Scientists discover humans may have been living in Australia for 120,000 years
When did the first people arrive in Australia?…did they follow the routes we’re told about?
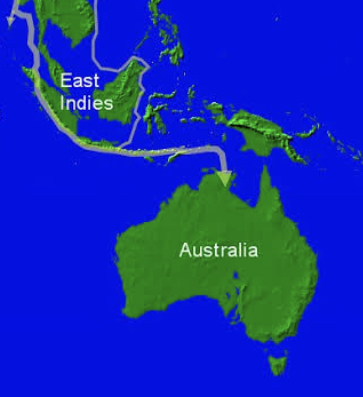
Makes sense, doesn’t it?…coming down through Papua New Guinea, the Asian corridor to the top end of Oz, where we’re told the earliest evidence is found…but another site may push human migrations back even further…
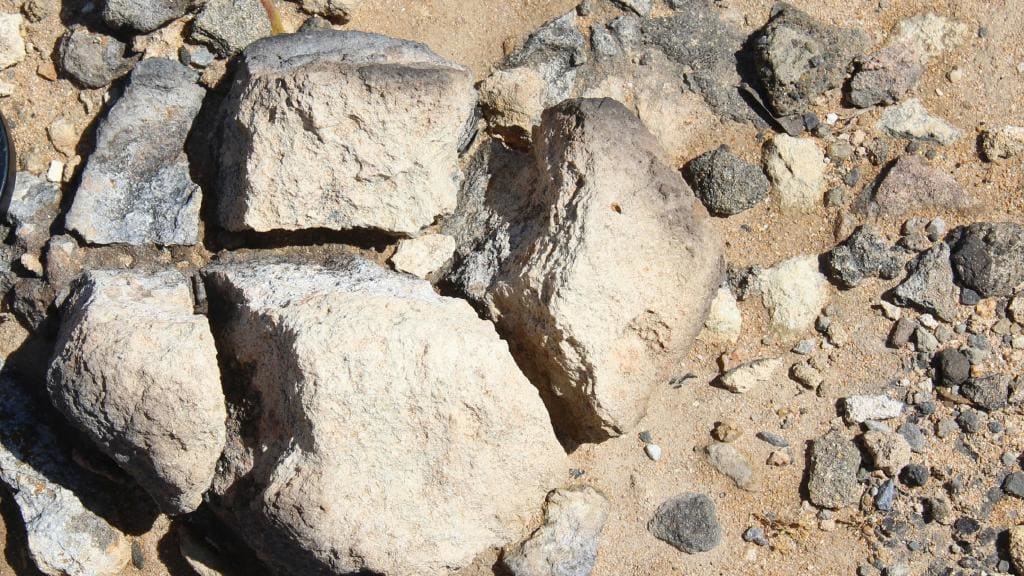
A site filled with blackened stones in southern Victoria, Australia has raised the possibility that humans existed on the continent 120,000 years ago — twice as long as the previously established timeframe of early human life in the land “down under.”

It seems when the topic comes up, it’s met with skepticism or almost claims of mental impairment…It’s safe to assume that anyone traveling, exploring or whatever to an unknown land would hug the coast…food is plentiful and fresh water can be found relatively close by…That’s where I believe the evidence would lie…think about it like this… you are at the beach all set up and the tide starts rolling in. What do you do?..you move further up the beach…
Some common counters are always along the lines of…show the evidence…it can’t be proven etc…and, to be honest, it’s probably a valid argument…but in some circumstances, the evidence may be difficult to produce…
As recently as 10,000 years ago…Tasmania was cut off from mainland Australia due to rising sea levels…
An example is a place an hours run south from Wollongong. During the ice age, the Shoalhaven and Crookhaven Rivers flowed across what is now the continental shelf. Silt deposits at the Nowra Bridge exceed 70 meters (with freshwater shells at that depth) and indicate that the river would have been flowing at the bottom of a 100m gorge.
The sea reached its present level approximately 6,000 years ago and from this time numerous archaeological sites survive…
In the past, scientific research suggestive of human habitation in Australia up to 120,000 years ago had been considered and then rejected.
Several habitation sites have produced discoveries pointing to a much earlier than expected period, but the controversy led to more conservative dating. The new finding should cause a rethinking of all relevant archaeological sites…
As far as I’m aware at no point has Asia and Australia been connected…or at least not recent enough as to allow a foot crossing…so at some point a sea voyage occurred, granted not a long one, but one all the same…
Research and analysis are still ongoing…but I think there’s a good chance a missing piece of the puzzle could be under the waves…
One other find of interest is a gene that potentially shows interbreeding with species not yet discovered…





