8000-year old underwater burial site reveals human skulls mounted on poles
A team of researchers with Stockholm University and the Cultural Heritage Foundation has uncovered the remains of a number of Mesolithic people in an underwater grave in a part of what is now Sweden.
In their paper published in the journal Antiquity, the group describes the site where the remains were found, the condition of the remains and also offer some possible explanations for the means by which the remains found their way to the underwater burial site.
People living during the Mesolithic were hunter-gatherers, the researchers note, which is why the burial site and its contents are so surprising.
At the time of its use, the burial site would have been at a shallow lake bottom covered with tightly packed stones upon which the remains of humans had been laid.
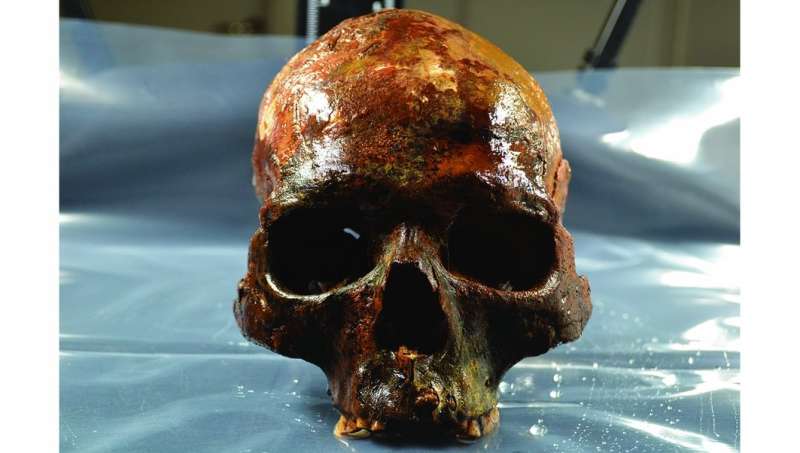
The remains were all skulls, save for one infant. The adult skulls (except one) were missing jawbones, and at least two of the skulls showed evidence of a stick thrust through the opening at the base through the top of the skull—normally associated with posting a skull to scare enemies.
But hunter-gatherers were not known for posting skulls or engaging in gruesome funeral rituals. Instead, they were known for disposing of their dead in simple, respectful ways.
The gravesite was found in what is now southern Sweden, near an archaeological site known as Kanaljorden.
Archaeologists have been working at the site since 2009, but it was not until 2011 that the human remains were found—until that time, researchers had been finding animal remains. To date, the researchers have found the remains of 11 adults.
In another surprise, the team discovered that all of the adult skulls bore signs of trauma—each had been whacked in the head multiple times. But the trauma was inflicted differently depending on gender.
The males were hit on top or near the front of the head, while the females were typically hit from behind. None of the wounds appeared life-threatening, however, though, without the rest of the corpse, it was impossible to identify what had killed them.
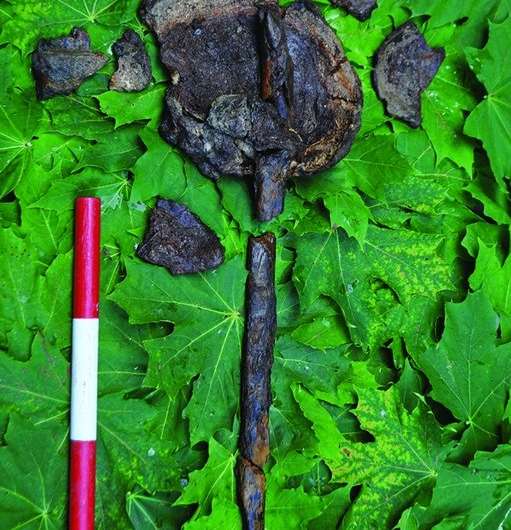

The researchers are unable to offer an explanation for what they have found at the site, though they suggest it was possible the victims had died or been killed elsewhere and then transported to the burial site. Possibly because they were considered exceptional in some way.





