Venetian Blue Beads Found in Alaska Predate Arrival of Columbus
Tiny glass beads from Venice made their way to Alaska decades before Christopher Columbus‘ arrival in the New World. The beads, the colour and size of blueberries, were uncovered in a house pit in Punyik Point, a seasonal Inuit camp near the Continental Divide in Alaska’s Brooks Range.
Archaeologists determined the objects were created between 1440 and 1480 following a radiocarbon-dating of twine that held the jewellery.
Researchers from the University of Alaska suggest the beads were among trinkets that passed hands through various trade routes — starting in Europe, then along the Silk Road to China, through Siberia and finally to the Bering Strait. According to the study, the new discovery resets the clock on when traded began between Europe and North America.
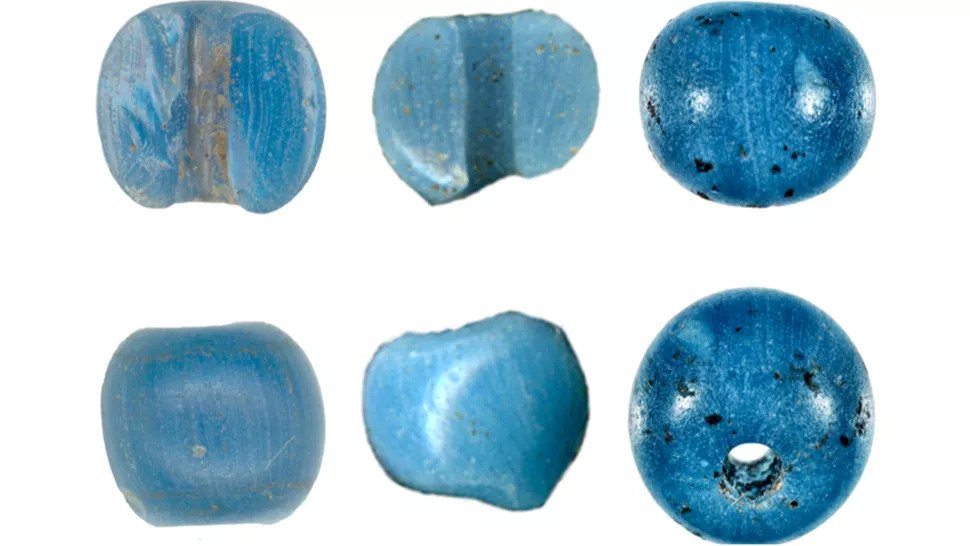

Mike Kunz, an archaeologist with the university’s Museum of the North in Fairbanks, discovered a total of 10 beads in three locations in the Brooks Range: Punyik Point, Kinyiksugvik and Lake Kaiyak House.
Kunz theorizes the baubles were just small piece of a number of trinkets that made their way various trade routes that began in Europe, then along the Silk Road to China, through Siberia and finally across the Bering Strait.
They were then presumably brought across the frigid Arctic Ocean to Alaska by kayak. Punyik Point was a popular stopping point for traders, Kunz says, because of the many caribou in the area.
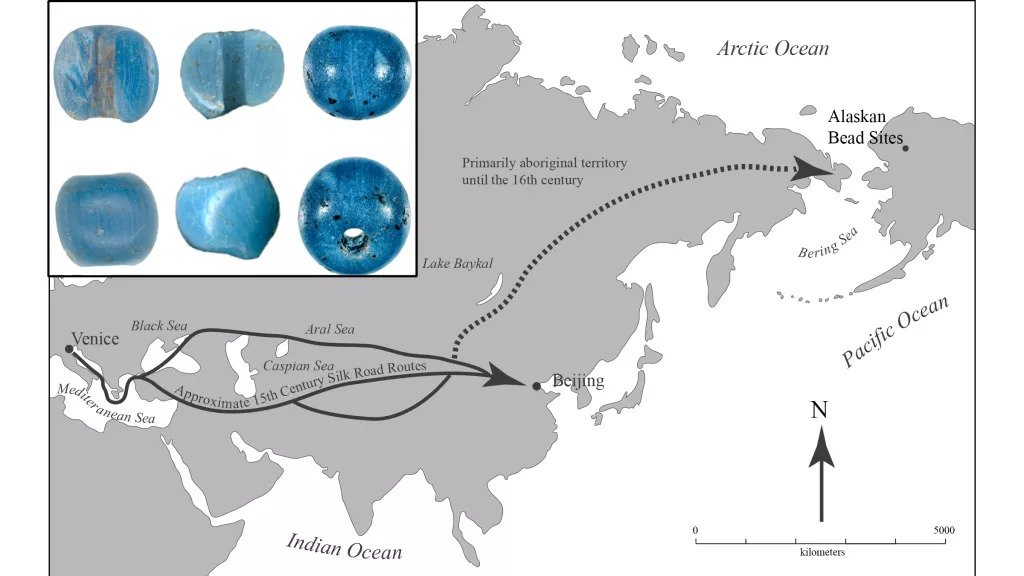
‘And, if for some reason the caribou didn’t migrate through where you were, [it also] had excellent lake trout and large shrub-willow patches,’ he added. University of Wisconsin archaeologist William Irving found several turquoise beads at Punyik Point in the 1950s and 1960s.
