A Pregnant Ancient Egyptian Mummy Has Been Discovered in a Shocking World First
A team of Polish scientists say they have discovered the only known example of an embalmed pregnant Egyptian mummy. The discovery was made by researchers at the Warsaw Mummy Project and revealed in the Journal of Archaeological Science on Thursday.
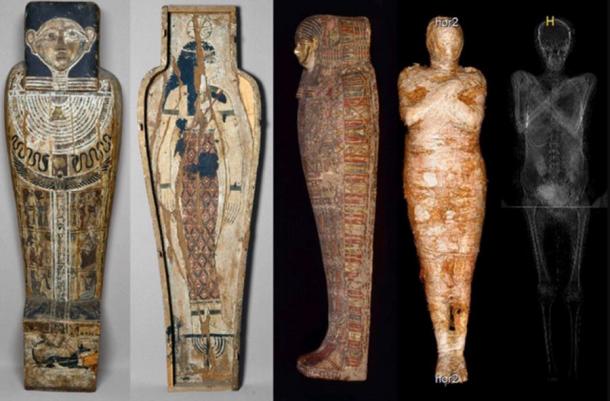

The project started in 2015, uses technology to examine artefacts housed at the National Museum in Warsaw. The mummy was previously thought to be a male priest but scans reveal it was a woman in the later stages of pregnancy.
Experts from the project believe the remains are most likely of a high-status woman, aged between 20 and 30, who died during the 1st Century BC.
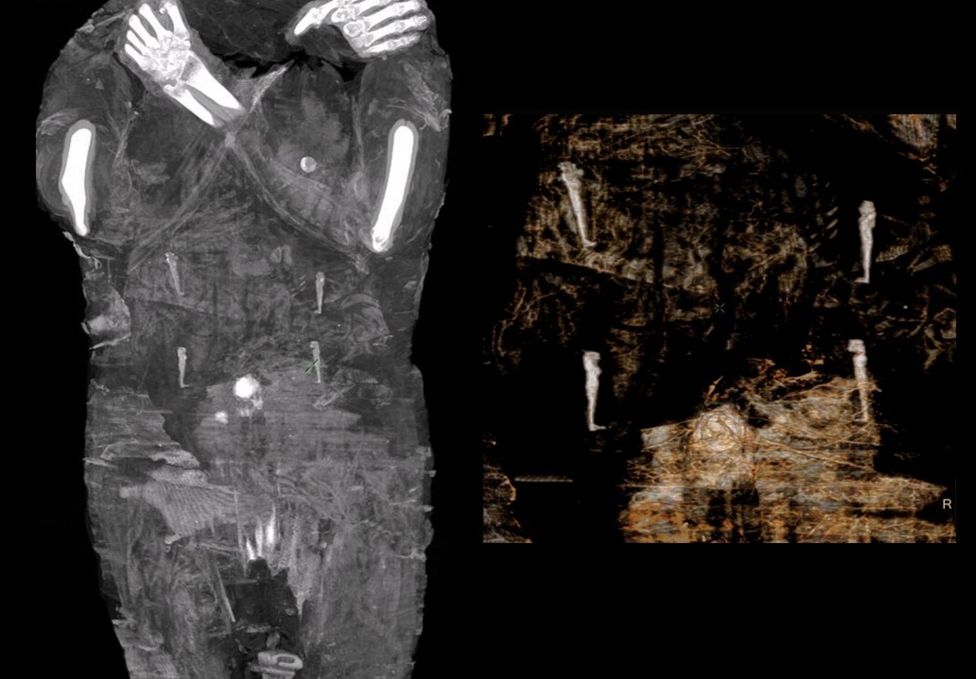
“Presented here is the only known example of a mummified pregnant woman and the first radiological images of such a foetus,” they wrote in the journal article announcing the find.
Using the foetus head circumference, they estimate it was between 26 and 30 weeks when the mother died for unknown reasons.

“This is our most important and most significant finding so far, a total surprise,” team member Wojciech Ejsmond of the Polish Academy of Sciences told the Associated Press.
Four bundles thought to be wrapped and embalmed organs were found within the mummy’s abdominal cavity but scientists say the foetus had not been removed from the uterus.
The scientists said it was unclear why it had not been extracted and embalmed separately, but speculated spiritual beliefs about the afterlife or physical difficulties with removal may have contributed.
‘The Mysterious Lady’
Researchers from the mummy project have dubbed the woman as the Mysterious Lady of the National Museum in Warsaw because of conflicting accounts around her origins.
They say the mummified remains were first donated to the University of Warsaw in 1826. The donor alleged the mummy was found in royal tombs in Thebes, but researchers say it was common in the 19th century to falsely ascribe antiquities to famous places to increase their value.
Inscriptions on the elaborate coffin and sarcophagus had led 20th Century experts to believe the mummy inside was that of a male priest named Hor-Djehuti.
But now scientists, having identified it as female with scanning technology, believe the mummy was at some point placed in the wrong coffin by antiquity dealers during the 19th Century when looting and re-wrapping of remains were not uncommon.
They describe the condition of the mummy as “well-preserved” but say damage to the neck wrappings suggest it was at some point targeted for valuables.
The experts say at least 15 items, including a “rich set” of mummy-shaped amulets, were found intact within the wrappings.
One of the researchers on the project, Dr Marzena Ożarek-Szilke, told the Polish state news agency that her husband had first spotted what appeared to be “a little foot” on one of the scans.
She told the outlet that the team hope next to study small amounts of tissue to establish the woman’s cause of death.





