Ancient Artifacts Discovered in Stomach of Huge Mississippi Alligator
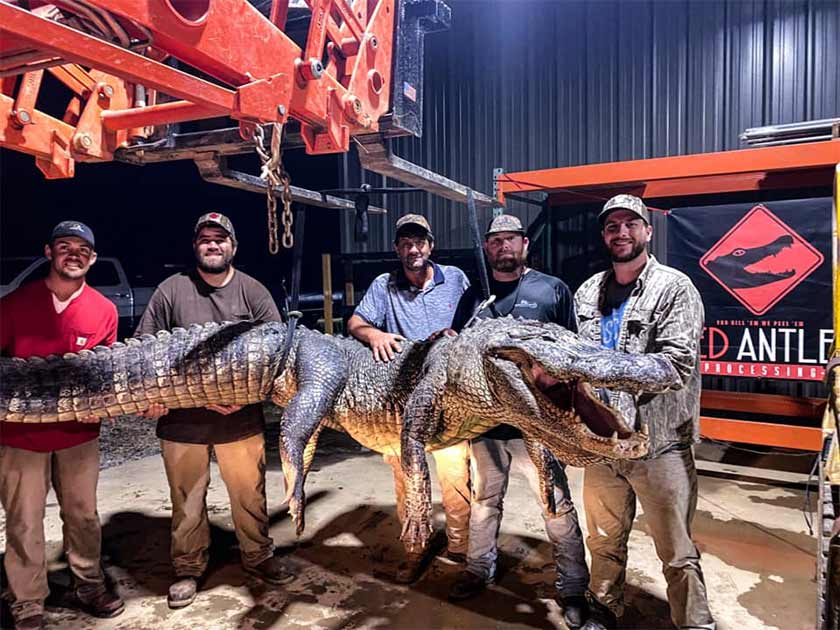
What does a 750-pound alligator eat? Well, just about anything it wants, but items found in this particular Mississippi alligator’s stomach defy odds and date back thousands of years. Shane Smith, the owner of Red Antler Processing in Yazoo City, said he was examining the contents of a 13-foot, 5-inch alligator that weighed 750 pounds and discovered two unusual objects. One he couldn’t identify, but the other was clearly a broken stone arrowhead.
The find was so unexpected, he almost didn’t let the news out.
“At first, I thought ‘I’m not posting this on Facebook,’ because no one will believe it,” Smith said.

Then, he had second thoughts.
“This is too cool not to post on Facebook,” he said. “This has probably never happened before. We gotta post this.”
Dog tags in an alligator’s stomach
The story first began to unfold in April when a wild game processor in South Carolina reported opening the stomach of an alligator and finding unusual items. Smith read it and was sceptical.
“The curiosity struck me when I saw a post online about someone finding dog tags in an alligator’s stomach,” Smith said. “I’m one that doesn’t believe in fake news.”
To satisfy that curiosity, Smith decided to examine the contents of the larger alligators he processed. The first was a 13-foot, 2-inch, 787-pound gator taken by Ty Powell of Columbia.

“We found a bullet in it and it had not been fired from a gun,” Smith said. “I don’t know how it got in there.”
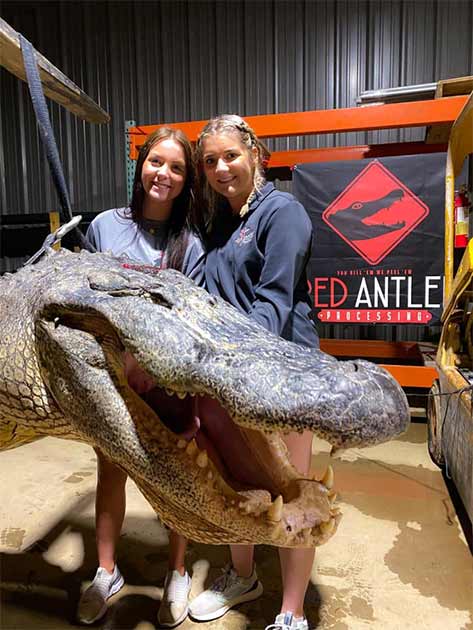
The second alligator he opened, which was harvested at Eagle Lake, contained many of the things the first did, including bones, hair, feathers and stones. Then, something else caught his eye.