But Irving had no way to know when they were deposited.
Flash forward to 2004, when Kunz and Bureau of Land Management archaeologist Robin Mills returned to the ancient campsite. They found three more beads there, along with copper bangles, metal loops that could have been earrings and other metal pieces that could have been part of a necklace or bracelet.
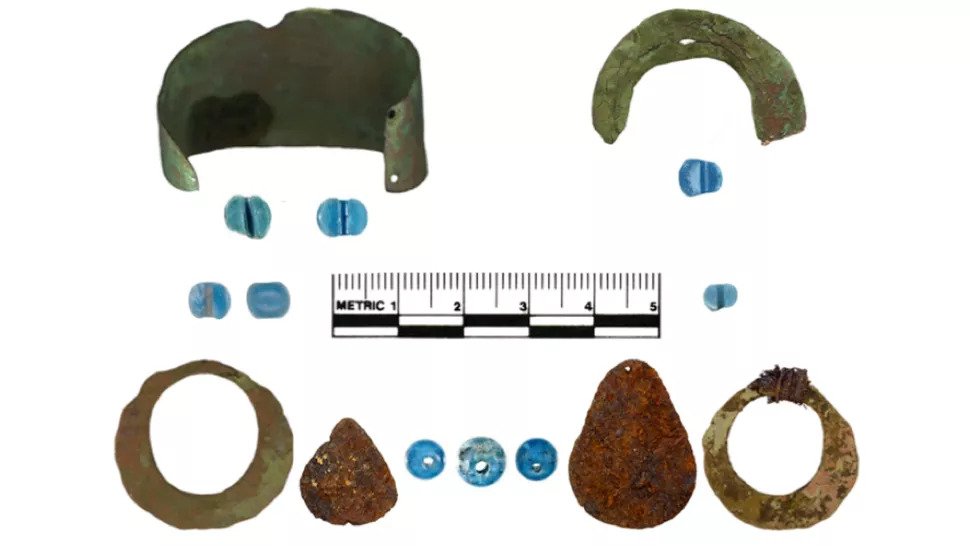

Wrapped around one of the bangles was a twine that had survived centuries of burial just a few inches below the surface. Because the twine is made of plant fibres — probably the inner bark of shrub willow, the scientists surmised— it meant they finally had an organic matter to conduct radiocarbon dating on using Accelerator mass spectrometry.
‘We almost fell over backwards,’ Kunz said in a release. ‘It came back saying [the plant was alive at] some time during the 1400s. It was like, Wow!’
With that information, along with radiocarbon dating of charcoal found nearby, they surmised the glass beads at all three locales arrived at some point between 1440 and 1480.
‘The beads challenge the currently accepted chronology for the development of their production methodology, availability, and presence in the Americas,’ the researchers wrote in a new paper in the journal American Antiquity.
‘This is the first documented instance of the presence of indubitable European materials in prehistoric sites in the Western Hemisphere as the result of overland transport across the Eurasian continent.’
According to Kunz and Mills, the beads probably made landfall at Shashalik, an ancient trading post north of modern-day Kotzebue, and then were transported further inland.
The archaeologists theorize they were part of a necklace or other piece of jewellery. The item’s location, at the entrance to an underground house, suggests it was dropped or discarded rather than intentionally buried.
Venice has been known as a glassmaking mecca for over 1,500 years, with the island of Murano the centre of production since at least the 13th century.
Columbus’ ships landed in the Bahamas in October 1492, before venturing on to Cuba and Haiti, where he started the first European settlement in the Americas since the Norse some 500 years earlier.
After briefly returning to Spain, Columbus made three more voyages to the New World between 1493 and 1502, exploring the Lesser Antilles, Trinidad, Puerto Rico and the northern coast of South America.
The bead variety, commonly known as ‘Early Blue’ and ‘Ichtucknee Plain,’ has been found throughout the Caribbean, the east coasts of Central and North America, and the eastern Great Lakes region, but only after Columbus’ arrival, generally between 1550 and 1750.





