Eighteenth-Century Mass Grave Unearthed in Romania
A mass grave from the eighteenth century was discovered in West Romania by the team of researchers from the West University of Timişoara according to a Romania-Insider report.
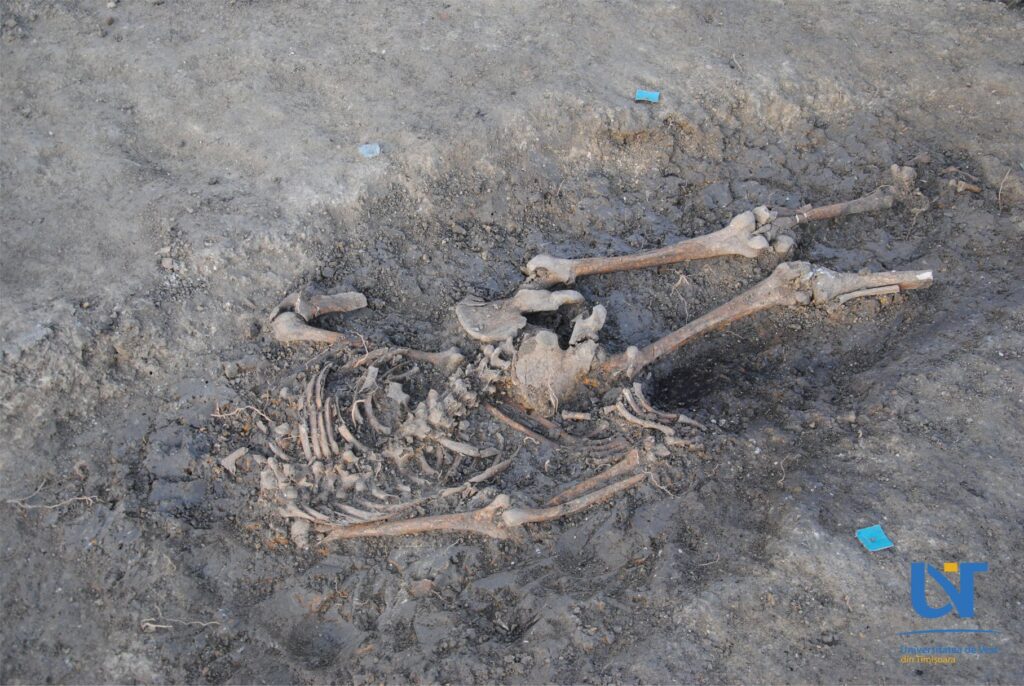
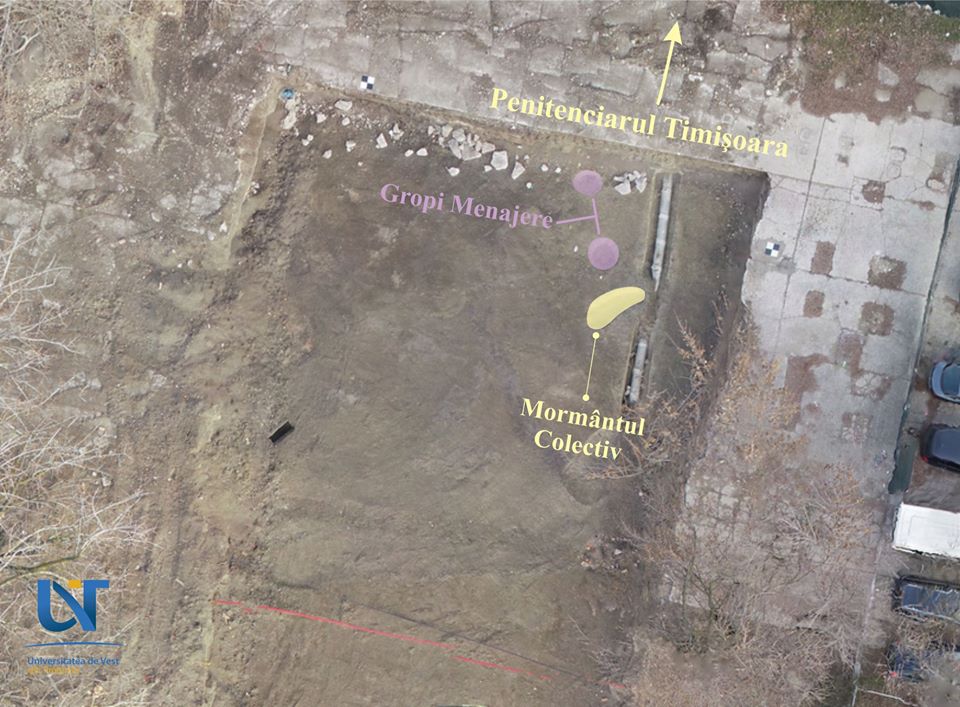
The grave holds the remains of six adults and one child who are thought to have died during a plague outbreak between 1737 and 1740.
