5,000-Year-Old Rock Art Depicting “Celestial Bodies” Revealed in Siberia
Some 5,000 years ago, artists in Siberia drew some of the most sophisticated artwork the region has ever seen. The ancient artists were depicting humanoid figurines with strange halos and horns and ensured their message was inscribed in history.
Analysis of the art has revealed the secrets of the prehistoric artists behind the stunning artwork known as the Karakol paintings, reports the Siberian Times.
Ancient Rock Art
Discovered in the remote Altai mountains, the ancient artists of the region drew a series of humanoid figurines with strange additions: some of them have round horns, halos, while others are depicted with feathers on their heads.
The artwork was discovered inside a burial in the Karakol village in the Altai Republic. And although the drawings were discovered back in 1985, it isn’t until now that they have revealed unexpecting secrets.
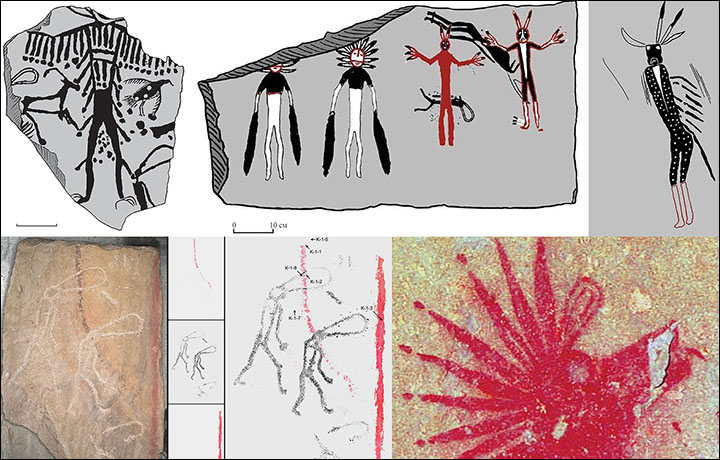
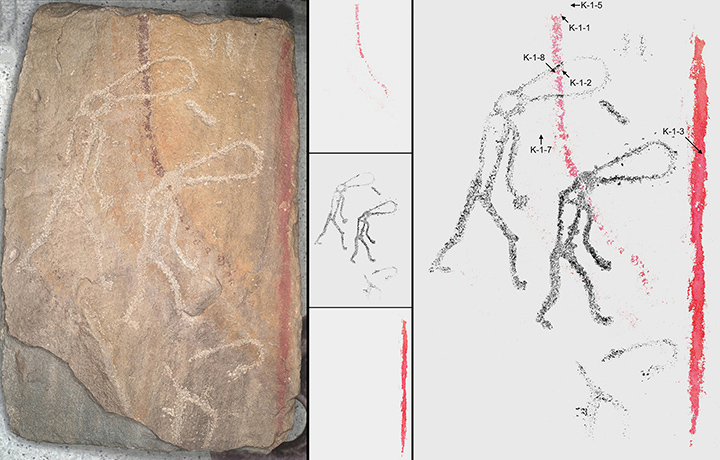
The mysterious interpretations of humanoid figurines were paintings on stone slabs that were later used as walls of the burials.
Scientists were stunned after finding out that the ancient drawings were made in three distinct colours: white, red, and black, marking the first case of polychrome rock paintings ever found in Siberia.
Intricate Burials
Not only did experts find evidence of rock art in the burials, but they also discovered that the remains of people inside the burials were also painted with the same colours.
The analysis revealed traces of red ocher and a black and silvery mineral called Specularite, used by the ancient artists to decorate the burials. Researchers have revealed that the images on the stones were drawn at different times using elaborate techniques.
Among the earliest rock art, we find depictions of elks, mountain goats, and humanoid figurines which the ancients drew, running around with round horns and halos on their heads.
To complete some of the drawings, the ancient humans did more than just mix engraving techniques and mineral paints. The research revealed that the ancient artists knew how to carry out chemical reactions more than 5,000 years ago, creating not just a colour but the precise tone they wanted to obtain.
“The results of the analysis of the composition of paints used in the funeral rite of Karakol people testify to the ability of the ancient inhabitants of Altai to distinguish pigments by colour and properties,” explained Alexander Pakhunov, one of the authors of the study.
Scientists from the Kurchatov Institute in Moscow, Russia’s leading research and development centre for nuclear energy, and experts from the Paleo-Art Centre of the Institute of Archeology discovered that the figurines were drawn in red colour are actually made of thermally modified ocher.
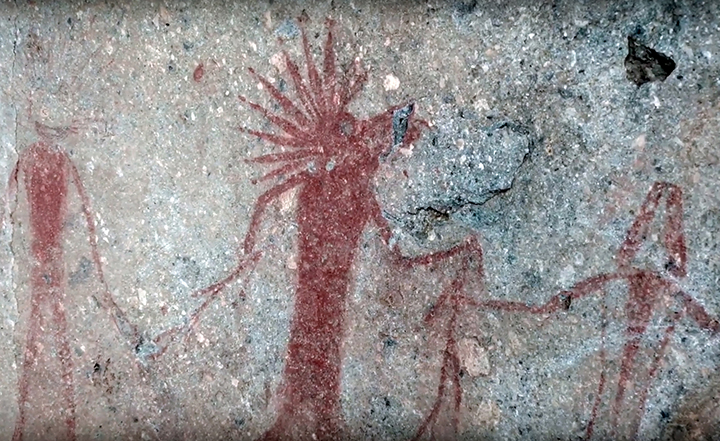

The Siberian Times noted that the white-coloured drawings were created by scraping, which revealed light-reflecting rock crystals.
While for the black colour, the ancient artists of Karakol made use of soot.
“We determined the phased composition of pigments, that is, the structure of the crystal lattice of individual grains of the dye. Some structures are not typical for natural samples but are the product of heat treatment,” revealed Roman Senin, the head of the Kurchatov Institute’s synchrotron research department.
“Simply put, the primitive artist heated the mineral to a certain temperature to get the colour he needed,” Senin added.





