Industrial-Sized Tannery Detected at Medieval Abbey in England
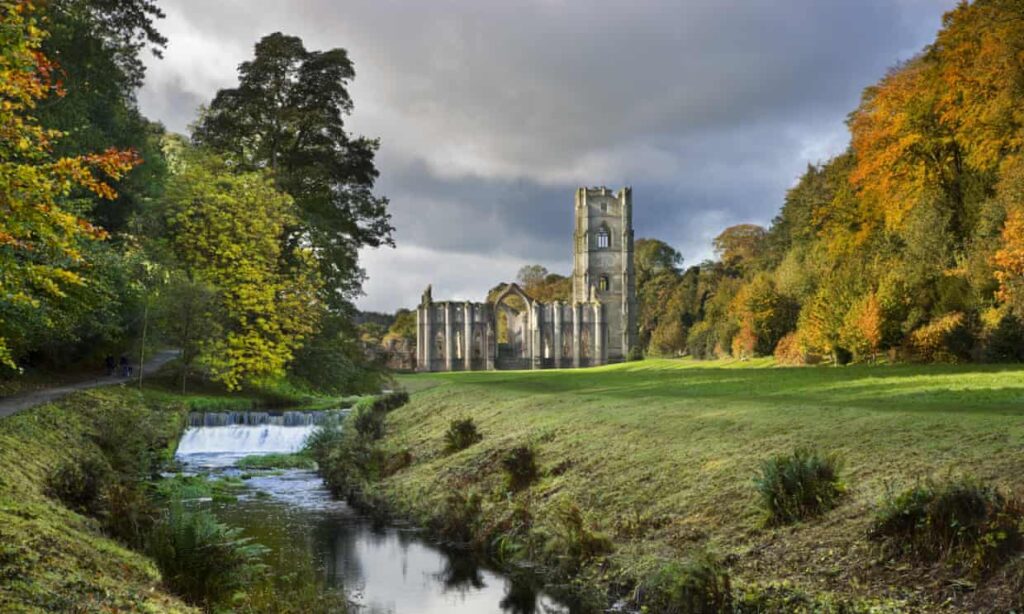
It is Britain’s biggest and most famous monastic ruin and one that conjures up bucolic images of peace, reflection and very little noise apart, perhaps, from the occasional waft of Gregorian chanting.
In reality, archaeologists have revealed, Fountains Abbey near Ripon was as busy, noisy and industrialised as anywhere in 12th- and 13th-century Britain.
The National Trust has announced the discovery of the foundations of a medieval tannery at the abbey, part of a world heritage site. Experts were astonished.

This really is a wonderful discovery, it is very important,” said Mark Newman, a trust archaeologist.
Fountains are probably the most investigated Cistercian abbey in Britain, “so when you discover a major building on this scale, that was completely unknown … you don’t get many of those in a career.
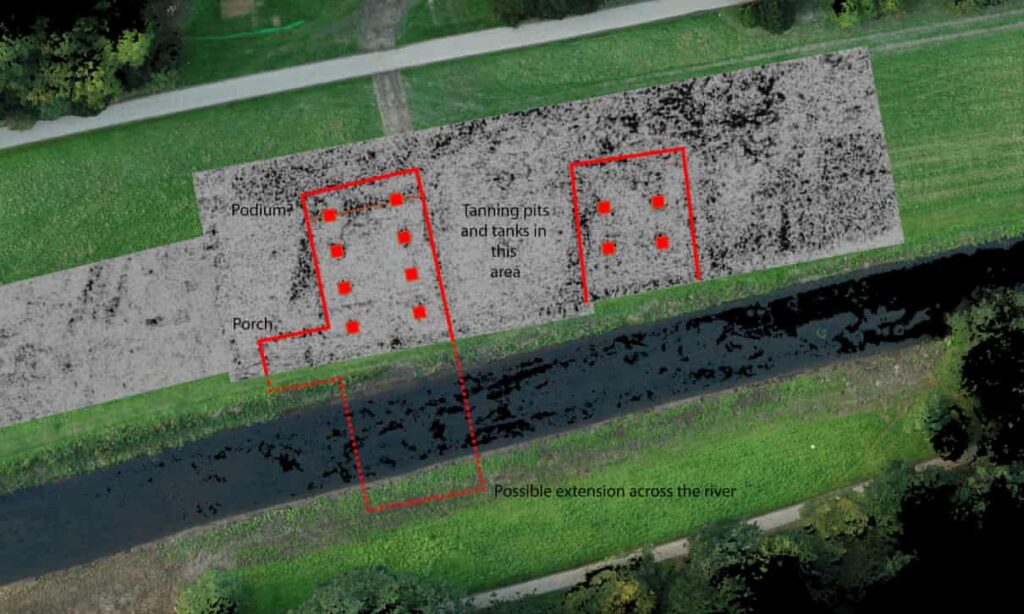
Newman said many assumed there was nothing more to be discovered about Fountains but one puzzle had always been what a long, bowling alley-type extension, close to the River Skell, was used for.
