World’s Oldest Known Figurative Paintings Discovered in Borneo Cave Indonesia
According to recent research that indicates that humans may have taken this art tradition with them as they moved from Africa, prehistoric cave paintings of animals and human hands in Indonesia are as old as similar paintings found in Western Europe.

“Until now, we’ve always believed that cave painting was part of a suite of complex symbolic behaviour that humans invented in Europe,” says archaeologist Alistair Pike of the University of Southampton in the United Kingdom. “This is actually showing that it’s highly unlikely that the origin of painting caves was in Europe.”
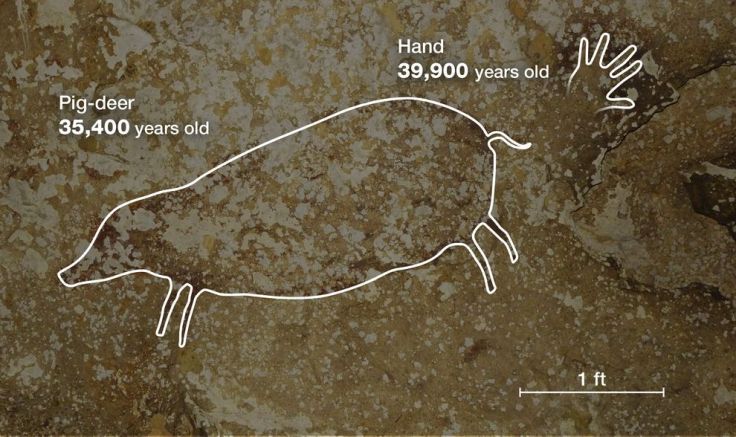
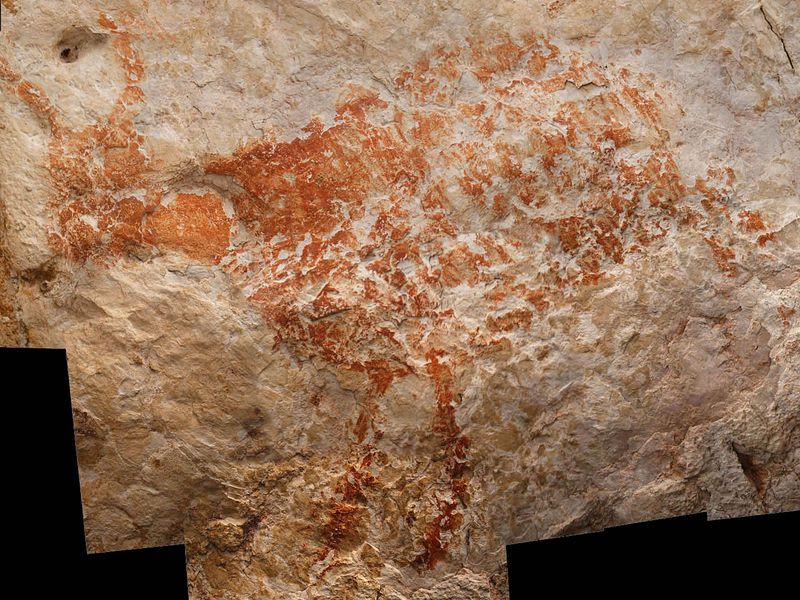
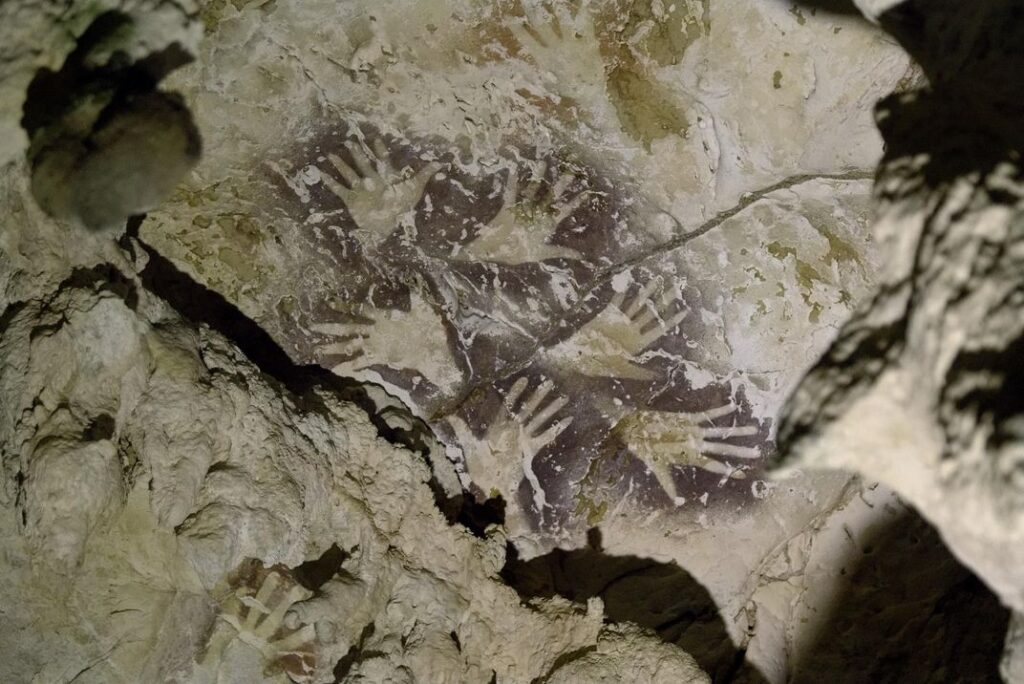
For decades, Indonesian researchers have known about rock art in limestone caves and rock shelters on an island called Sulawesi. The hand stencils and images of local animals, such as the “pig-deer,” or babirusa, were assumed to be less than 10,000 years old because scientists thought that the humid tropical environment would have destroyed anything older.
“The truth of it was, no one had really tried to date it,” says Matt Tocheri of the Human Origins Program of the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History. “It’s not easy to date rock art.”
Now, though, in the journal Nature, a group of researchers from Indonesia and Australia, led by Maxime Aubert and Adam Brumm, have analyzed mineral deposits that formed on top of these paintings in seven caves.
Their analysis shows that one hand stencil is at least 39,900 years old and a painting of a babirusa is at least 35,400 years old.
Those ages are comparable to the age of a painted rhinoceros from the famous Chauvet Cave in France, which has been dated to 35,300 to 38,827 years ago. The oldest known cave painting is a red disk found on the wall of a Spanish cave that’s at least 40,800 years old.

