Israeli archaeologists find 3,000-Year-old ‘Biblical royal purple dye’
In Israel, fragments of dyed thread uncovered dating back 3,000 years refer to the accounts in the Bible of the purple garments worn by royalty including King Solomon. Researchers from Israel find traces of woven fabric, a tassel, and fibers of wool dyed in so-called ‘royal purple’ from a dig site in the Timna Valley.
The area is rich in copper ore in the country’s south and has been mined since the 5th millennium BC. It belonged to Edom, the biblical kingdom. The discovery is the first time that purple cloth from about 1,000 BC has been discovered and represents a glimpse into the Biblical Kings’ wardrobes.
Purple dye was coveted for its vibrant colour and longevity — but its origins, being sourced in minute amounts from shellfish — made it expensive to use.
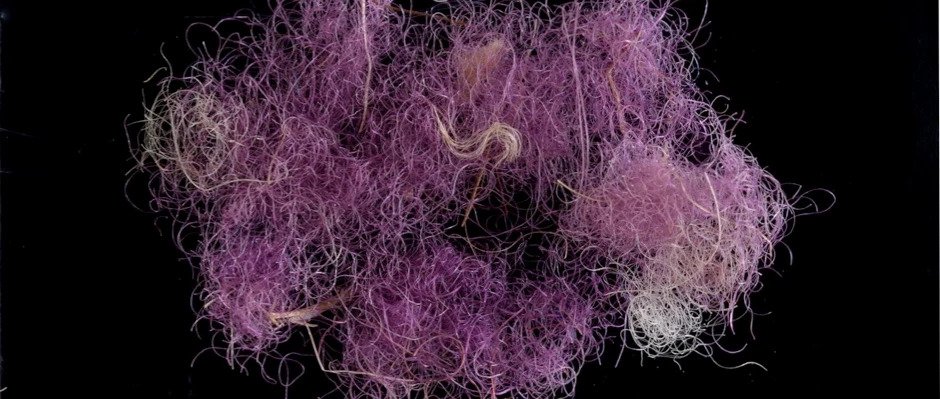
‘This is a very exciting and important discovery,’ said the Israel Antiquities Authority’s curator of organic finds, Naama Sukenik. This is the first piece of textile ever found from the time of David and Solomon that is dyed with the prestigious purple dye.’
‘In antiquity, purple attire was associated with the nobility, with priests, and of course with royalty.’ Direct radiocarbon dating has confirmed that the finds date from around 1,000 BC, matching the times of the biblical monarchies of David and Solomon in Jerusalem.
In the Old Testament, the colour is mentioned in the ‘Song of Songs’, chapter 3, verses 9–10.
‘King Solomon made for himself the carriage; he made it of wood from Lebanon,’ the scripture reads. Its posts he made of silver, its base of gold. Its seat was upholstered with purple, its interior inlaid with love.’
Royal purple dye — made from molluscs found in the Mediterranean, over 186 miles (300 km) north of Timna — is described in various Jewish and Christian texts. However, this is the first time that purple-dyed Iron Age textiles have actually been found in Israel — or, indeed, anywhere throughout the Southern Levant.
‘The gorgeous shade of the purple, the fact that it does not fade, and the difficulty in producing the dye — which is found in minute quantities in the body of molluscs — all made it the most highly valued of the dyes,’ explained Dr Sukenik. The dye, he continued, often cost more than the equivalent amount of gold.
‘Until the current discovery, we had only encountered mollusc-shell waste and potsherds with patches of dye, which provided evidence of the purple industry in the Iron Age.’
‘Now, for the first time, we have direct evidence of the dyed fabrics themselves, preserved for some 3000 years.’
Other organic materials — including Iron Age textiles, cords and leather — were also preserved at the Timna site thanks to the region’s extremely dry climate. These artefacts — which also date back to the time of David and Solomon — offer a unique glimpse into life during biblical times, the researchers said.
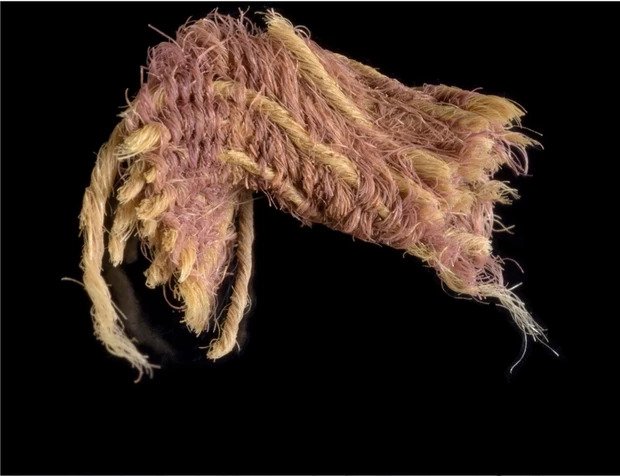

‘Our archaeological expedition has been excavating continuously at Timna since 2013,’ said Erez Ben-Yosef of Israel’s Tel Aviv University. If we excavated for another hundred years in Jerusalem, we would not discover textiles from 3,000 years ago.’
‘The state of preservation at Timna is exceptional and it is paralleled only by that at much later sites — such as Masada and the Judean Desert Caves.’
In recent years, the archaeologists have been excavating a relatively new site in the region, which is referred to as ‘Slaves’ Hill’.
‘The name may be misleading since, far from being slaves, the labourers were highly skilled metalworkers,’ added Professor Ben-Yosef. Timna was a production center for copper, the Iron Age equivalent of modern-day oil,’ the archaeologist continued.
‘Copper smelting required advanced metallurgical understanding that was a guarded secret and those who held this knowledge were the “hi-tech” experts of the time,’ he said.
‘Slaves Hill is the largest copper-smelting site in the valley and it is filled with piles of industrial waste such as slag from the smelting furnaces,’ said Professor Ben-Yosef.
‘One of these heaps yielded three scraps of coloured cloth. The colour immediately attracted our attention, but we found it hard to believe that we had found true purple from such an ancient period’.
According to the researchers, the purple dye — thought to have been called argaman in Hebrew — was produced from three species of mollusc that are indigenous to the Mediterranean Sea.
These species included the Banded Dye-Murex, the Spiny Dye-Murex and the Red-Mouthed Rock-Shell. The dye was made from a gland inside the body of the mollusc via a complex chemical process that lasted several days.

Today, most experts agree that two different precious dyes — the purple argaman and the light blue, or azure, tekhelet — were both produced from the purple dye molluscs, but using different levels of exposure to light.
These two colours are often mentioned together in ancient texts and still have symbolic value and religious significance to this day. Temple priests, the Kings David and Solomon and also Jesus of Nazareth are described as having worn purple-coloured clothing.
To reconstruct the mollusc dyeing process, Professor Amar travelled to Italy where he cracked open thousands of molluscs to extract raw material from their innards. This was then used in hundreds of attempts to reconstruct the ancient dye.