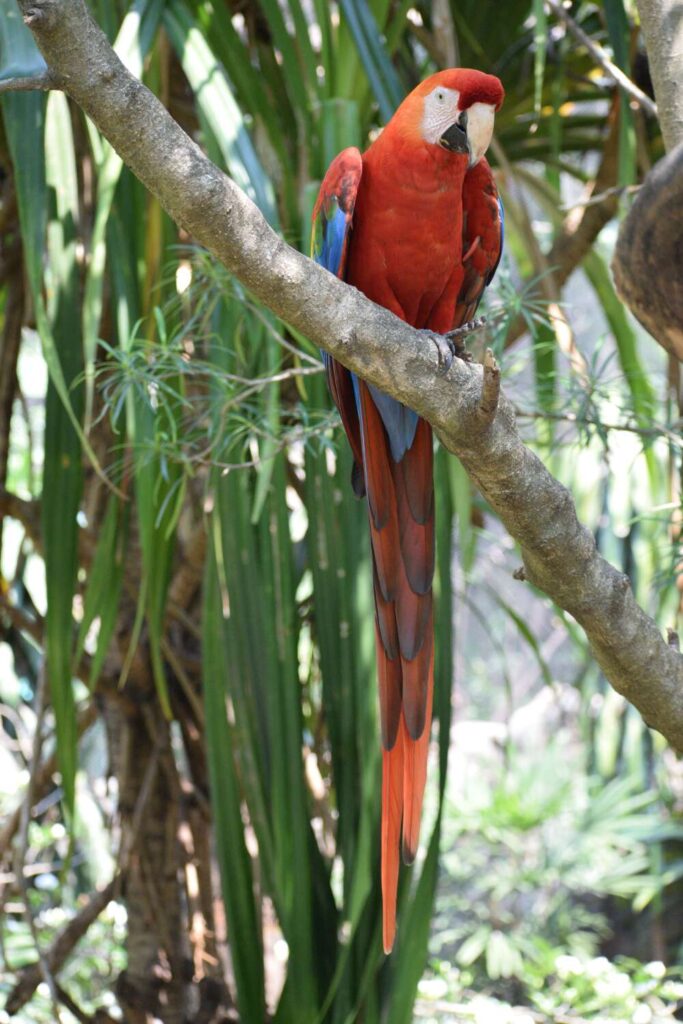
Mummified Parrots Found In The Atacama Desert Transported Hundreds Of Miles While Alive
The more we delve into Chile’s desolate Atacama Desert, the more we discover, Phenomena both mystifying and wonderful, occasionally bordering on alien. But in this incredibly dry place, it wasn’t just the climate that was unforgiving. Its ancient human inhabitants, making do in a parched place not best suited to hosting them, traded in whatever they could get their hands on.
Sometimes, it seems, that was the brilliant feathers of colourful birds brought unceremoniously to a desert they didn’t belong to, but were destined to be buried within. What we consider acceptable interactions with animals under our care was very different back then, says anthropological archaeologist Jose Capriles from Pennsylvania State University.
“Some of these birds did not live a happy life. They were kept to produce feathers and their feathers were plucked out as soon as they grew in.” Capriles is something of a specialist when it comes to discovering the exotic oddities of pre-Columbian American culture.

This time, his mother – Eliana Flores Bedregal, an ornithologist by profession – came along for the ride, co-authoring a new study examining the life and death of over two-dozen mummified and partially mummified parrots found within the Atacama Desert.
In total, at least six species of parrots originally recovered from five of the desert’s archaeological sites were studied in the research, with the remains variously dating from between 1100 to 1450 CE.
