500 Year Old Map Was Discovered That Shatters The “Official” History Of The Planet
How many times has the rise and fall of human civilization actually occurred on planet Earth? It has been said that the conventional wisdom that has been passed down for generations (at least that’s where we think the knowledge came from) is not old enough, or there was some disconnect somewhere.
There’s a lot of fake things out there on this topic, but the fact is if you really look close, we can’t account for the existence of many of the world’s mysterious monolithic or archaeological sites.
From the Bosnian Pyramids to the amazing site of Gobekli Tepe in Turkey, to the South African site of Adam’s Calendar, they all irrefutably bring up questions about the origin of humanity itself.
Some sites seem to pre-date human civilization. How can that be explained? Knowing so many other things in life generally are not how they seem, and around every corner in what we were told about the history there is a deception, why wouldn’t there be an official deception located in this field of thought? Who, or what kind of entity could have possibly constructed so many elaborate and practically difficult to understand structures around the planet, millennia ago?
Obviously, our amnesia about the origin of humanity and literally everything about our existence is just a feature of this life. However, it doesn’t have to be such a mystery when it comes to things more concrete than the past-life amnesia people believe we were born with: we can concretely understand the history of humanity a little more.
Many people believe that before about 6,000 years ago in Mesopotamia, the official narrative for how old civilization gets, there must have been other intelligent and/or advanced human civilizations before that time.
Mapmaking itself was once considered much more of a complex task, characteristic of what they call civilized society. Some Babylonian clay tablets that seem to find origin around 1000BC seem to be the first known evidence of map-making.
One piece of the puzzle is thought to be this: the Admiral Piri Reis world map of 1513.
The official first sight of Antarctica reportedly was accomplished by a Russian expedition in 1820. Today it is believed that the continent’s ice caps formed about 34-45 million years ago. With some basic logic that means prior to 1820 Antarctica should not be present on any map, and of course, the continent should contain polar ice caps.
However, Ottoman cartographer and military admiral Piri Reis made a map that seems to contain Antarctica about 500 years ago.
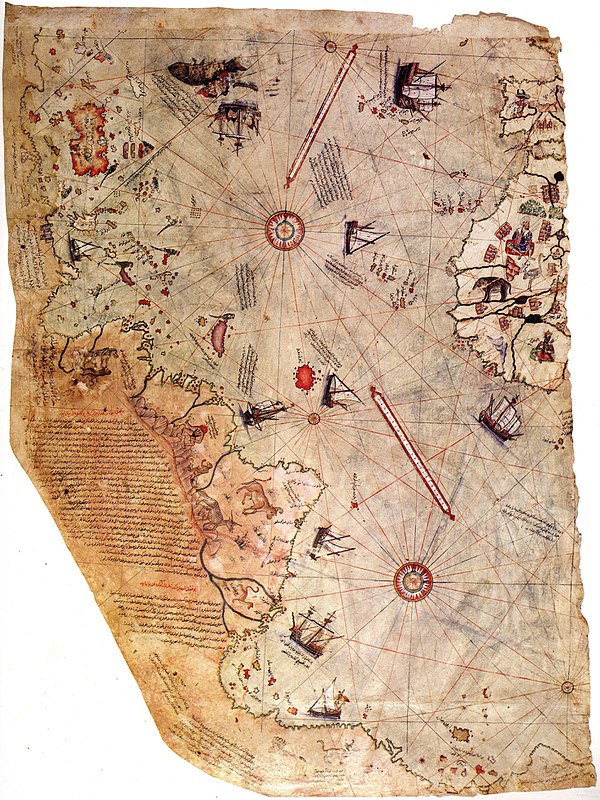
The Piri Reis map has a central focus on the East Coast of South America, Western Africa, and it includes the Northern Antarctic Coast. It seems to illustrate in a surprising amount of detail just what Queen Maud Land in Antarctica looks like. It’s accurate, and in the map, the ice-cold continent was not depicted as a barren wasteland, but rather as a continent full of dense vegetation.
A New Hampshire history professor named Charles Hapgood believed that a much different view of ancient history is depicted by this map, and the findings are unforgettable. Albert Einstein himself wrote a supportive forward to a book written by Charles Hapgood in 1953:
“His idea is original, of great simplicity, and – if it continues to prove itself – of great importance to everything that is related to the history of the Earth’s surface.”
The map is certifiably not a hoax, absolutely authentic by every measure. Here’s where it gets strange: Piri Reis did not say that he or his people specifically discovered Antarctica, but he noted that the information sourced for it was from other, much older maps, logs, and charts.
Hapgood suggests that perhaps the maps had been repeatedly copied and re-translated before the destruction of the Library of Alexandria in Egypt. The destruction of the Library of Alexandria was the book burning of the new world, wiping out an incomprehensible treasure trove of info about the history of humanity, casting the historical knowledge of antiquity into the wind.
So Hapgood for some reason brought this info to the US Air Force of all people, and they performed testing of seismic data in Antarctica. Warning: these are not the people to trust. According to Fingerprints of the Gods:
“…the geographical detail shown in the lower part of the map agrees very remarkably with the results of the seismic profile made across the top of the ice-cap by the Swedish-British Antarctic Expedition of 1949. This indicates the coastline had been mapped before it was covered by the ice-cap. The ice-cap in this region is now about a mile thick. Learn how to enter parallel worlds of consciousness We have no idea how the data on this map can be reconciled with the supposed state of geographical knowledge in 1513. – Harold Z. Ohlmeyer Lt. Colonel, USAF Commander”
Was Antarctica a grassy, green land where life could thrive a mere 500 years ago, or perhaps several thousand years ago?





