Did Romans Eat Special Foods at Funerals?
In the 1950s, a Roman necropolis (or cemetery) was found in the centre of Barcelona, hailing from the second and third centuries AD.
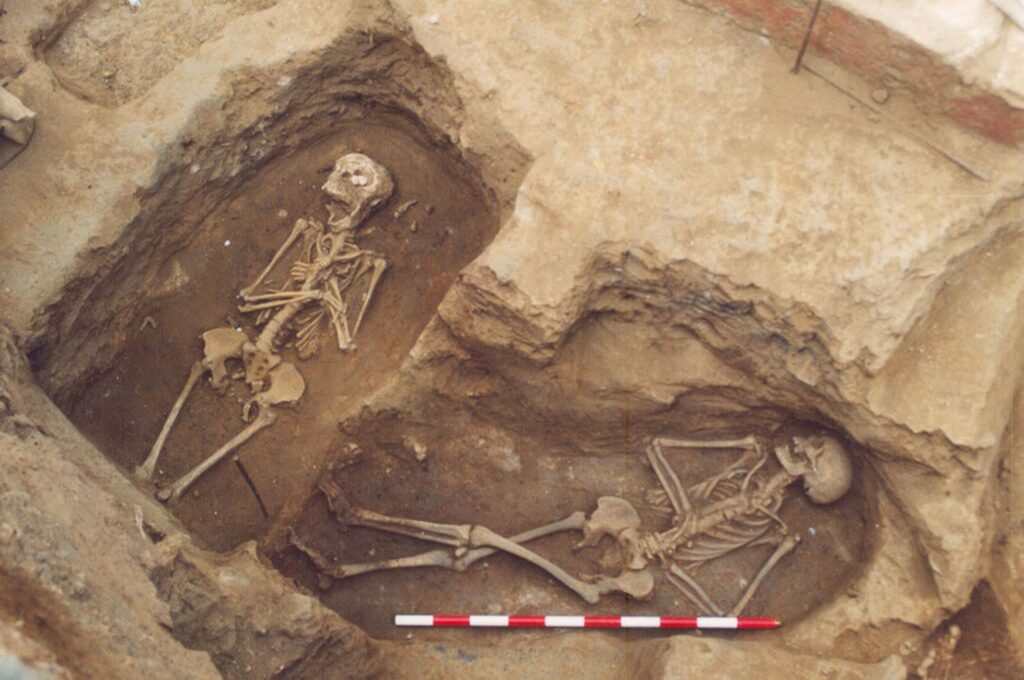

The site – Plaça de la Vila de Madrid – was excavated again between 2000 and 2003, when a funerary complex of about 500 square feet was discovered. This collective grave – containing the remains or ashes of 66 individuals – was set up to bury slaves or low-income free people.
By paying a monthly fee during their lifetimes, Romans of the lowest echelons could secure decent burials. However, problems arose when relatives had to carry out obligatory ritual banquets in front of the tombs, for not everyone could celebrate the deceased as tradition dictated. For instance, according to authors like Cicero, a tomb was only considered a tomb following the sacrifice of a pig – a high-priced animal beyond the reach of slaves or most citizens.
Within the necropolis, in addition to human remains, some animal bones have also been found, confirming that the funerary rites required by law – such as banquets and offerings – were indeed carried out.
A hole was made in the graves, through which food and drink were introduced. Offerings, banquets and animal sacrifices were made to ensure the nourishment and protection of the deities and the memory of the deceased. Archaeologists have also unearthed pottery and plants inside the tombs.
In a study for the academic journal Plos One titled “Food for the soul and food for the body: studying dietary patterns and funerary meals in the Western Roman Empire,” the authors explain that “the age, sex, offerings and diet of the buried individuals show some differences… suggesting that the inequalities present in life could have also persisted in the funerary rituals.”
The human remains found in Vila de Madrid have been subjected to carbon and nitrogen isotope analysis to determine the diet of the buried individuals, so as to contrast it with the remains of the animals consumed during the funerary banquet. And, in addition to human remains, animal bones have also been analyzed.
The analysis has determined that 30 per cent of identified animals were pigs, 27.1 per cent bovines, 24.3 per cent goats and 10 per cent chickens. Remains of roe deer, hare, rabbit and fox were also documented.
The most frequent bones documented were scapulae, humeri, radii, ulnae, pelvis, femurs and tibias, indicating that the parts richest in meat were consumed, although they came from old animals in order to reduce the costs of the banquets.
“This is an important point, as it suggests that only animals that could not be exploited for other purposes were being slaughtered… therefore, the economic burden of slaughtering could be minimized,” notes the article in Plos One.
Women and men in Rome did not eat the same protein sources – men generally ate more meat.
“This could mean that sociocultural tastes for food were different between the sexes, or that more males than females had access to protein-rich resources perhaps due to custom, social status, wealth, or medical advice.”
Roman doctors advised “eating different types of food depending on mood.” Men, they thought, were “hot and dry,” so it was recommended that they eat “cold and wet food,” such as fish. Women, on the other hand, were “cold and wet,” so they had to eat “hot and dry food, like oats.”
In short, the study reveals that “although the offerings and banquets were stipulated by law, not everyone could afford to make sumptuous or rich offerings.
The presence of bird remains and portions rich in meat suggests that the relatives of the deceased tried to follow the law as closely as possible.” Yet, it is clear that the poor did not eat like the rich… even in death.





