Archaeologists find an ancient skeleton buried with ‘2,100-year-old iPhone’
In the mysterious burial site called the “Russian Atlantis” AN extraordinarily 2,137 years-old “iPhone” was excavated from the tomb of a young lady.
After a large, man-made reservoir in Siberia was drain during the summer, the tomb of the old fashionista – nicknamed Natasha by archeologists – was discovered.

It dates back to the ancient Xiongnu empire – a huge nation of nomads that ruled the area from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD.
In fact, what looks strikingly like a smartphone is actually made of black gemstone jet rock – with a regular pattern of semi-precious stones inlaid.
And rather than being a pre-historic piece of tech, the block was actually used as an ornate belt buckle.
Archaeologist Dr. Pavel Leus said: “Natasha’s’ burial with a Hunnu-era (Xiongnu) ‘iPhone’ remains one of the most interesting at this site.”
The intricate inlays are made of turquoise, carnelian, and mother-of-pearl – as well as a form of ancient Chinese coin.
Atlantis Necropolis
Dr. Leus added: “Hers was the only belt decorated with Chinese wuzhu coins which helped us to date it.”
The find is from the Ala-Tey necropolis in the so-called Sayan Sea – a giant reservoir upstream of the Sayano-Shushenskaya Dam, Russia’s biggest power plant.
The 7inx3in treasure was discovered in the normally submerged “Atlantis necropolis” this summer month – when the reservoir is temporarily drained.
The ancient burial plot is usually up to 56ft underwater, according to The Siberian Times.
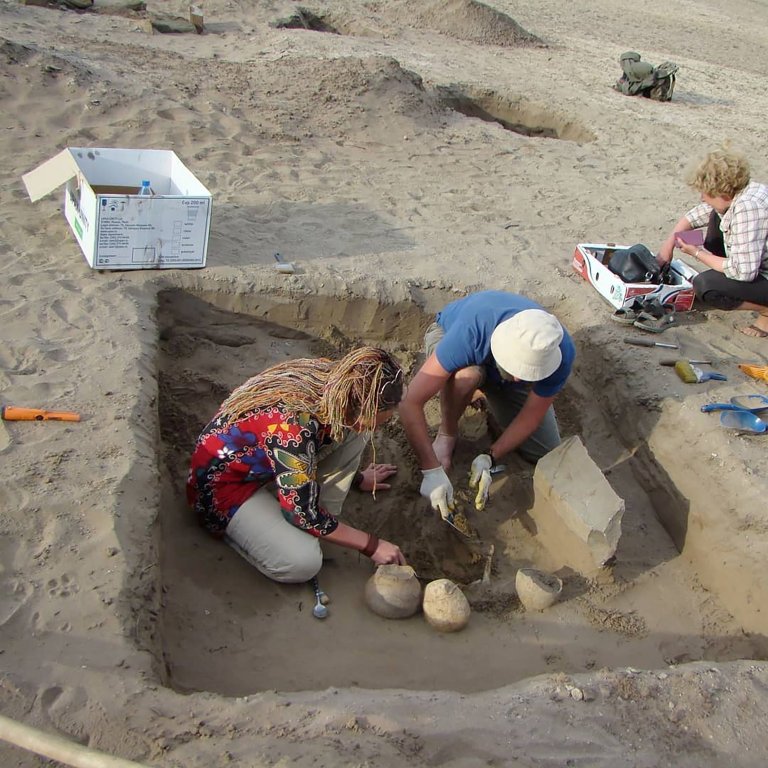
Graves of prehistoric civilizations dating from the Bronze Age to the time of Genghis Khan are also located there.
It comes after the two partly-mummified prehistoric women were found – they were buried with the tools of their trade.
One called “Sleeping Beauty” – dressed in delicate silk for the afterlife – was at first believed to be a priestess but is now thought to have been a leather designer.
The second was a weaver laid to rest with her wooden spindle packed inside a sewing bag. The reservoir covers 240sq miles but in summer the water level falls by almost 60ft – giving its floor the appearance of a desert.
A total of 110 burials have so far been discovered on an island in the reservoir.

“This site is a scientific sensation”, said Dr Marina Kilunovskaya from the St Petersburg Institute of Material History Culture.
She added: “We are incredibly lucky to have found these burials of rich Hun nomads that were not disturbed by (ancient) grave robbers.”
Another Atlantis site in the reservoir is called Terezin and has at least 32 graves closer to the shore. Scientists admit they are in a race against time to examine the sites and save priceless treasures from damage by the returning water.





