 79 AD — the town had its own unique features. Its aqueduct, for instance, ran underneath its city blocks, as well as along the streets (the more common design for that time period). The researchers also found temples at the edge of the city, suggesting a sacred use of the land.
“Although we are yet to understand how this sacred landscape functioned, the survey provides new insights into the variety of planning concepts underlying what are sometimes incorrectly considered to be ‘standardized’ Roman town plans,” the researchers wrote. “By providing a contrast with more familiar towns such as Pompeii, this work also raises important questions about the planning of Roman towns more generally.”
Falerii Novi contained hidden shops, baths, and temples
Falerii Novi was built around 241 BCE. By the first century AD, it was one of around 2,000 cities in ancient Rome. Many of these towns were buried over time as the ground level steadily began to rise, or intentionally buried so Romans could build new settlements on top.
The city’s last human inhabitants left during the early medieval period in around 700 CE. The discoveries from the Belgian and UK researchers, published Tuesday in the scientific journal Antiquity, represent the first use of ground-penetrating radar to map an entire city below ground.
The researchers determined that Falerii Novi is about half the size of Pompeii: around 75 acres. Documenting each one of these acres took around eight hours, leaving them with more than 28 billion data points by the end of the survey.
While the team wasn’t able to analyze every single data point, they did outline the site’s major landmarks — shown on the map below. The map paints a picture of life more than 1,300 years ago, filled with theatre performances, shopping, worshipping, exercising, and bathing.
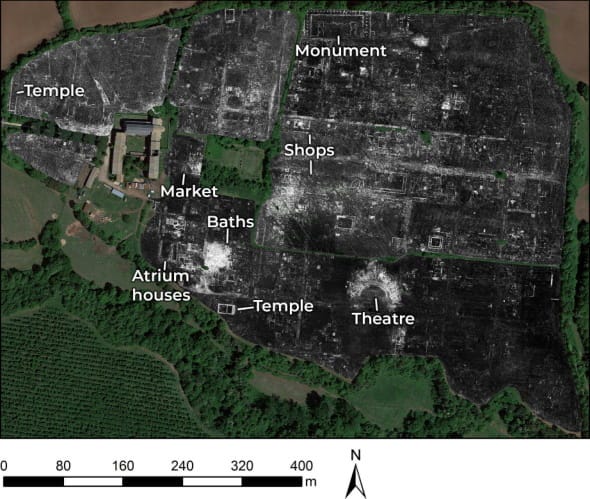
A massive public monument sits near the north gate, surrounded on three sides by a covered passageway with a central row of columns. The researchers estimated that the passageway is more than 550 feet long and opens out to the street. On the inside of the monument, a pair of structures (each with their own alcove) face toward one another.
“We know of no direct parallel to this structure,” the researchers wrote.
To the south-east are a market building and a public bathhouse. Both of these are new discoveries.
“While these buildings fall within the expected repertoire of a Roman city, some are architecturally sophisticated — more elaborate than would usually be expected in a small town,” the researchers wrote.
A temple directly south of the bathhouse straddles the edge of the city. To its west is a housing complex, consisting of two or three homes with atria. The researchers found evidence that the homes had been remodelled over time.
Some of the walls had been removed by stone robbers. The complex also includes a plunge bath, vaulted rooms with central heating, and a U-shaped area that likely served as an exercise room.
A second housing complex, located to the south at the foot of a slope, is lined with decorative passageways. Water pipes below this building connected to the town’s aqueduct.
These detailed discoveries, often obscured by rubble, were “previously only possible through excavation,” the researchers wrote. Their new survey method, they added, “has the potential to revolutionize archaeological studies of urban sites.”





