Ice Age ‘megafauna’ remains including a mammoth, rhino, hyena and wolf dating back up to 60,000 years are discovered in a Devon cave
The development of Sherford began in 2015 and appeared rather promising. A new town in Devon, England, it would have 5,500 homes and sit near the bustling port city of Plymouth. Fortunately, developers requested archaeologists comb the area before breaking ground — leading to the discovery of animal remains that date back to the Ice Age.
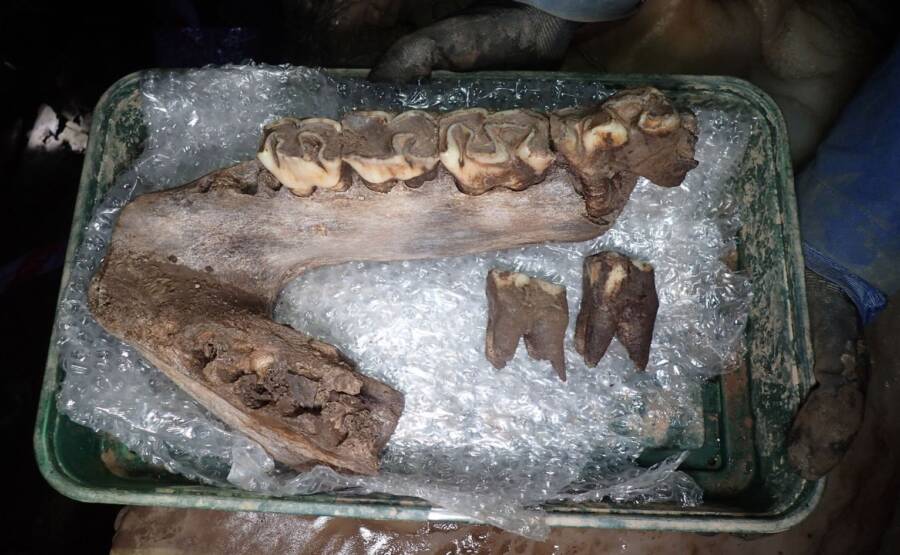
These remains included the tusk, molar tooth, and other bones of a woolly mammoth.
Experts also found the lower jaw and partial skull of a woolly rhinoceros, with a complete wolf skeleton to follow. Other findings include partial remains of a hyena, horse, reindeer, mountain hare, and red fox, plus the bones of bats and shrews.
Led by AC Archaeology and Orion Heritage, the ongoing excavations took place in a cave near old lime kilns and a local quarry.
According to Sherford officials, the animals died at some point between 30,000 and 60,000 years ago. For the experts involved, this extinct megafauna from Britain’s last Ice Age speaks a thousand words.
“This is a major discovery of national significance — a once-in-a-lifetime experience for those involved,” said lead archaeologist Rob Bourn. “To find such an array of artefacts untouched for so long is a rare and special occurrence. Equally rare is the presence of complete or semi-complete individual animals.”
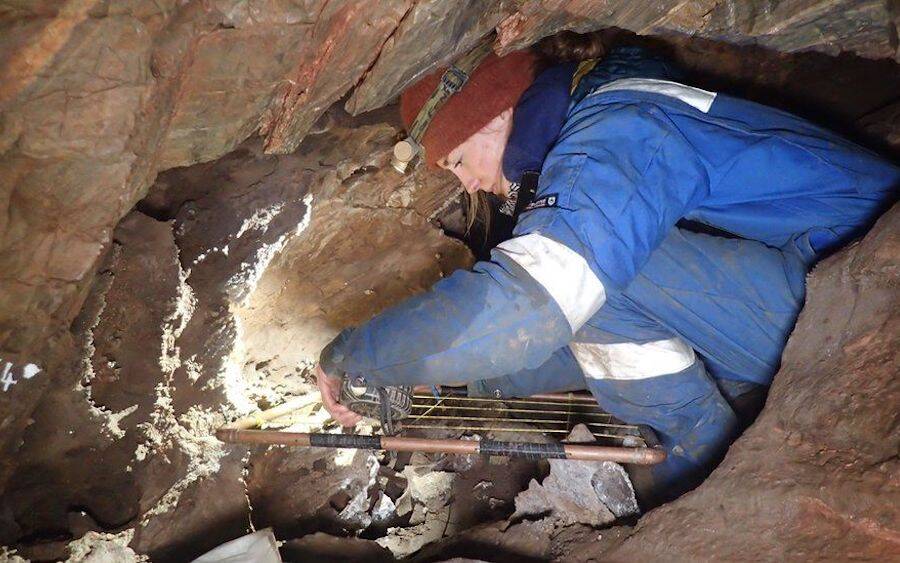

Fortunately for scientists and historians, requesting heritage institutions to thoroughly search an area prior to construction is commonplace in the United Kingdom.
