Archaeologists Discover 1,500-year-old Skeletons Of Couple Buried Together In China
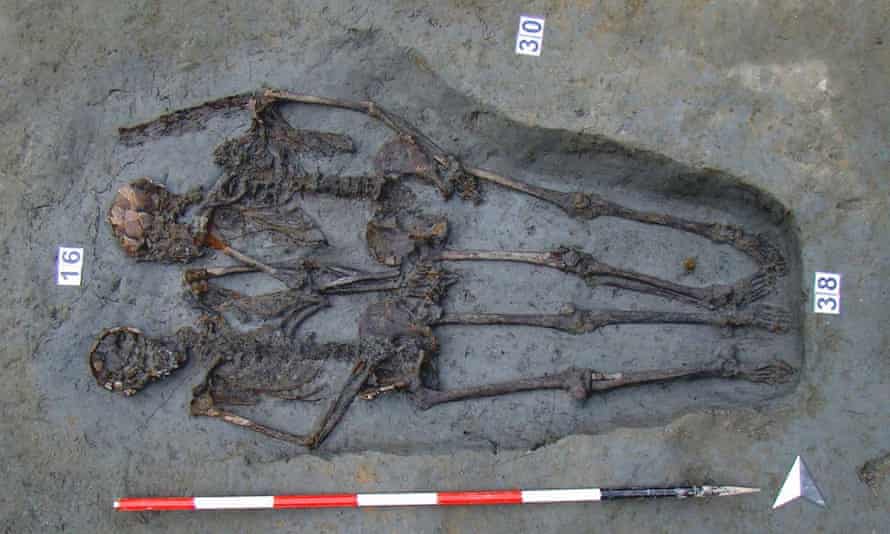
Archaeologists in China have discovered a rare double burial, or “lovers’ tomb,” featuring the skeletons of a man and woman locked in an eternal embrace.
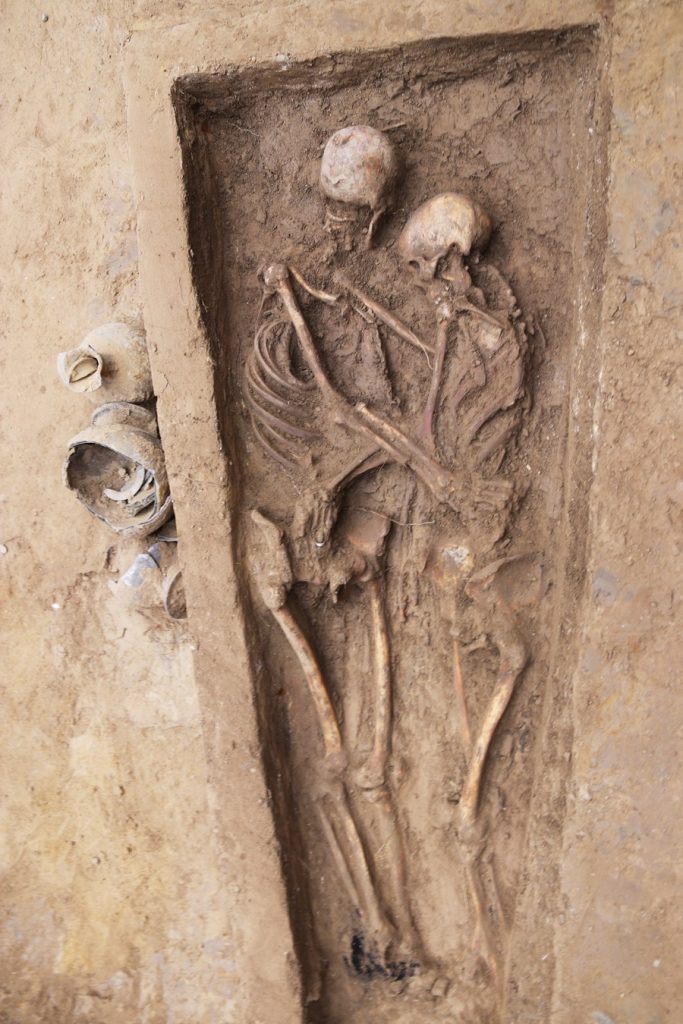
Though the grave is 1,500 years old, she still wears a plain silver band on her ring finger.
“The message was clear—husband and wife lay together, embracing each other for eternal love during the afterlife,” a group of ten scholars wrote in a study published in the International Journal of Osteoarchaeology.
“This joint burial could be direct evidence of a full display of love and the importance of the rings in love.”
The tomb was one of 600 found in an ancient cemetery unearthed at a construction site in Datong, in Shanxi province. The excavation was carried out in 2020.

The couple likely lived during the Northern Wei dynasty (386–534), a politically turbulent time. Buddhism was spreading rapidly, with cultural diffusion helping shape ideas about death and the afterlife.
“This discovery is a unique display of the human emotion of love in a burial,” Qun Zhang, an associate professor at the Institute of Anthropology at Xiamen University, told the South China Morning Post.
“[It] offer[s] a rare glimpse of concepts of love, life, death, and the afterlife in northern China during a time of intense cultural and ethnic exchange.”
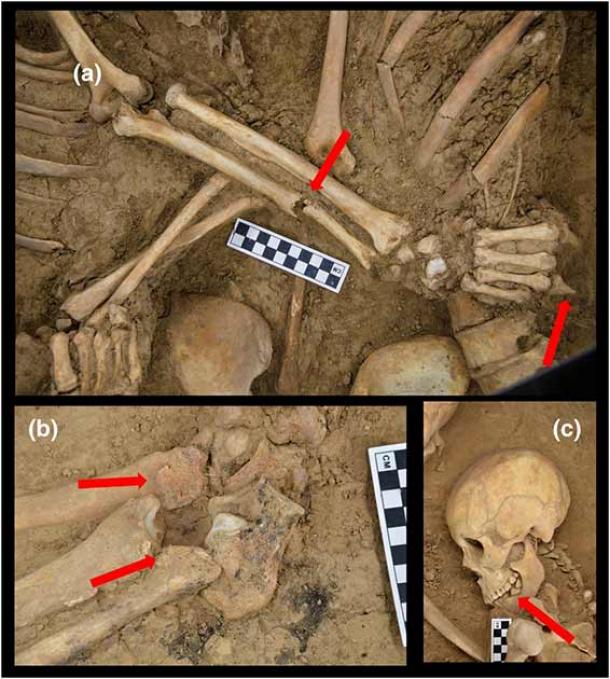
Researchers believe it is likely that the man—whose body showed signs of an unhealed traumatic injury on his right arm—died, and that the woman died by suicide to be buried with him.
Other possibilities include a double death by suicide, or that they both died of illness at the same time.
This is the first known double burial from Chinese antiquity.
Another famous dual grave, Italy’s Lovers of Modena of two skeletons holding hands, was discovered to be two men, rather than a man and a woman, as previously believed.






