Excavation of Elite’s Tomb in China Reveals Sport of Donkey Polo
Legend tells the story of loyal horses, whereas it relegates their equine cousins, the donkeys, to the role of mere pack animals. But a new analysis of bones buried with a ninth-century Chinese noblewoman may help raise the status of the lowly ass: It may have served as her steed during polo matches in the royal court.

Sandra Olsen, an archeologist at the Kansas University of Lawrences, a museum of natural history who was not involved with the work said, “It’s about the time that donkeys get their proper recognition. She calls the new finding of their role in ancient sports “particularly exciting.”
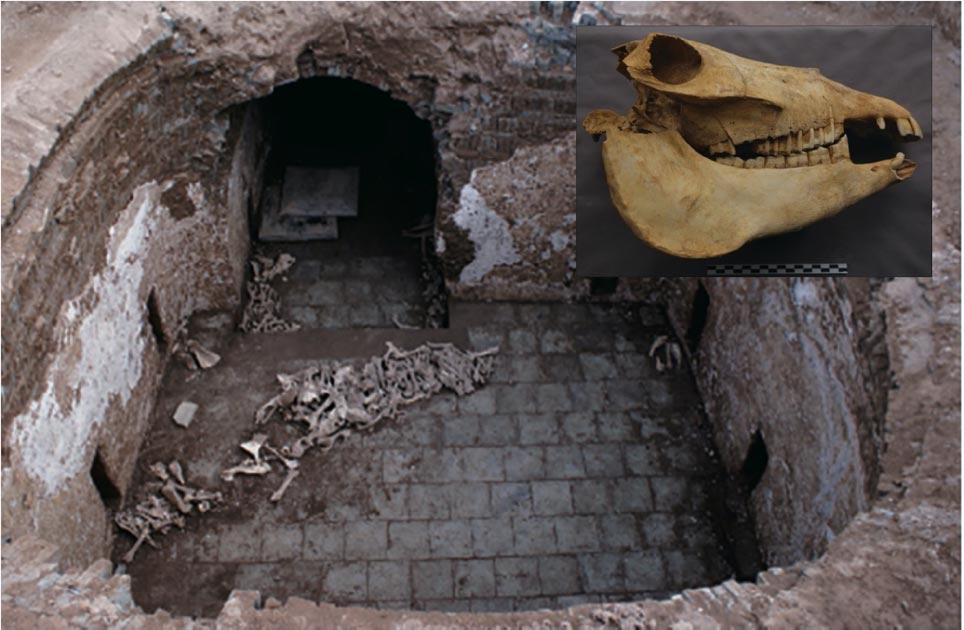
The bricked-in tomb of a woman named Cui Shi, who, according to official records, died at 59 years of age on 6 October 878 C.E, a team of Chinese archaeologists from the ancient capital of the Tang Dynasty, Xi’an, excavated in 2012.
Murals on her tomb walls of workers preparing a sumptuous feast suggest she was of high status. Although looters had ransacked the tomb, they left behind a bevy of animal bones, including those of at least three donkeys.
Donkeys would have been a common sight in Xi’an in the ninth century. The bustling Tang capital was the eastern terminus of the Silk Road trade route, and donkeys were frequently used as pack animals.
But humble beasts of burden aren’t usually buried alongside elite members of society, says study co-author Fiona Marshall, an anthropologist at Washington University in St. Louis. “Donkeys … are not associated with high-status people,” Marshall says. “They were animals used by ordinary folk.”

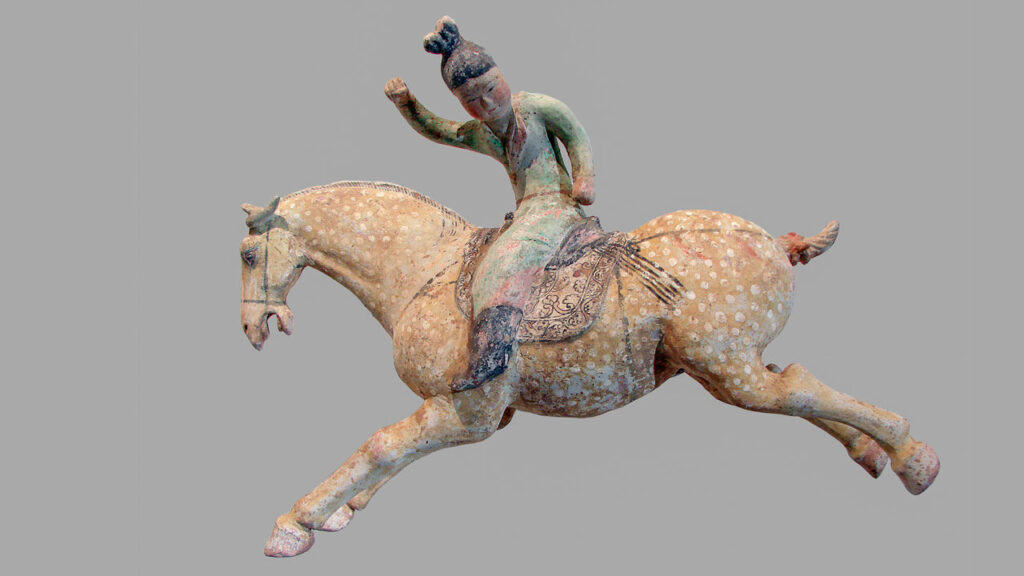
One hint to why they were in Cui’s tomb, she says, may lie in the identity of her husband, Bao Gao. Ancient texts reveal that the polo-obsessed Emperor Xizong promoted Bao to the rank of general because of his skills on the polo fields.
Polo was wildly popular during the Tang dynasty—for both women and men—but it was also dangerous; riders thrown from their horses were frequently injured or killed. If a woman like Cui wanted to join a game, then riding a donkey—slower, steadier, and lower to the ground—might have been a safer alternative.