Sherford Consortium developers did so from the very beginning — thereby preventing the destruction of these priceless remains.
The team has since taken the remains off-site for a thorough examination. While they’ve dated them to the Middle Devensian period, it’s unclear if all the animals involved lived during the same timeframe or died millennia apart. For Victoria Herridge, an expert in fossil elephants at the Natural History Museum in London, much is left to learn:
“Devon then would have been a bitterly cold and dry place to be, even in summer,” she said.
“However, it was also a huge open grassland, capable of supporting vast herds of cold-tolerant animals like the woolly mammoth, the woolly rhino and reindeer, as well as the big carnivores like hyena and wolf that preyed upon them.”
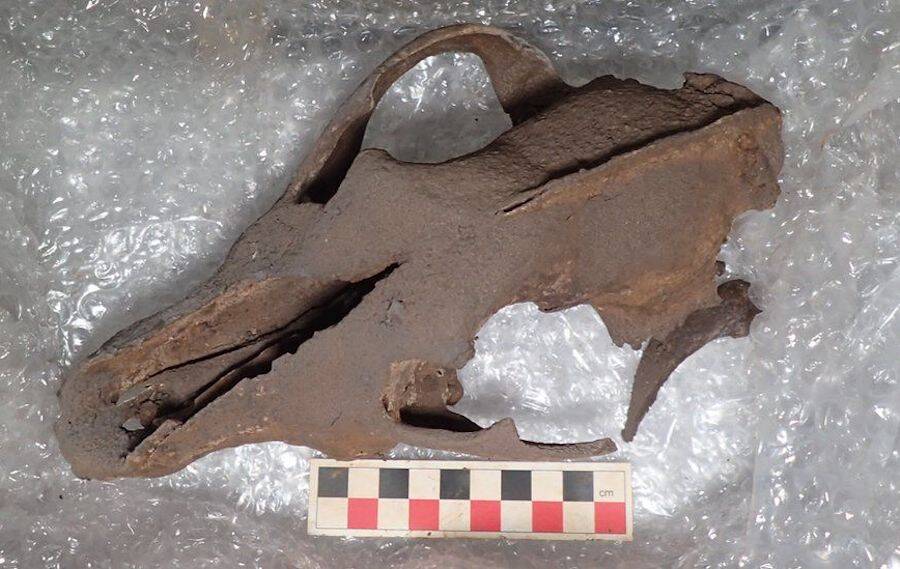

“This is vital knowledge. Scientists are still unravelling what role climate and humans played in the extinction of the woolly mammoth and the woolly rhino — and what we can learn from that to protect species threatened by both today.”
While the fact that these bones were preserved for millennia is astounding, Bourn was more impressed that they stayed intact during the human activity of the modern age: “Construction happening at Sherford is the sole reason these findings have been discovered and it is remarkable that they have laid undisturbed until now.”
On the other hand, the discovery site itself isn’t particularly easy to access for regular folk. It’s likely precisely because of this that the bones remained so well-preserved.
The Sherford Consortium has since guaranteed that this underground area will be closed off, with no public access allowed — or construction atop to follow.
