Princely tomb of Iron Age mystery man discovered in Italy. And there’s a chariot inside.
A lavish ‘Princely tomb’ belonging to an Iron Age man was found in Italy full of treasures including a bronze helmet, weapons and a whole chariot. The tomb of a pre-Roman prince has been saved from ‘imminent’ destruction after aerial photos revealed the ancient treasure trove before it could be built over.
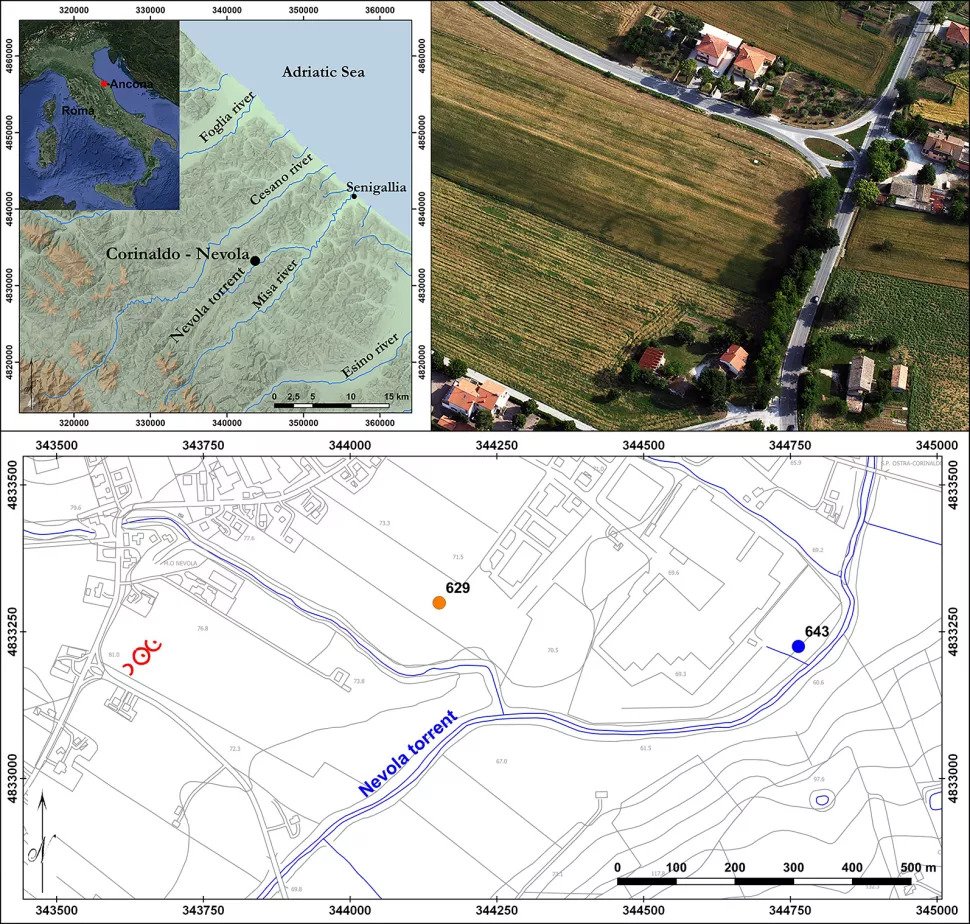
The body of the unidentified prince has not been found and no mound remains to mark his resting place – it may have been lost while the site was used for farming. The hoard, found in Corinaldo, Italy, was on the site of a future sports complex and wasn’t spotted until a survey of the land was carried out before the building started.
The value of the discovery and the site is now being assessed before any decision over whether to move the tomb or move the sports complex is made.