The fact that people in Indonesia were also painting cave walls way back then suggests “it is possible that rock art emerged independently at around the same time and at roughly both ends of the spatial distribution of early modern humans,” the research team writes in Nature.
But another possibility is that this type of art is much older, though scientists haven’t found evidence of it in the archaeological record.
“When something like this shows up almost instantaneously, all over the distribution of humans, within say 10,000 years, the odds are it’s something from our ancestors,” says John Shea of Stony Brook University in New York.
In Africa, our species goes back 200,000 years, Shea notes. But archaeological sites there tend to be found in shallow caves that are relatively exposed to wind and the hot, humid conditions — unlike the deep, cold caves in Europe that are ideal for preserving artwork.
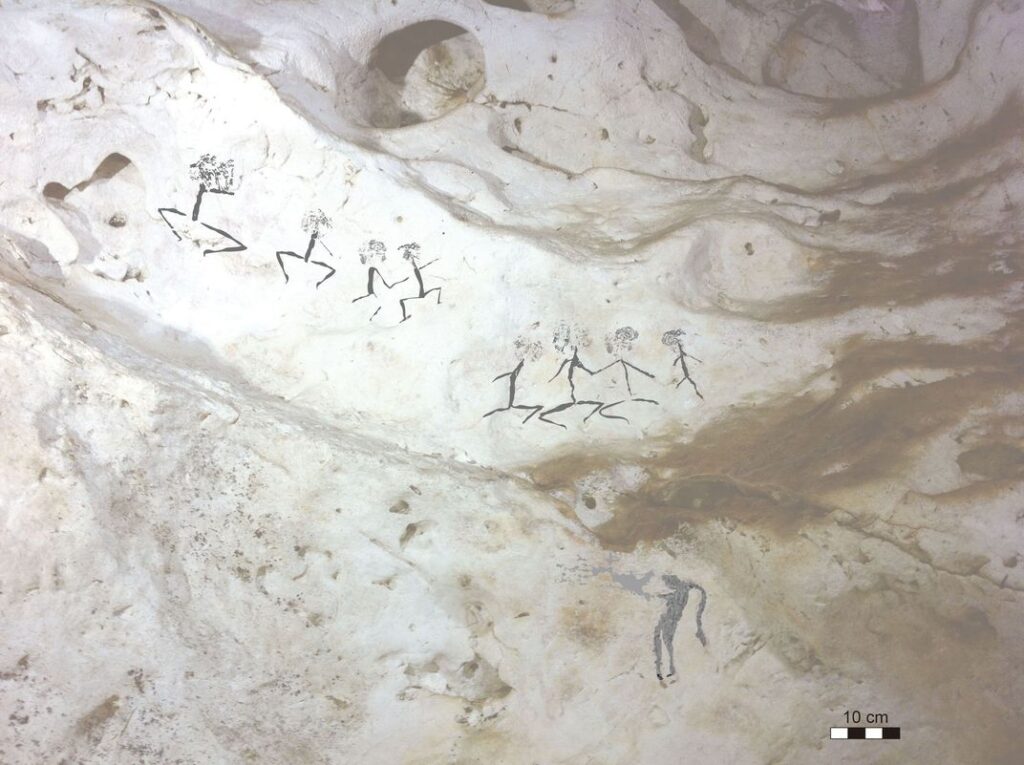


“What we can find in older archaeological sites is evidence of symbolic behaviour, such as the production of little beads and personal adornments, the production of mineral pigments — of red ochre and other kinds of coloured pigments that people used, presumably, to decorate themselves — and traces of artistic embellishments on stone tools and on bone artefacts,” says Shea.
Figurative artwork depicting animals has been found on stone slabs in a rock shelter known as Apollo 11 in Namibia, points out Alison Brooks of George Washington University, who says these images were made more than 30,000 years ago.
“What this suggests is that this whole ability to make these things and possibly the tradition of making them is part of the cultural repertoire of the people who left Africa,” says Brooks.
She says that the paintings in Indonesia are very similar to images seen in Europe — for example, the babirusa in profile, with hair, is similar to European depictions of hairy mammoths.
But the Indonesian animals have stick legs and feet, instead of more detailed limbs. And there’s a hint of a red line that might depict the ground surface of the land that the animal is standing on, which is not found in other places.
“There are some things that are a little bit different about this,” says Brooks, though “it does seem to be that its part of the tradition.”