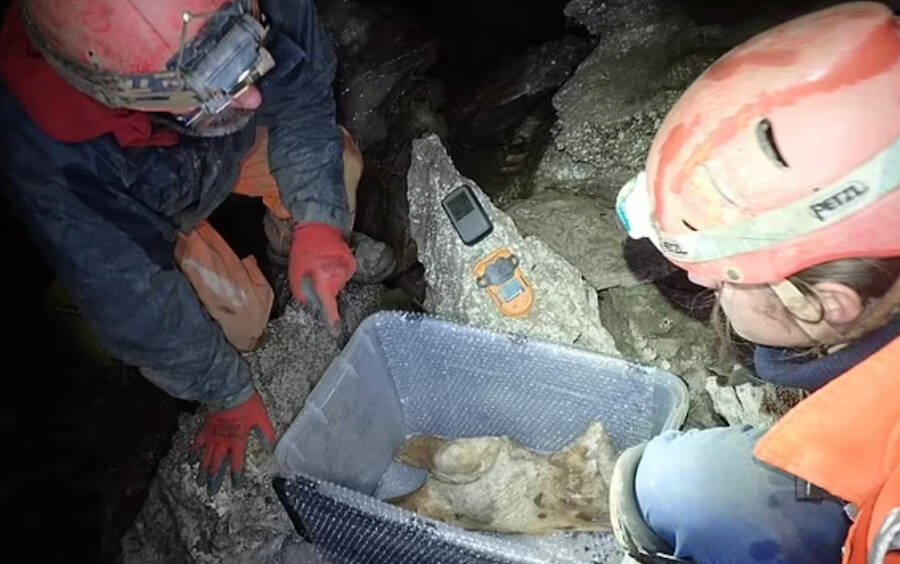

“To have found partial remains of such a range of species here in Devon gives us a brilliant insight into the animals which roamed around Ice Age Britain thousands of years ago, as well as a better understanding of the environment and climate at the time,” said Duncan Wilson, the chief executive of Historic England.
As for the future of these ancient remains themselves, it’s been decided that Plymouth’s new museum The Box will put them on display. With the history of the region safeguarded by those who inhabit it today, museum CEO Victoria Pomery hopes locals will gain warranted insight into their heritage.
“Once all the analysis work is completed it will be a huge honour to care for and display these newly discovered finds, and to play an ongoing part in the public’s understanding of Plymouth and the animals that were here during the Ice Age,” said Pomery.
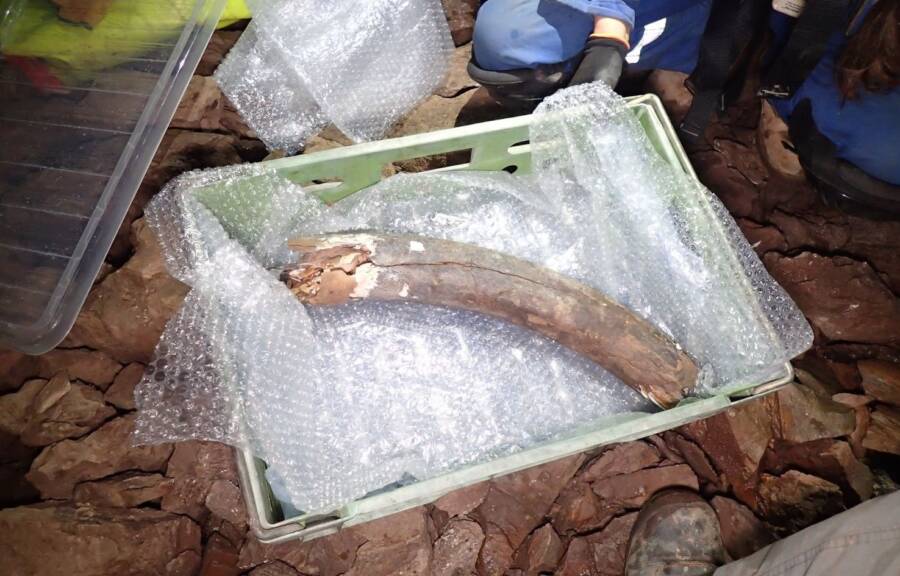

Whether the animals in question all fell into the pit and died together or merely washed into the cave over time is still a mystery. What is clear, however, is that Devon’s Joint Mitnor cave discovered in 1939 yielded over 4,000 animal bones — and was robbed in 2015 by thieves who stole a 100,000-year-old elephant tooth.
Fortunately, that’s unlikely to occur again, as those in charge appear to be determined to properly guard the newfound site.





