Crimean Atlantis: Remarkable Ancient Underwater City Of Akra
The ancient city of Akra was once a beautiful place famous for its outstanding architecture. Then, its glory and prosperity came suddenly to an end. About 2,000 years ago, the city of Akra was submerged.
Underwater archaeologists have discovered several of the ancient city’s ruins, defensive walls, houses, and a mysterious tower.
The underwater city of Akra still remains vastly unexplored and has many more secrets to reveal.
Ancient City Of Akra Belonged To The Bosporus Kingdom
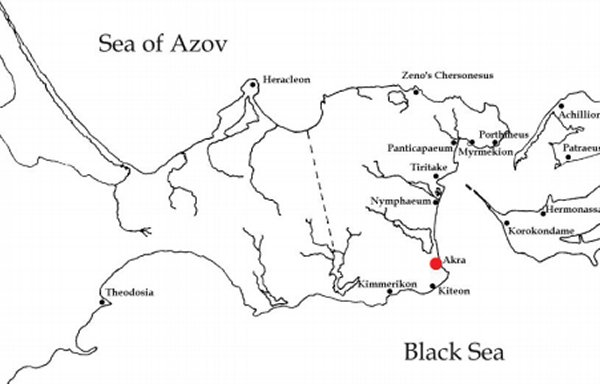
Ancient historians such as Strabo and Ptolemy mentioned the city’s existence. Akra was part of the Bosporus Kingdom, an ancient state on the northern coast of the Black Sea, founded ca 480 B.C through an alliance of existing Greek city-states.
The kingdom’s capital was Panticapaeum (present-day Kerch). It was ruled by the Archaeanactid and then by the Spartocid dynasty, which endured for over 300 years.

Founded by the settlers from Nymphaeum or Panticapaeum in the late 6th century B. C, the city of Akra was a large shopping centre visited by many people from various corners of the ancient kingdom.
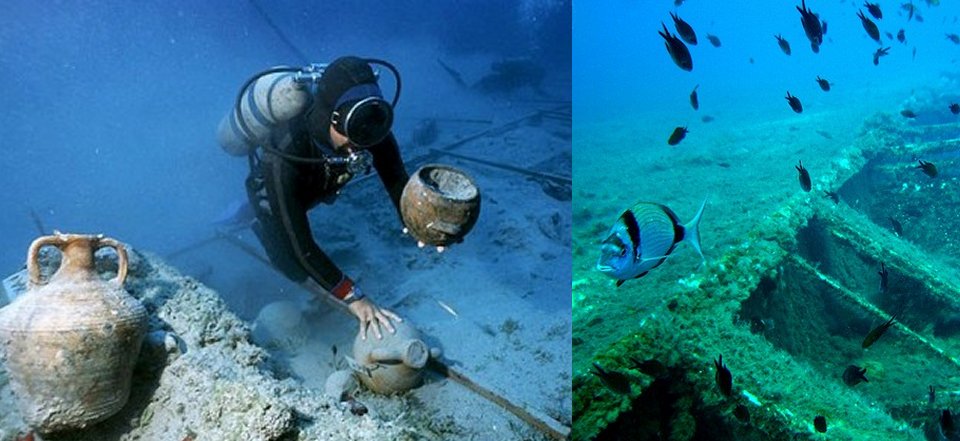

Many Of The Ancient Underwater Ruins Are Well-Preserved
The underwater city of Akra was accidentally discovered in 1981 when a high school boy walking along the beach found 150 ancient coins in the sand. This discovery prompted researchers to launch an expedition to find out what ancient treasures were resting underwater.
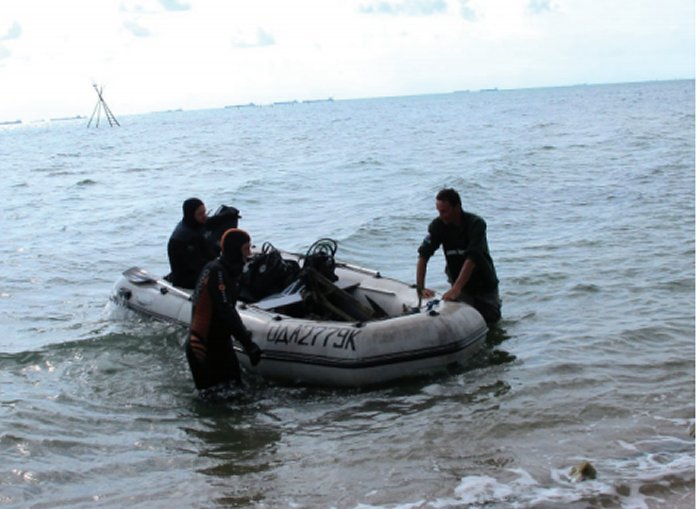

Since then, a team of underwater archaeologists from Ukraine and Russia has discovered thick defensive walls, two towers, remains of well-preserved ancient houses, and other valuable ancient artefacts such as coins, amphorae, arrowheads, and pottery.
One of the discovered towers is still in very good condition. Considering the towers have survived underwater for more than 2,000 years it clearly shows the ancient people of Akra possessed sophisticated knowledge of architecture. The tower probably served as part of the city’s defence buildings.
In 2011, researchers also found remains of the wreck of a wooden ship in the distance of several kilometers from Akra on the depth of 4 meters. The observed length of the ship was about 30 meters; its hull was covered with brass plates.

While other ancient cities of the Black Sea region – Pantikapea, Olbia, and Chersonesos were almost completely destroyed by the sea, it can be said that the ancient city of Akra was lucky.
According to underwater archaeologists Viktor Vakhonieiev and Sergey Solovyev, features of the wave conditions in this part of Kerch Peninsula led to the fact that the cultural layers of the ancient city were not mainly washed away, and its building constructions were not completely destroyed, but only partially covered with sea sand deposits.
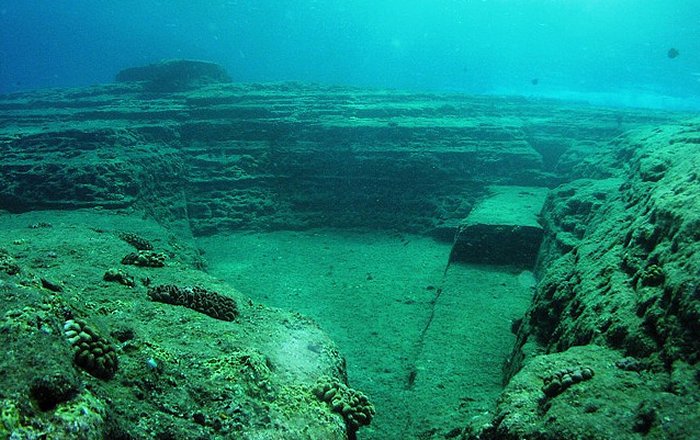

The Black Sea can become a significant region for future underwater archaeologists. Not only are natural well-preserved here, but there are also many intact submerged ancient vessels, sites, and cities resting beneath the waters.
In May 2013, the ancient underwater city of Akra became a tourist attraction. However, according to the Crimean Ministry of Culture and Tourism, permissions to visit the underwater city of Acre are extremely limited. Tourists are only allowed to visit the flooded city from late May to early June.
Scientists say they have much more to explore, and they still haven’t been able to reach many of the underwater ruins of ancient Akra.
All these amazing underwater discoveries Make you wonder what more is hidden beneath the waters of the Black Sea.