A find like no other
“Everybody was standing around like I was opening a Christmas present,” Smith said. “We kind of put it all in a bin.
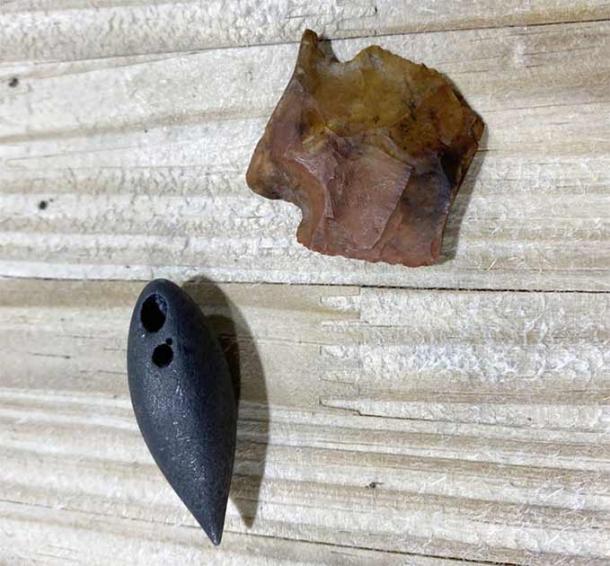
“I looked over and saw a rock with a different tint to it. It was the arrowhead.”
Smith said he was dumbfounded.
“It was just disbelief,” Smith said. “There’s just no way he had an arrowhead. Your first thought is it ate (a Native American) or (a Native American) shot it in the stomach.”
Smith knew that wasn’t the case, though.
“My best hypothesis is wherever he scooped up those other rocks, he got that Indian point,” Smith said. “We joked about it and said I’m probably the only person on Earth to pull an arrowhead out of an alligator’s stomach.”
Point dates back thousands of years
James Starnes, Director of Surface Geology and Surface Mapping for the Mississippi Department of Environmental Quality examined a photograph of the point. He estimated it was made about 5000-6000 BC. That is the latter part of the Early Archaic and early part of the Middle Archaic (periods),” Starnes said. “How the base is made is real tell-tale in estimating the time period.” Starnes also noted the object is not an arrowhead. It’s a point used on an early weapon that launches a spear using a second piece of wood with a cup on one end which acts as a lever to increase velocity.
“That’s an atlatl dart point,” Starnes said. “People think all heads are arrowheads, but those (arrowheads) would be the little bitty points.”
As bizarre as the find was, it was about to get even stranger. Smith found a heavy, tear-shaped object roughly 1½ inches in length. Both he and the hunter who was permitted to harvested the alligator, John Hamilton of Raleigh, though it was something more modern — a lead weight used for fishing.
“It’s heavy as lead,” Hamilton said. “It looks like it’s got two holes in it, but they don’t go through it.
“It’s got a little hole and a bigger hole on top. I guess it goes in and comes back out.” Hamilton researched the object online but wasn’t successful in identifying it.
“I haven’t found anything the shape of it in fishing stuff,” Hamilton said.
What’s a plummet, and why would an alligator eat it?
Starnes said it’s known as a plummet and dates back to the Late Archaic Period, or about 1700 BC. The weight is accounted for because it’s made of hematite, an iron oxide traded between early groups and shines when polished. Starnes said what the purpose plummets served is unknown.
“The plummets, we really have no idea what they were used for,” Starnes said. “These things had some significance, but we have no idea. We can only guess.”
So, how did these ancient objects get into the alligator’s belly? Ricky Flynt, Mississippi Department of Wildlife, Fisheries, and Parks Alligator Program coordinator, explained very hard objects, typically stones, aid the reptiles indigestion.
“Alligators, like other animals such as birds and other reptiles, are known for ingesting grit and rocks to help with digestion,” Flynt said. “We know alligators and crocodiles do that.”
However, alligators differ from fowl such as chickens and ducks. Those animals have gizzards and the grit and sand are stored there to help grind seeds and grains they consume. Alligators don’t have gizzards and the stones go into the stomach.
“Sticks, wood; things they can’t digest get into their stomachs,” Flynt said. “I found a piece of cypress in an alligator’s stomach that was 15 inches long.”