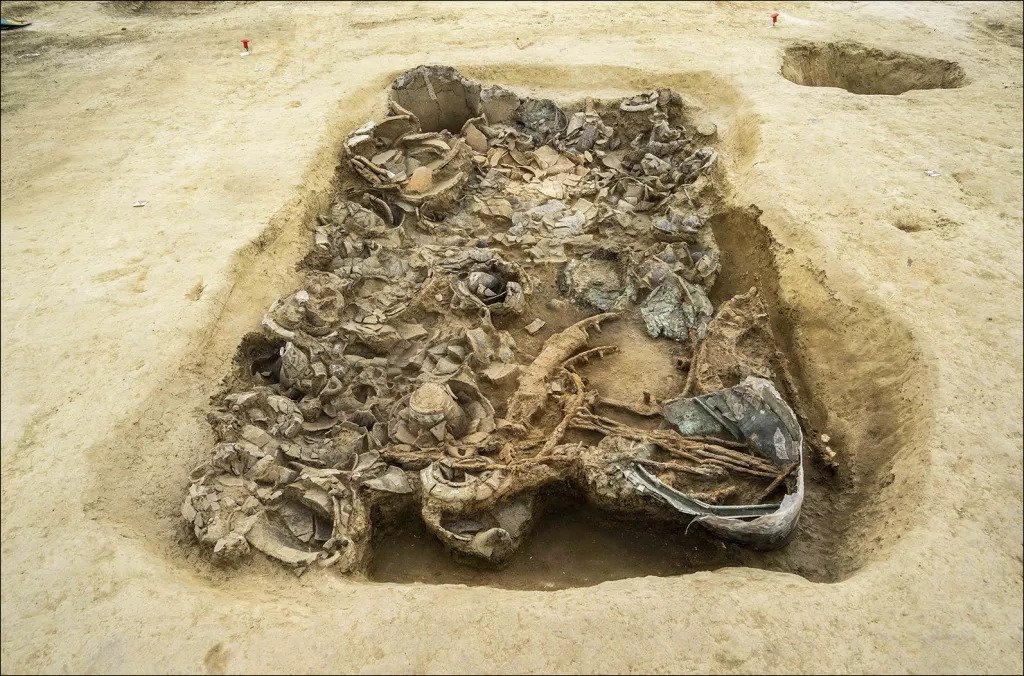
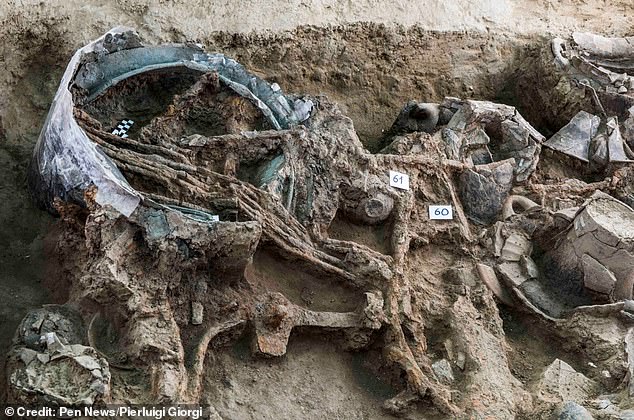


The tomb is believed to date back to the seventh century BC when it was constructed for a prince of the largely-unknown Piceni people, whose land was eventually annexed by Rome in 268 BC.
‘We identified circular crop marks, comparable to large funerary ring ditches,’ said Federica Boschi, an archaeologist at the University of Bologna.
‘A large and slightly off-centre pit contained an extraordinary collection of cultural material.’
It is the only discovery of its kind in the region, the archaeologist confirmed.
‘As the first such monument identified and excavated in northern Marche this has provided an extraordinary opportunity to investigate a site of the Piceni culture,’ said Professor Boschi.
‘Until now, this culture has been poorly documented and little understood despite its undoubted importance in the pre-Roman development of the area.’
She added: ‘The recovery from complete obscurity and imminent danger of archaeological material of this scale and importance is a rare event within contemporary European archaeology.’
The body of the unidentified prince has not been found and no mound remains to mark his resting place – possibly both were destroyed during the land’s long history of agricultural use.
Nonetheless, Professor Boschi believes that the lavish tomb is evidenced enough of his status.
She said: ‘The extraordinarily rich funerary deposit testifies to a high-status tomb dedicated to a princely leader within the early Iron Age society of the region.
‘One outstanding find among the hundred or more ceramic vessels recovered from the pit was an olla imported from ancient Daunia.
‘This undoubtedly symbolises the commemorated leader’s significant political, military and economic power.
‘The full study of the pottery and other finds will undoubtedly prompt entirely new insights into the cultural, trading and gift-exchange relationships of the aristocracy in the area.’
After seeing aerial photos of the tomb site, archaeologists initially performed a resistivity survey, where electrical currents are run through the ground to see if anything metallic is buried there.
‘Aerial photography led to the first identification of the site,’ said Professor Boschi.
‘A resistivity survey then provided an initial understanding of the extent and internal articulation of the funerary area, including a third ring-ditch not revealed by the aerial photographs.
‘A targeted geomagnetic survey then produced significant information about the survival of the underground deposits, providing supporting secure evidence for a massive deposit of ironwork.’
It’s not entirely clear what will happen to the site next, whether the tomb and its contents will be moved or whether a new home will be found for the sports centre. The findings have to be properly valued, both for their financial worth and their cultural worth, before anything can happen.
‘The next steps are going to move toward the valorization and public fruition of the site within and in agreement with the project of the new sports complex,’ said Professor Boschi.





