HUNDREDS Of Megalithic Monuments Discovered Around Stonehenge
In a groundbreaking news release, archaeologists have revealed the results of a four-year-long project to map the hidden landscape beneath the surface of the Stonehenge environs, and what they found is nothing short of amazing.
Through their high-tech devices, they could see a landscape teeming with burial mounds, chapels, shrines, pits, and other structures, which had never been seen before, including another massive megalithic monument composed of 60 giant stones stretched out along a 330-metre long c-shaped enclosure.
According to The Independent, the discovery dramatically alters the prevailing view of Stonehenge as the primary site in the landscape. Instead, it presents the Salisbury Plain as an active religious centre with more than 60 key locations where ancient peoples could carry out sacred rituals and fulfil their religious obligations.
“This is not just another find,” said Professor Vince Gaffney of the University of Birmingham. “It’s going to change how we understand Stonehenge.”
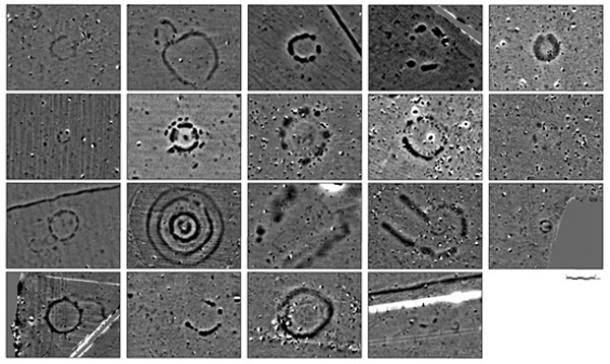
Using powerful ground-penetrating radar, which can scan archaeological sites to a depth of up to four metres, investigators from Birmingham and Bradford universities and from the Ludwig Boltzmann Institute in Vienna discovered hundreds of hidden monuments and features that cover the landscape in all directions.
The biggest surprise was a 330-metre-long line of up to 60 buried stone pillars, inside the bank of a large, bowl-shaped feature called Durrington Walls, Britain’s largest henge, which sits beside the River Avon.
The 3-metre long and 1.5-metre wide stones are laid horizontally inside the mound, although they may have once stood vertically.
“Up till now, we had absolutely no idea that the stones were there,” said Professor Gaffney.
The line of megalithic stones seems to have formed the southern arm of a c-shaped ritual enclosure which faced directly towards the river, the rest of which was made up of an artificially scarped natural elevation in the ground.
The monument was later converted from a c-shaped to a roughly circular enclosure, now known as Durrington Walls – Britain’s largest pre-historic henge, roughly 12 times the size of Stonehenge itself.
In addition to this monumental discovery, the research team found more than 60 other previously unknown pre-historic monuments scattered across Salisbury Plain, including 20 large ritual pits up to 5 metres in diameter, 8 previously unknown Bronze Age burial mounds, 4 Iron Age shrines or tombs, 6 Bronze Age and Iron Age livestock enclosures, and 17 other henge-like Neolithic and Bronze Age structures, each between 10 and 30 metres in diameter.
Some may well have consisted of circles of large timber posts – wooden equivalents of conventional prehistoric stone circles.
“It shows that, in terms of temples and shrines, Stonehenge was far from being alone,” said Professor Gaffney.

Another significant discovery was a mound between Durrington Walls and Stonehenge, located approximately 3 km from Stonehenge, which has been revealed as a 33-metre long, wooden ‘House of the Dead’.
Archaeologists found evidence of ritual practices including excarnation, in which the skin and organs of the deceased were removed. The building is thought to have been used for seven generations by a single family before it was buried in chalk and forgotten for thousands of years.

The research team is now analysing the data in an attempt to piece together exactly how Neolithic and Bronze Age people used the Stonehenge landscape. Using computer models, they are trying to work out how all the newly discovered monuments were connected with each other.
This incredible discovery has been announced ahead of a two-part special BBC Two documentary titled ‘Operation Stonehenge: What Lies Beneath, in which the research team will release the full extent of their findings.
Watch trailer of the Operation Stonehenge BBC series:





