Possible shaman’s snake stick from 4,400 years ago discovered in a Finnish lake
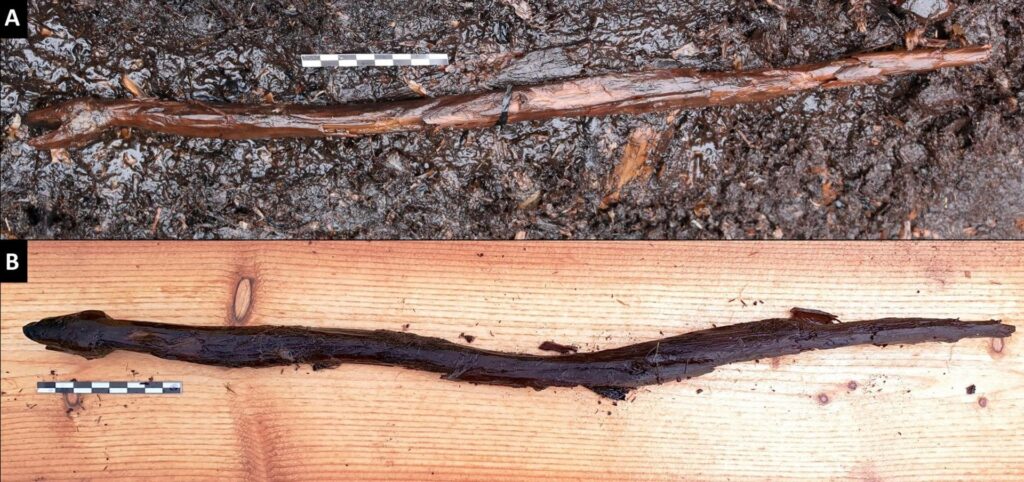
Archaeologists in Finland have uncovered an intricately carved wooden staff that may have been used by Stone Age shamans for rituals. More than half a metre long, the perfectly preserved life-sized wooden stick is a carving of a snake, shaped as if it is slithering away.
It was found at Järvensuo 1, a wetland site in Finland’s southwest that was occupied between 4000 BC and 2000 BC, and is ‘unlike any other wooden artefact found in Northern Europe’ during this period.
The archaeologists say the object is 4,400-years-old, meaning it dates back to the Neolithic period – the final division of the Stone Age.
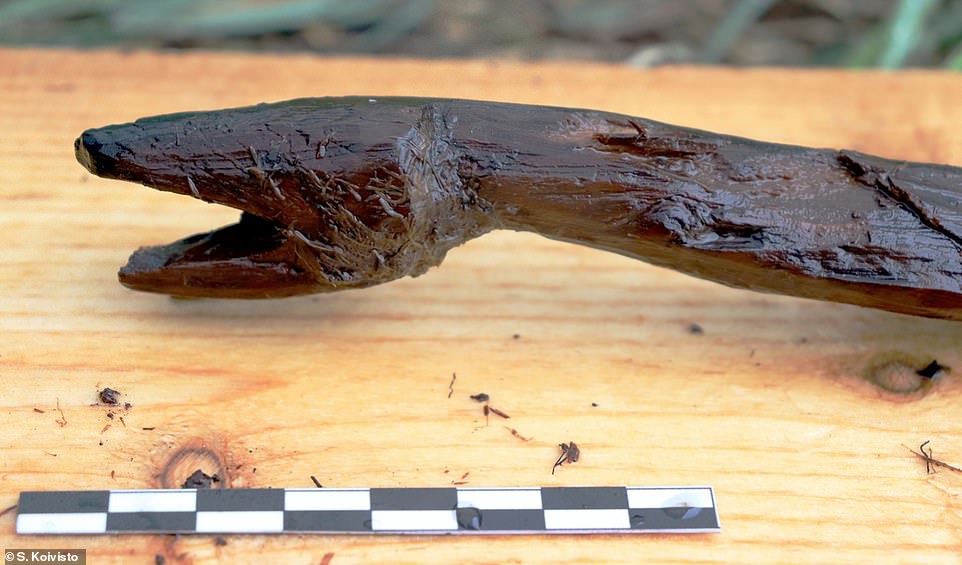

‘This delicately carved natural-sized snake figurine is a magnificent, thought-provoking glimpse from far back in time,’ said study author Dr Satu Koivisto at the University of Turku.
‘I have seen many extraordinary things in my work as a wetland archaeologist, but the discovery of this figurine made me utterly speechless and gave me the shivers.’
Contemporary rock art shows snake-shaped objects being held by human-like figures, which is why the experts think the carving was a Stone Age shaman’s staff for rituals.

