Boy Found Million-Year-Old Fossil by Tripping Over It
For example, while walking through the New Mexican desert, something turns out to be a fossil of Stegomastodon from 1.2 million years ago, you could see some benefits.
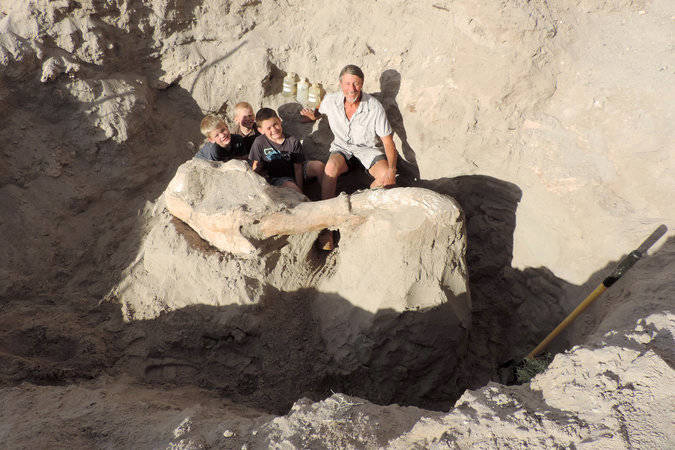

Jude Sparks, 9, was doing this last October when he and his parents visited the Orange Mountains.
The brother of Jude, a hunter, was not initially convinced that the finding was awesome.
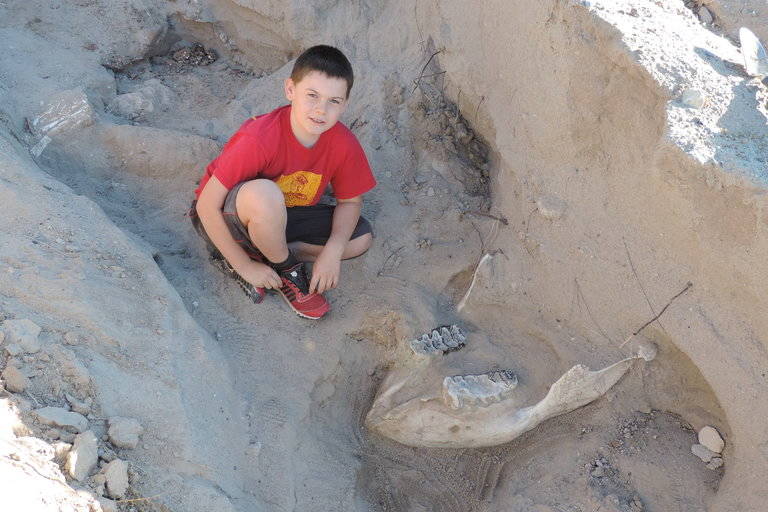
“Hunter said it was just a big fat rotten cow,” Jude told KVIA TV. “I didn’t know what it was. I just knew it wasn’t usual.”
To him, the discovery looked like “fossilized wood.”
His parents agreed and contacted Peter Houde, a professor at New Mexico State University, who returned with the family to the site the next day. Sure enough, the boy had stumbled over a fossilized tusk.
It’s a big discovery — both literally and metaphorically. The ancient mammals were cousins to the wooly mammoth and modern-day elephant, so the remains are large.
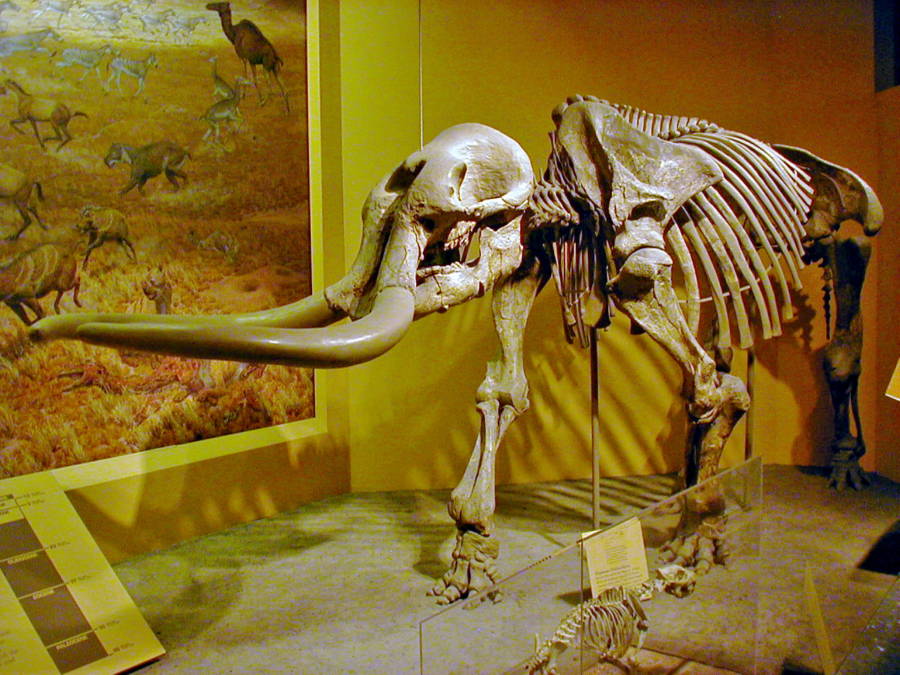
They’re also rare since prehistoric bones typically disintegrate quickly after being exposed to the elements. Houde suspects the Sparks family came across the tusk just after erosion had brought it to the surface.
“This is really very unusual to find,” he told The New York Times.
With Houde’s help, the family reburied the remains and set about fundraising for a formal dig.
It took them months to organize a team and secure a permit — but in May they finally uncovered an entire skull made of fragile “egg-shell thin” pieces.

“We’re really, really grateful that they contacted us, because if they had not done that if they had tried to do it themselves, it could have just destroyed the specimen,” Houde, who hopes to display the remains at the university, said. “It really has to be done with great care and know-how.”
Oddly, this isn’t the first accidental Stegomastadon find. In 2014, a hiking bachelor party found a 3-million-year-old skull belonging to the dino in New Mexico’s Butte Lake State Park.
Humans may have hunted the Stegomastodon toward the end of its existence, though it’s likely that its mammoth competitors kicked it off the evolutionary tree.
The creatures remain — a bit smaller than the average African elephant — are easily identified by their broad, upward-curving tusks.
As for Jude, he isn’t really as into fossils as he was when he was “little.”
He’ll take the attention, though.
“I’m not really an expert,” the now-10-year-old told the Times. “But I know a lot about it, I guess.”