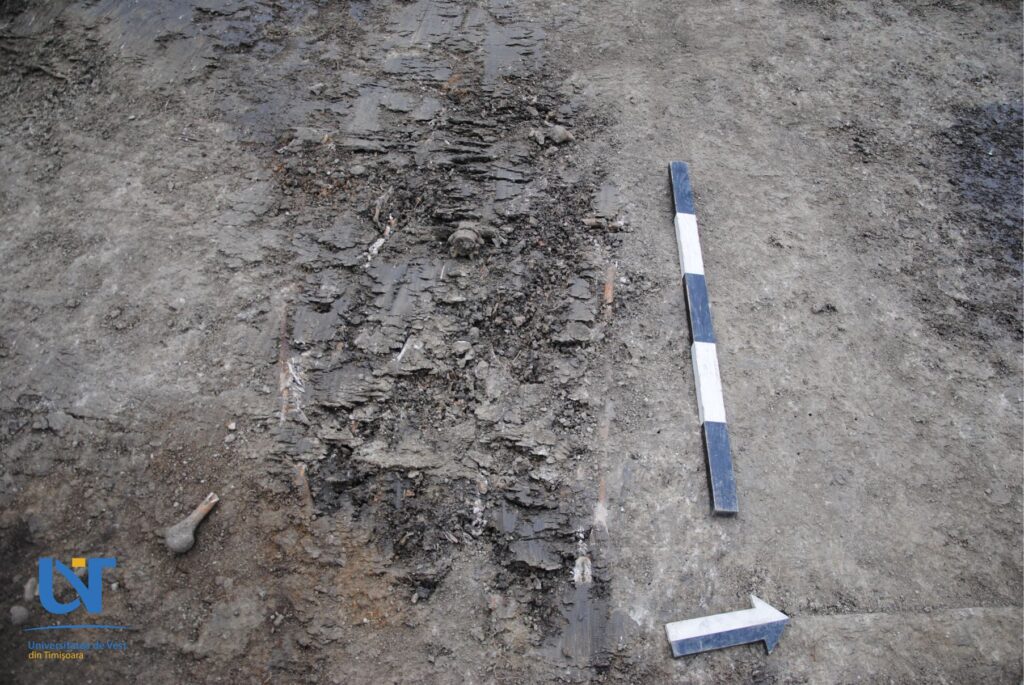
It was discovered in the area of the city’s Oituz street, on a site open for the building of a school campus.
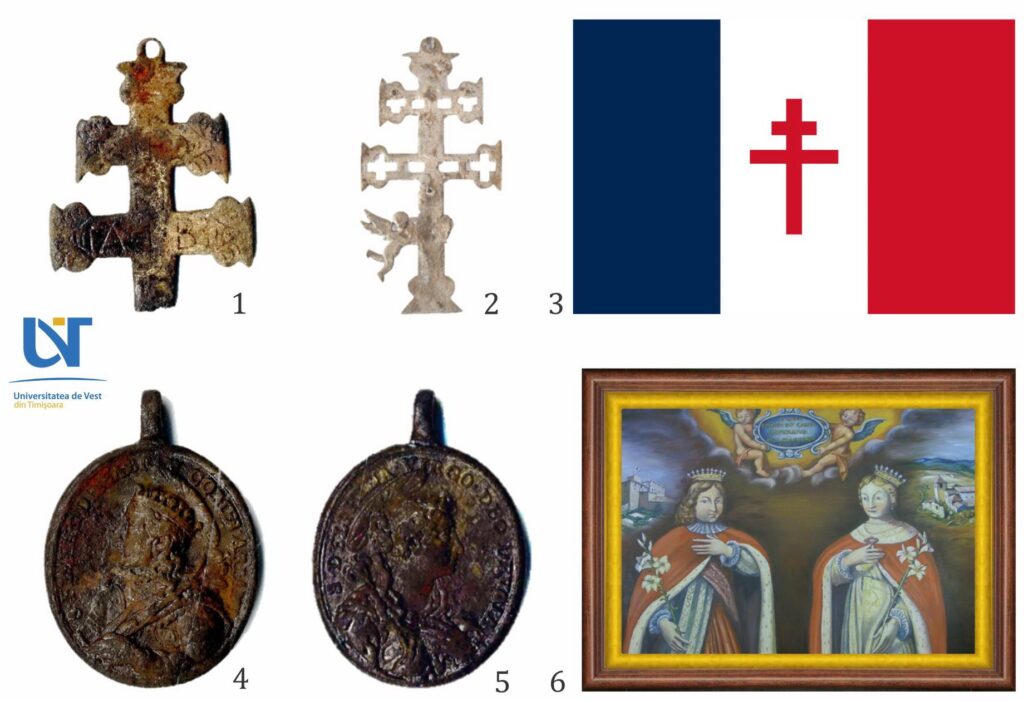

In the tomb, the archaeologists found the remains of six adults and one child, who was carrying a cross similar to the Lorraine one and a pendant showing Blessed Delphina and Saint Elzear, saints of the Franciscan Order.
