Ancient skeletons reveal the history of worm parasites in Britain
Britons have suffered from worms since the Bronze Age, new research shows, with parasite infections peaking during the Roman and Late Medieval periods.
Things began to get better during the Industrial period, in part thanks to improvements in hygiene in parts of the UK, before the Victorian ‘Sanitary Revolution’ ushered in a nationwide reduction in infections.
Oxford researchers analysed ancient skeletons in an effort to establish the size and scale of parasitic worm infections in the UK over the course of history.
They hope that understanding how parasitic worm infections changed in the past, it could help public health measures in regions of the world still experiencing problems today.
Infections with parasitic worms are a big problem in some tropical and sub-tropical regions of the world.
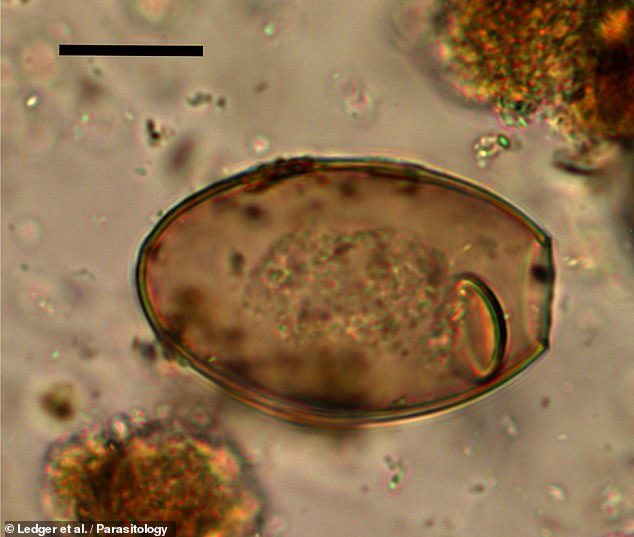


But in the past, they were much more widespread and were common throughout Europe.
The research team looked for worm eggs in the soil from the region where the infected intestines of 464 human skeletons would have been, at 17 sites dating from the Bronze Age to the Industrial Revolution.
They found that worm infections peaked in Britain during the Roman and Late Medieval periods when infection rates were similar to those seen in the most affected regions today.
Things changed in the Industrial period. Worm infection rates differed a lot between different sites – some sites had little evidence of infection, while in others there was a lot of infection.
The researchers think that local changes in sanitation and hygiene may have reduced infection in some areas before nationwide changes during the Victorian ‘Sanitary Revolution’.
The co-first authors, Hannah Ryan and Patrik Flammer said: ‘Defining the patterns of infection with intestinal worms can help us to understand the health, diet and habits of past populations.
‘More than that, defining the factors that led to changes in infection levels (without modern drugs) can provide support for approaches to control these infections in modern populations.’
Humans are infected with roundworms and whipworms through contamination by faecal matter and catch some tapeworms by eating raw or undercooked meat or fish.
The team will next use their array of parasite-based approaches to investigate other infections in the past. This includes more large-scale analyses of human burials, as well as continuing their ancient DNA work.
Their ambition is to employ a multidisciplinary approach, working closely with archaeologists, historians, parasitologists, biologists and other interested groups to use parasites to help understand the past.
The study has been published in the journal PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases.





