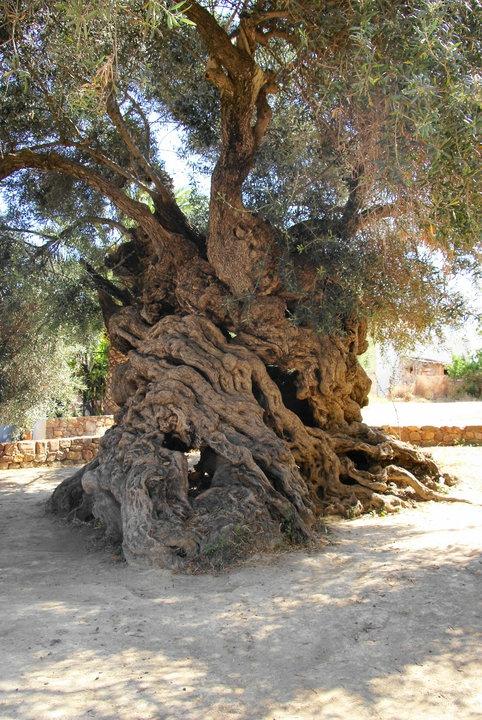
3,000-Year-Old World’s Oldest Olive Tree on the Island of Crete Still Produces Olives Today
One day about 3,000 years ago, at a time when the Minoan civilization still ruled over Crete and long before the rise of Classical Greece, an olive fell to the ground in the area of Vouves. Or perhaps it was deliberately planted there by a human hand.

Whichever the case, that olive seed sprouted and grew into a tree. And incredibly that tree is still alive today – and still producing fruit – one of the so-called ‘monumental olive trees’ of Crete.
The Olive tree of Vouves is an olive tree in the village of Ano Vouves in the municipal unit of Kolymvari in Chania regional unit, Crete, Greece. Probably one of the oldest olive trees in the world, it still produces olives today.
The exact age of the tree cannot be determined. The use of radioisotopes is not possible, as its heartwood has been lost down the centuries, while tree ring analysis demonstrated the tree to be at least 2,000 years old.
And on the other end of the scale, scientists from the University of Crete have estimated it to be 4,000 years old. A possible indicator of its age are the two cemeteries from the Geometric Period discovered near the tree.

Current research in Crete and abroad indicates that earlier estimates of the age of olive trees are to be debated as far as their accuracy. There is not yet an agreed-upon scientific method to ascertain the age of olive trees.
In the case of the Vouves Olive, it could be much younger than earlier estimates or even than the ancient tree in Finix (Sfakia).

In 2012, the Municipality of Platanias and Terra Creta organized for the first time a harvesting event where 55 kg of olives has been collected and 5.0 kg of olive oil was produced in a specially designed olive mill.

In 1997, the tree was declared a protected natural monument, and in October 2009, the Olive Tree Museum of Vouves was inaugurated in a nearby 19th-century house, displaying the traditional tools and process of olive cultivation.
Branches from the tree were used to weave victors’ wreaths for the winners of the 2004 Athens Olympics and the 2008 Beijing Olympics. A terrestrial laser scanner ILRIS 3D for the external and a Minolta Vivid 910 for internal scans were used.
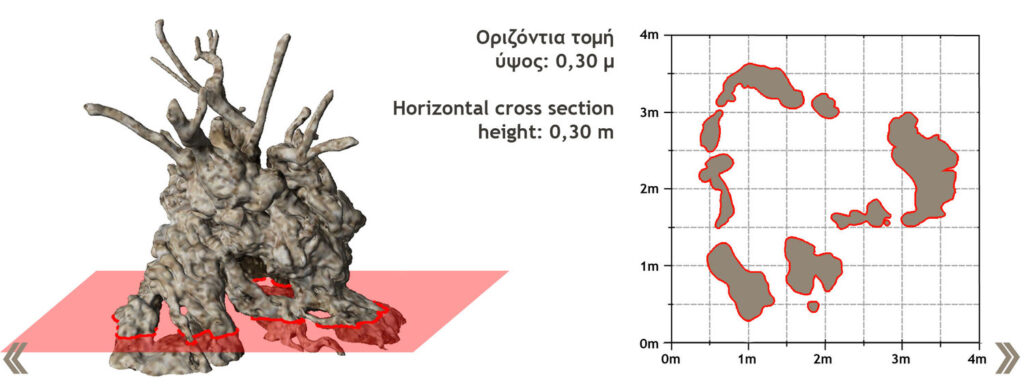
The final produced result is a complete three-dimensional model of the trunk of the Monumental Olive Tree of Vouves with a geometry accuracy of 0.5 cm. Thousands of tourists visit the stunning tree every summer to marvel at it and learn its history.
Mostly they are impressed by its enormous shape and the imposing volume of the trunk, but also by the fact that it remains alive and fruitful for 3,000 years without pause.