The remains could be of colonists who came from the region of Lorraine, the archaeologists believe, taking the clue from the cross and the pendant found. The high number of people interred in the grave points to the epidemic.
“We believe they died during the worst epidemic, which remained for a long while in the collective memory and forever in the written one, namely the plague that swept Timişoara between 1737 and 1740,” archaeologist Andrei Stavilă explained in a Facebook post.
This is not the first time the inhabitants of Timisoara experience the bad consequences of an epidemic. Typhus or plague are plague that frequently deviated on the city, both during the Ottoman rule (1552-1716), but also later during the Habsburg (1716-1860). The collective tomb investigated on the archaeological site in the area of Oituz Street area documenting such an unfortunate episode of the city’s history.
Several are elements that suggest this fact. First of all, a large number of deceased in the same grave, six adults and one child. On the other hand, the double cross and the pendant, found at the child’s neck, come to complete the story of the archaeological complex.
The cross resembles, in shape, to Lorraine, with multiple analogies and uses throughout the time in sunset Europe.
More interesting is, however, the pendant that illustrates, on the avers and reverse, saints of the Tertiary Franciscan Order: Saint Delphina and Saint Elzear. This is the only Franciscan couple canonized or formally beatified, they are patrons of newlyweds, poor and lepers.
The pendant that illustrates them is important for our discovery. This is because the tomb cannot date before 1694, which is known to be that of Delphina’s beatification, and the information that the two are owners of lepers is important for our hypothesis.
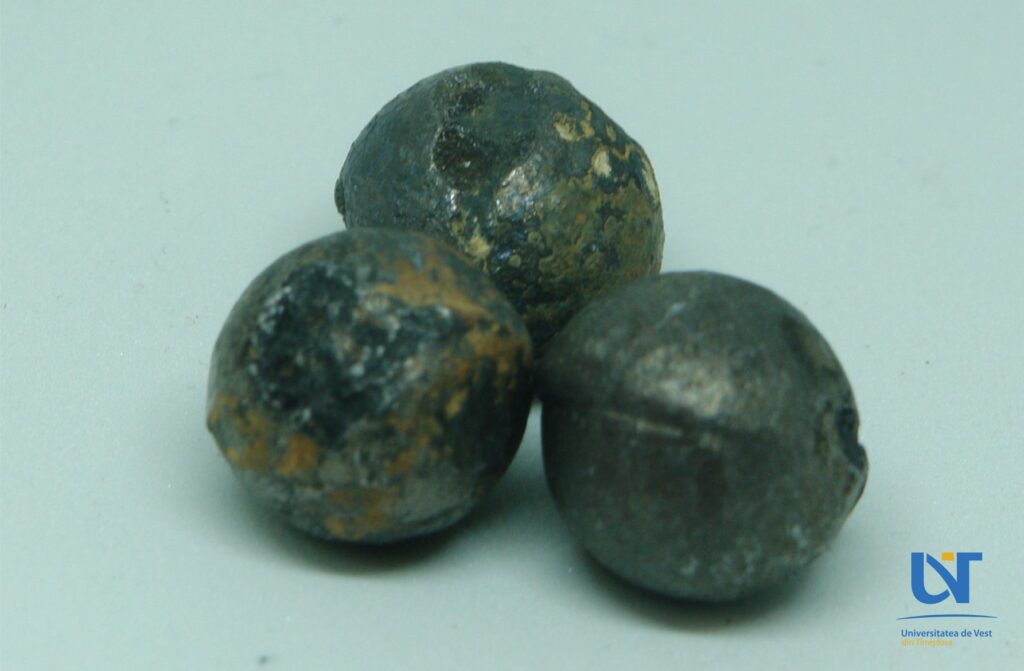
But they surprise our flint balls found among the earthly remains of adults. Could they have been shot? For sure but why? What was the child’s fault? Did the seven form a family? What was the context of their disappearance?

At this point, gathering the data, we appreciate that the tomb may belong to some settlers, even from the region of Lorena. We believe that their deaths occurred in the context of the worst epidemic for a long time left in collective memory and forever in scripts, namely the plague that haunted Timișoara between 1737-1740.
Under these circumstances, lead may have them ended suffering or were punished for failing to comply with the rules imposed by the authorities during the epidemic time