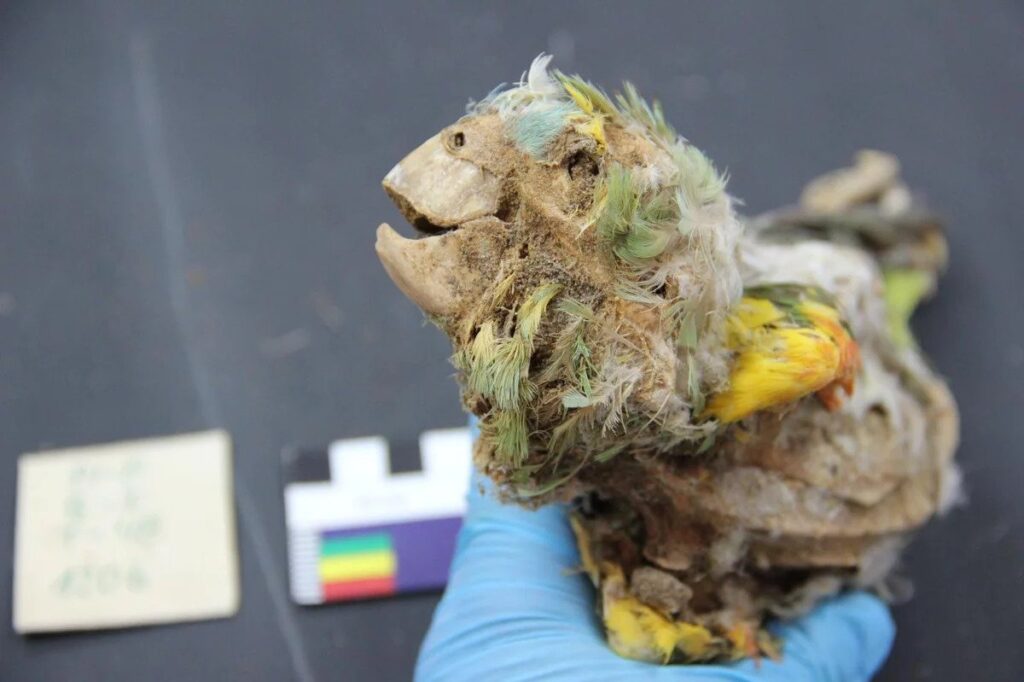
“The feathers of tropical birds were one of the most significant symbols of economic, social, and sacred status in the pre-Columbian Americas,” the authors write in their study.
In the Andes, finely produced clothing and textiles containing multicoloured feathers of tropical parrots materialized power, prestige, and distinction and were particularly prized by political and religious elites. Behind the folds of this marvellous drapery, the colourful birds likely lived a miserable existence in captivity, far from the Amazonian rainforests that were once their home.
Sometimes, the feathers were plucked elsewhere and imported into the Andes in special containers, but the remains of the 27 parrots and macaws analyzed here suggest many other birds were specifically brought to the desert for their vibrant plumage.
The feather trade in the region dates back much longer than this, at least to the Chinchorro mummies of around 5050 BCE. Thousands of years later, feathers were still a cherished feature used in garments, hats, headdresses, and other ornaments.
Most of the mummified birds examined in the new study were originally recovered from an archaeological site called Pica 8, located close to an oasis community within the Atacama Desert that still exists today.