Ground-penetrating radar has made discoveries of previously unknown monastic buildings, including one 16 metres wide and 32 metres long. They have lined pits and tanks around them. These and the close proximity to water have led to the firm conclusion that it is the remains of a tannery, a place for producing materials for clothing, belts, bedding and book bindings.
It is the scale of the tannery and how close it is to the monks that have further surprised archaeologists. “A tannery of this size, spanning such a large area of the site, reveals an operation on an industrial scale,” said Newman.
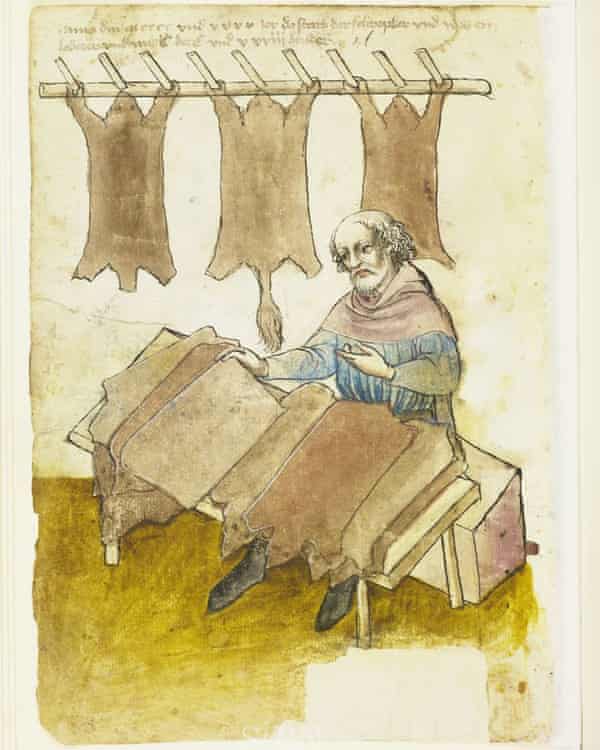

A medieval tannery was a horrible place. Animal skins and hides would first have hooves and horns removed before they were washed to remove dung, dirt and blood. Fat, hair and flesh were then removed, usually by being submerged into a lime or urine solution and being scraped with knives.
Newman said the noise, activity and stench of tanneries had led to an assumption it would be sited much further away from monks and their worship. “We see now that the tannery was much closer and a far cry from the idea of a quiet, tranquil abbey community,” he said.
Newman said people would have been astonished at the number of people who lived and worked so industriously at Fountains, with Cistercian monks being “the first ones to apply themselves to these industrial scales of living and managing the landscape”.
He said the findings also showed the importance of lay brothers at the site. Lay brothers were not literate, like the monks, and were often recruited to do more physical jobs. That left monks more time to study, pray and worship.
The lay brothers, considered “separate but equal” to monks, were provided with weatherproof animal skin capes for outdoor work and slept under sheepskins. “Fountains recruited hundreds of lay brothers in its early decades, all of whom needed to be equipped this way,” said Newman. “This tannery provided the means for that.”
He said though he was taken aback by the scale of the operations that had been discovered, it all made sense. The monks at Fountains were, by necessity, “pioneering farmers and land managers on an industrial scale”.
The radar research was carried out with partners including the University of Bradford. Chris Gaffney, a professor of archaeological sciences, said the technology provided “stunning, unexpected and intriguing glimpses” into life at the abbey.
The trust said it was the largest tannery discovered at a monastic site in Britain and was being seen as a kind of “missing link” in the history of the abbey, which operated from the early 12th century to 1539 and the dissolution of the monasteries.
“It is so easy with a place like Fountains to think this is exactly as the monks saw it,” said Newman. “What we are finding is that there is a whole unrecognised history.”





