The Varna Man, who lived around the 5th Millennium BC, is the wealthiest burial at that time
The site, located on the outskirts of the Black Sea resort of Varna, was discovered accidentally when tractor operator Raicho Marinov was cutting a trench to lay an electric cable for a local factory.
He suddenly noticed small squares of shiny yellow metal, bracelets of the same material, green-coloured artefacts, and flakes of flint.
Rushed to the local museum, the objects were soon identified as prehistoric stone tools, corroded copper axes, and, clearly associated with them, golden ornaments. The association was what mattered: the implication was that the gold artefacts were older than any others ever discovered anywhere.

Museum curator Michail Lazarov and Sofia University professor Georgi Georgiev immediately set about organising a rescue excavation, and the museum’s young archaeologist, Ivan Ivanov, was appointed to lead it.
Ivanov’s team eventually uncovered 281 graves, more than half with grave goods, 18 of them exceptionally rich, and one of them among the richest graves ever excavated.
The date of the cemetery has recently been pushed back to the 5th millennium BC. A radiocarbon determination now gives it as c.4500 BC.
The discoveries
About 200 crouched or, far more commonly, extended inhumations have been uncovered in the two-thirds of the cemetery so far excavated. Both males and females are represented.
The bodies were placed in flat graves formed of shallow pits without mounds. The remaining graves are ‘cenotaph graves’ – where nobody is present but where grave goods have been laid out – or ‘mask graves’, where a life-size ceramic mask has been substituted for an actual body.
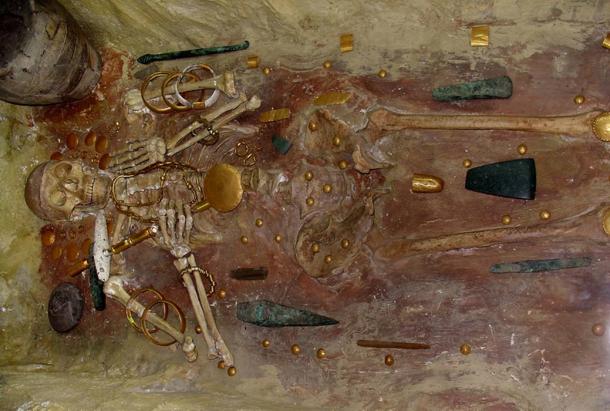
Three cenotaph graves, three mask graves, and a number of the inhumations are extremely rich. The total assemblage includes 3,000 gold artefacts weighing over 6kg.
The richest burial is of a man in his mid-40s buried with no less than 990 separate gold objects, including beads, rings, and a variety of decorations for body, clothing, and hair, among them a penis sheath. This man was also buried with copper axes, other copper tools, and a sceptre in the form of a perforated stone axe or mace.

In addition to gold and copper, the exotic materials represented among the grave goods include graphite, spondylus shell, dentalium shell, carnelian, and marble. Ceramic containers were also present in many graves.
The deductions
Varna implies three major developments in the mid-5th millennium BC. First, given the range of exotic material, Varna must have been part of an extensive trading network, allowing some members of this Early Chalcolithic community to become rich and powerful.
Second – presumably because of its role in trade – the Varna community appears to have developed extreme social differentiation at a very early date, judging by the fact that most graves contain no or few grave goods, while a minority are exceptionally rich. The social gap between the many unfurnished inhumations and the Grave 43 man seems huge.
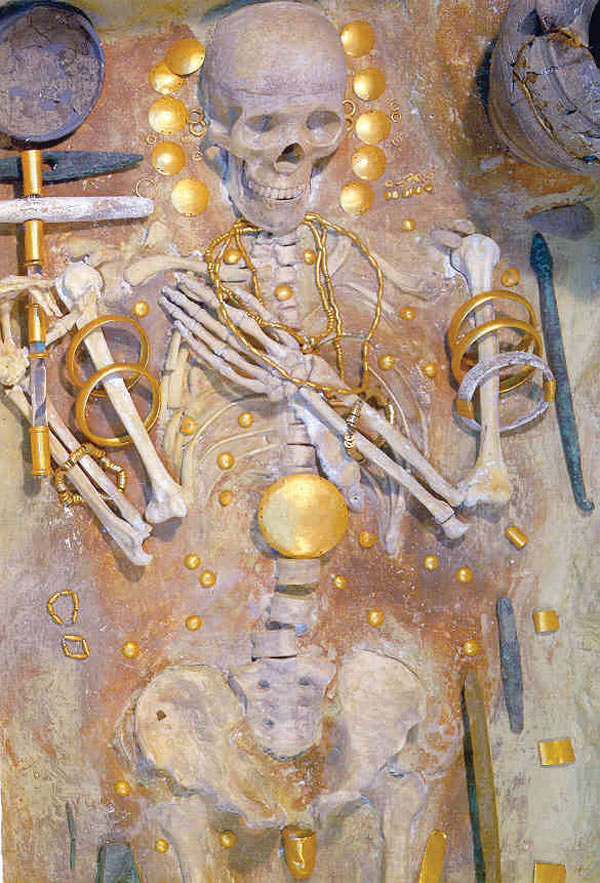
Third, on the evidence of Grave 43 – by implication that of a warrior, a ruler, and perhaps, given the common character of early chieftainship, some sort of priest-king – the transition from a more matriarchal Neolithic to a more patriarchal Chalcolithic/Bronze Age form of social organisation was well advanced at Varna.
The presence of bull-shaped objects among the goldwork – most of which is otherwise non-representative – coupled with the penis sheath certainly implies a cultural preoccupation with virility and male power.