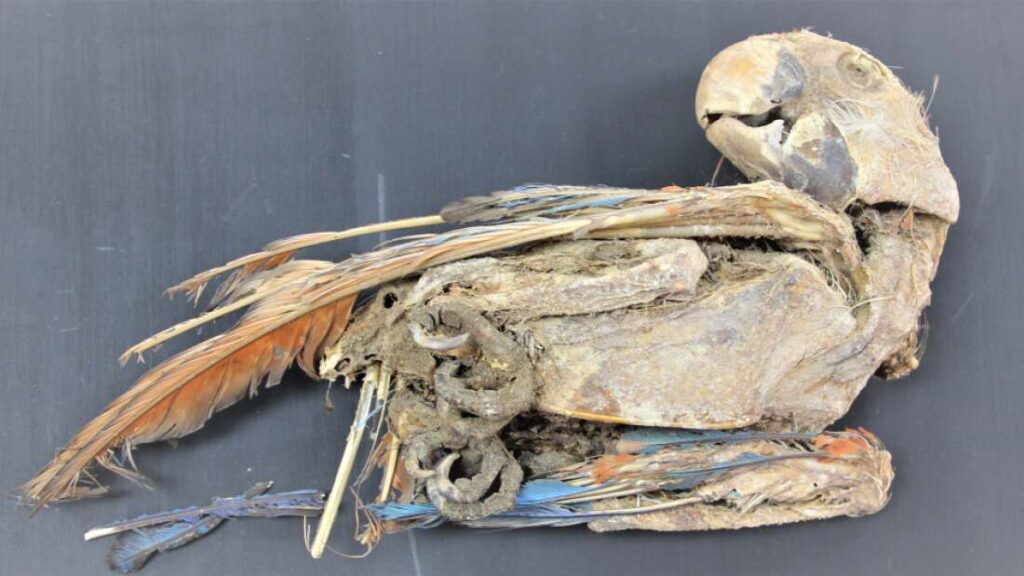
Once upon a time, though, the people here buried their birds alongside themselves.
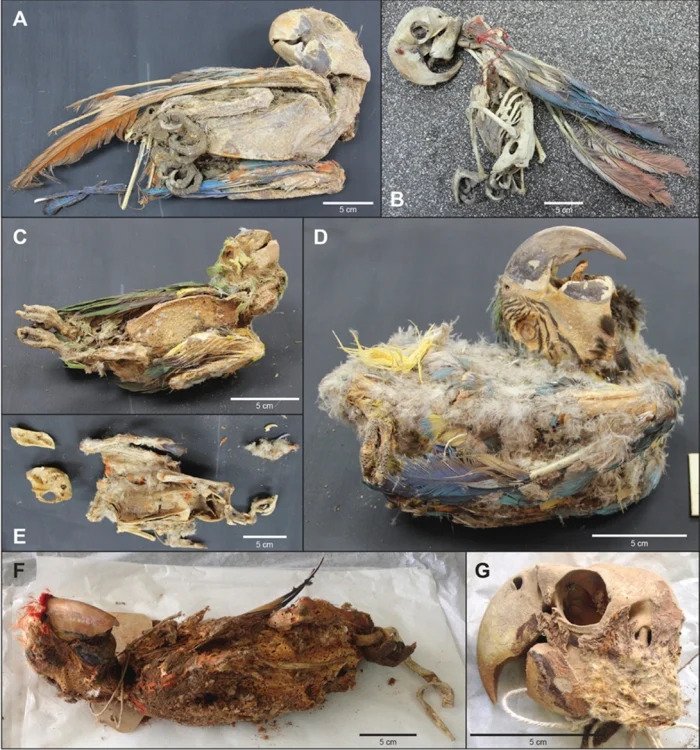
“Most birds were placed in direct association with human burials,” the researchers write, noting the parrots’ tails were often removed.
Sometimes the animals were positioned in elaborate stances, with beaks opened and tongues sticking out, perhaps tied to ritualistic practices invoking parrots’ ability to mimic human speech. Others had their wings spread as if to forever soar in the afterlife.
During their life on Earth, it seems many had their wings broken and their feet strapped, although the researchers also observe care was taken with some of the animals, with evidence of clipping of their beaks and claws, in addition to healing processes for fractures sustained by the parrots.
“We have absolutely no idea why they were mummified like this,” Capriles says.
“They seem to be eviscerated through their cloaca (a common excretory and reproductive opening), which helped to preserve them. Many times, they were wrapped in textiles or bags.”
What is certain is that it can’t have been easy to get these grounded birds to the desert. Transported by llama caravans, it’s likely the journey from the Amazon would have taken months, the researchers think, although it’s possible some of the birds were procured from regions closer to the desert.
Once there, they were held as valuable pets, treasured for their wondrous palette of feathers, with each enticing shade certain to be stolen.





