Discovery of massive island ritual site where people gathered 5,500 years ago
The discovery of a cursus monument site at Tormore on the Isle of Arran, which is more than a kilometer long, is helping to reshape Neolithic history in Scotland with such landmarks usually associated with the east coast.

Cursus monuments were often defined by long lines of timber posts, forming a long rectangle, and were amongst the most spectacular features in the Neolithic landscape.
The posts may have served as a procession route, perhaps to honour the dead. Some were burned to the ground in an almighty display which is believed to have been part of the ceremonies associated with these huge monuments.
Dave Cowley, Rapid Archaeological Mapping Programme Manager at Historic Environment Scotland, who discovered the site following a laser scan of Arran, described the cursus monument as a “cathedral of the day”.
He said: “I think if you asked the survey team what they thought they were most likely to find on Arran, I would bet you no one would say a Neolithic cursus monument
“There is no other on Arran, it’s unique on the island, there is one more in Kilmartin Glen and that is pretty much it for the western seaboard.
“What this example at Tormore tells is there are probably actually many more on them but because they were built from timber, you are not likely to see them in the unimproved peat landscape of the west coast.
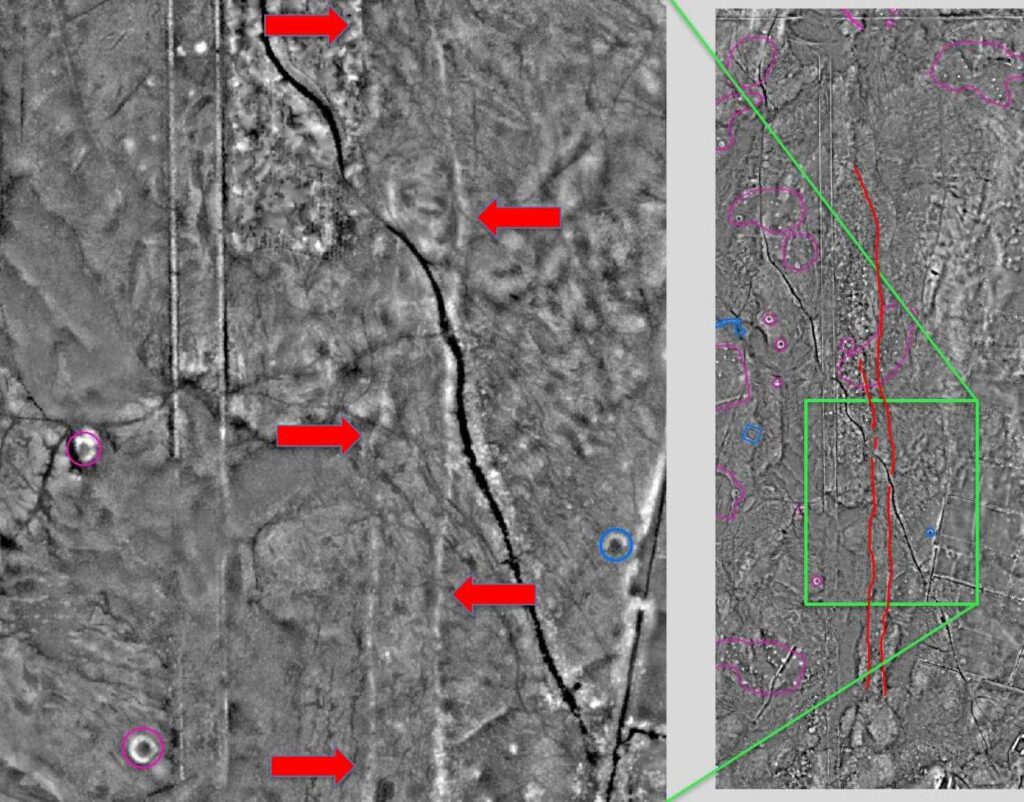
“Arran has got some cracking Neolithic and Bronze Age archaeology but we are still surprised that this monument is here.
“It adds a whole additional dimension to what the archaeology of the Neolithic on Arran can tell us. It is like finding a whole new layer in a box of chocolates of new things.”
Mr. Cowley detected the site after picking up two lines of mounds, which lie roughly parallel and stand 30 to 40 centimeters high, and which run for around a kilometer.
He said: “When you look at the topography, it very slightly runs to the crest of a ridge. They have been very careful about how they have positioned this monument. There probably was a superstructure here but we won’t know for sure without excavation.
“It would have had an impact. There is an element of design to it, a form of landscape architecture.
“It does seem likely that there were timber elements built into it. Whether or not it was set on fire we just don’t know at the moment. “
Mr Cowley said the monuments probably brought together “quite dispersed populations together in a communal activity” and that different community built different parts of the monument.
The site was discovered following an aerial laser scan of the site using Light Detection and Ranging (Lidar) technology, which uses laser pulses to measure objects.
Images can then be reworked by filtering out vegetation or by changing the way it is lit which can then reveal previously unknown characteristics in the land. More than 1,000 unknown archaeological sites have been found on Arran using the technology.