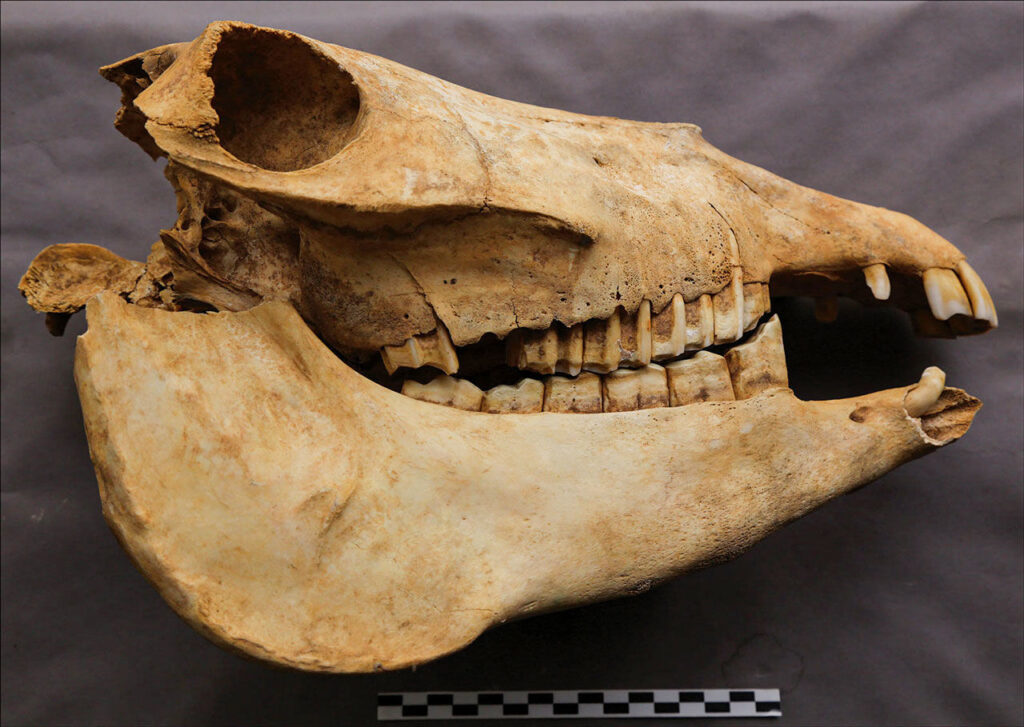
When the researchers, led by archaeologist Songmei Hu of the Shaanxi Provincial Institute of Archaeology, analyzed the size of the donkey bones in Cui’s tomb, they found that they were too small to have been good pack animals.
Computerized tomography scans of the leg bones revealed patterns of stress similar to an animal that ran and turned frequently, rather than one that slowly trudged in a single direction. Taken together, the evidence suggests Cui played polo astride a donkey, the researchers report today in Antiquity. The noblewoman’s donkeys may have been ritually sacrificed when she died to allow Cui to continue to play in the afterlife.
“There’s no smoking gun … [but] there’s really no other explanation that makes sense,” Marshall says, adding that the finding suggests Tang dynasty donkeys were held in higher regard than believed.
William Taylor, an anthropologist at the University of Colorado, Boulder, who studies human-animal relationships, agrees the donkeys in the tomb were not simple pack animals.
But although polo-playing is one plausible explanation, he says, the biomechanical stress patterns may also match other activities, such as pulling a cart or milling grain. Still, if the researchers are right, Olsen says, “it is doubly rewarding than another underdog in ancient history, women’s sports, is also [getting credit].”





