31,000-year-old burial holds the world’s oldest known identical twins
The presence in the history of human twins is not unheard of. It is nothing short of fascinating to find relatively well-preserved skeletons of a pair of baby twins from thousands of years ago, though.
A burial site from 31,000 years ago was found by an international team of scientists, and in it, the world’s oldest known buried remains of identical twins.
The graves of the Upper Paläolithic period, which lasted from 40,000 to 10,000 years ago, are widely known as the Old Stone Age, according to a team of multidisciplinary researchers. The scientists found not only the remains of the two twins in the burial site, but also a third infant, who is most likely a cousin.

“To discover multiple burials from the Paleolithic period is a speciality in itself. The fact that sufficient and high-quality old DNA could be extracted from the fragile, child’s skeletal remains for a genome analysis exceeded all of our expectations and can be compared to a lottery ticket,” said, Maria Teschler-Nicola, lead researcher of the study, in a statement.
Together In Death
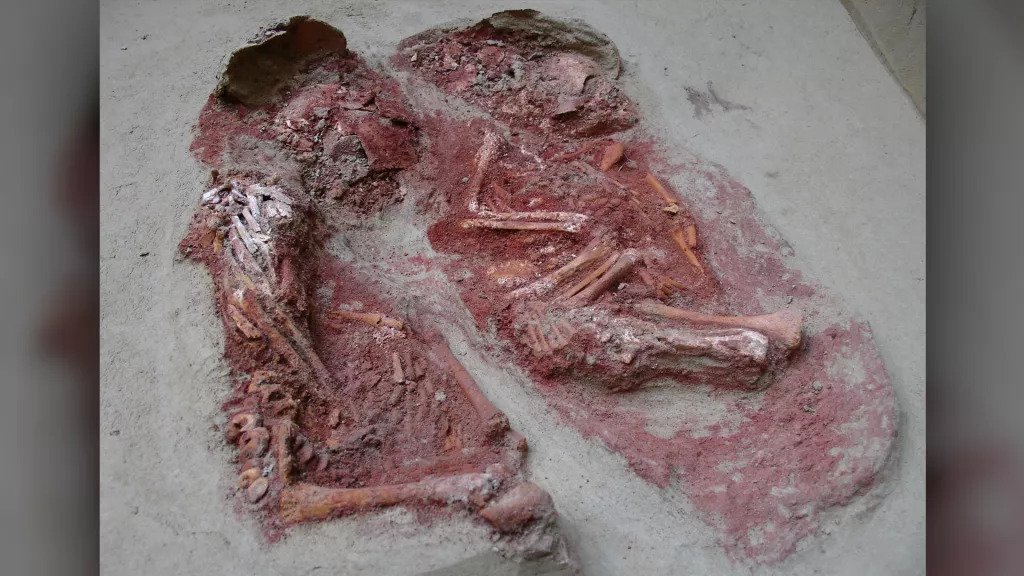
The oval-shaped grave of the twins was located at an archaeological dig in Krems-Wachtberg, an ancient settlement, along the banks of the Danube River near the town centre of Krems an der Donau, Austria in 2005. Found covered in ochre— and earthy pigment consisting of ferric oxide that was used in burials in ancient times—where the mortal remains of the two babies.
In order to confirm the relationship between the infants, the archaeologists conducted a genomic analysis of the ancient DNA.
The examination led the authors to conclude that two were not just twins, but identical twins. Also, the third baby, believed to be around 3-months-old and buried around 1.5 meters (5 feet) from where the twins were laid to rest, was possibly a cousin.
Another interesting aspect of the finding was that the twin, who lived for a few weeks longer than his brother, was reburied along with him after his demise. Therefore, reopening of the grave would have been required for the “reburial”.
This confirms a newly uncovered cultural-historical phenomenon of opening graves for re-interring corpses—something that was not known for the Paleolithic period.
Buried With ‘Treasures’
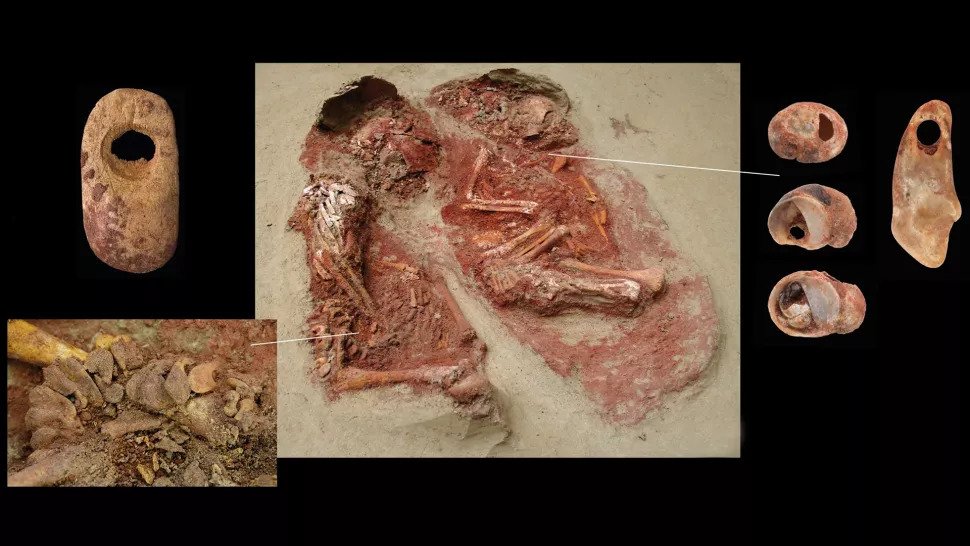
The twins were not buried without any treasures. Unearthed in the graves of the brothers were 53 beads fashioned out of mammoth ivory which were probably strung on a thread like a necklace.
Along with the beads, a pierced fox incisor and three perforated molluscs, which were likely pendants on a necklace, were also found according to the study. Protecting the infant bodies from the elements above, a mammoth shoulder blade had been placed over their bodies.
Their supposed cousin, who was buried not far from them, was also smeared in ochre. In his possession was a mammoth-ivory pin measuring 8 centimetres (3 inches), which might have been used to hold a leather garment in place during the burial, explained the researchers.
Life, Struggles and Death

While the genetic analysis revealed the relationship between the three ancient remains, a scrutiny of the upper lateral deciduous incisors aided the researchers in pinpointing their age.
The authors focused on the “newborn line or neonatal line (NNL)—a dark line on the tooth enamel which separates enamel that was formed prenatally from the enamel formed post-birth.
The NNL, along with the skeletal structures suggested that the brothers completed nearly-full or full term, and belonged to a hunter-gatherer group. Upon chemical analysis of several elements in the tooth enamel, including isotopes such as barium, carbon, and nitrogen, it was learnt that the twins had been breastfed.
The authors posited that one of the babies died not long after birth, while his twin brother survived only for 6-7 weeks. The cause of their death, however, is yet to be ascertained.
Though their cousin lived for three months, the “stress lines” on his teeth indicate that he was marred by feeding difficulties. This probably was because his mother struggled from mastitis—a painful infection of the breast—or succumbed during childbirth.
According to the authors, the early deaths of the babies is perhaps a reflection of a lean phase of food supply among the Paleolithic hunter-gatherer group who settled in the area 30,000 years ago.