‘There seems to be a certain connection between snakes and people,’ said co-author Dr Antti Lahelma from the University of Helsinki.
‘This brings to mind northern shamanism of the historical period, where snakes had a special role as spirit-helper animals of the shaman.
‘Even though the time gap is immense, the possibility of some kind of continuity is tantalising – do we have a Stone Age shaman’s staff?’
Järvensuo 1 was discovered by accident by ditch diggers during the 1950s but had not been fully excavated. As such, archaeologists have been working to explore the site since 2019.
The prehistoric lakeshore has wetland conditions conducive to preserving wooden items. Previous excavation work at the site unearthed a wooden scoop with a handle like a bear’s head.
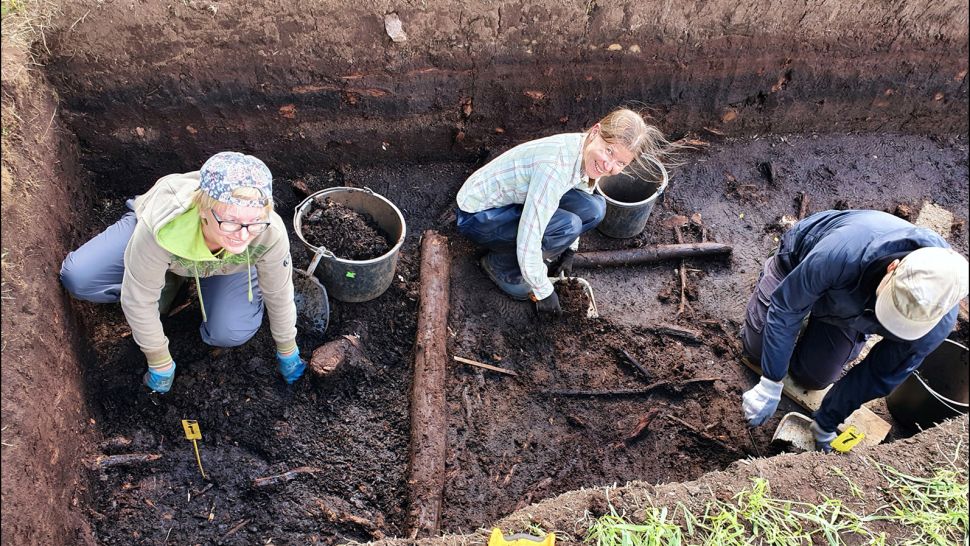
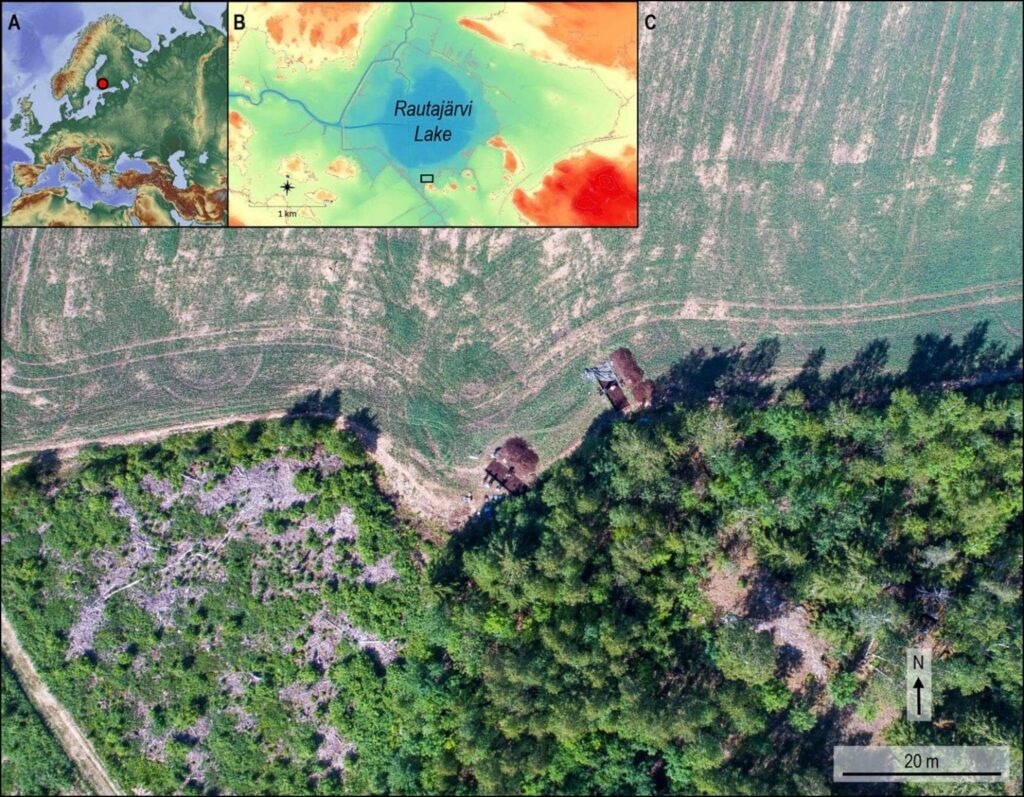

Several other wooden artefacts have been found by the new investigations, including wooden utensils, structural remains and pieces of fishing equipment.
According to archaeologists, this indicates Järvensuo 1 was the site of not just bizarre rituals involving the snake figurine, but practical activities as well-meaning it offers a snapshot of all aspects of ancient life.
‘Well-preserved finds from wetlands help our understanding of ancient peoples and the landscape where they performed both mundane and sacred activities,’ said Dr Koivisto.
Sadly, Järvensuo 1 and the historical treasures within are under threat from drainage and other changes to the local environment, exacerbated by climate change.
‘The signs of destruction caused by extensive drainage are already clearly evident at the site and its organic treasures are no longer safe,’ said Dr Koivisto.





