Ancient city discovered deep in Amazonian rainforest linked to the legendary white-skinned Cloud People of Peru
A lost city discovered deep in the Amazon rainforest could unlock the secrets of a legendary tribe. Little is known about the Cloud People of Peru, an ancient, white-skinned civilization wiped out by disease and war in the 16th century.

But now archaeologists have uncovered a fortified citadel in a remote mountainous area of Peru known for its isolated natural beauty. It is thought this settlement may finally help historians unlock the secrets of the ‘white warriors of the clouds’.
The tribe had white skin and blonde hair – features that intrigue historians, as there is no known European ancestry in the region, where most inhabitants are darker-skinned.
The citadel is tucked away in one of the most far-flung areas of the Amazon. It sits at the edge of a chasm which the tribe may have used as a lookout to spy on enemies.

The main encampment is made up of circular stone houses overgrown by the jungle over 12 acres, according to archaeologist Benedict Goicochea Perez.
Rock paintings cover some of the fortifications and next to the dwellings are platforms believed to have been used to grind seeds and plants for food and medicine.
The Cloud People once commanded a vast kingdom stretching across the Andes to the fringes of Peru’s northern Amazon jungle, before it was conquered by the Incas.
Named because they lived in rainforests filled with cloud-like mist, the tribe later sided with the Spanish-colonialists to defeat the Incas. But they were killed by epidemics of European diseases, such as measles and smallpox.
Much of their way of life, dating back to the ninth century, was also destroyed by pillaging, leaving little for archaeologists to examine.
Remains have been found before but scientists have high hopes of the latest find, made by an expedition to the Jamalca district in Peru’s Utcubamba province, about 500 miles north-east of the capital, Lima.
Until recently, much of what was known about the lost civilization was from Inca legends. Even the name they called themselves is unknown. The term Chachapoyas, or ‘Cloud People’, was given to them by the Incas.
Their culture is best known for the Kuellap fortress on the top of a mountain in Utcubamba, which can only be compared in scale to the Incas’ Machu Picchu retreat, built hundreds of years later.
Two years ago, archaeologists found an underground burial vault inside a cave with five mummies, two intact with skin and hair.
Chachapoyas chronicler Pedro Cieza de Leon wrote of the tribe: ‘They are the whitest and most handsome of all the people that I have seen, and their wives were so beautiful that because of their gentleness, many of them deserved to be the Incas’ wives and to also be taken to the Sun Temple.
‘The women and their husbands always dressed in woollen clothes and in their heads they wear their llautos [a woollen turban], which are a sign they wear to be known everywhere.’
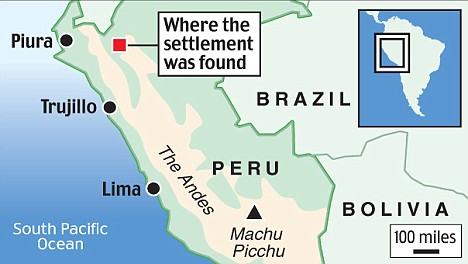
The Chachapoyas’ territory was located in the northern regions of the Andes in present-day Peru.
It encompassed the triangular region formed by the confluence of the Maranon and Utcubamba rivers, in the zone of Bagua, up to the basin of the Abiseo river.
The Maranon’s size and the mountainous terrain meant the region was relatively isolated.





