How did an 8000-year-old community deal with climate change?
Cosmos Magazine reports that archaeologists including Rick J. Schulting of the University of Oxford have determined that Yuzhniy Oleniy Ostrov, a cemetery on an island in northern Russia’s Lake Onega, was used for a 200-year period during the so-called mini–Ice Age.
Some 8200 years ago, a great sluice of meltwater from a now-vanished ice sheet pulsed into the North Atlantic, causing a mini-Ice Age that lasted for around 200 years.
Across vast swathes of northern Europe, plant life began to change – broadleaf trees were outcompeted by hardier pines suited to the frigid temperatures – and animals and humans alike would have been forced to adapt to the sudden, drastic changes.
Now, in a new study out today in Nature Ecology & Environment, archaeologists from the University of Oxford have opened a small, misty window into this early Holocene upheaval, to see how one community changed in response.
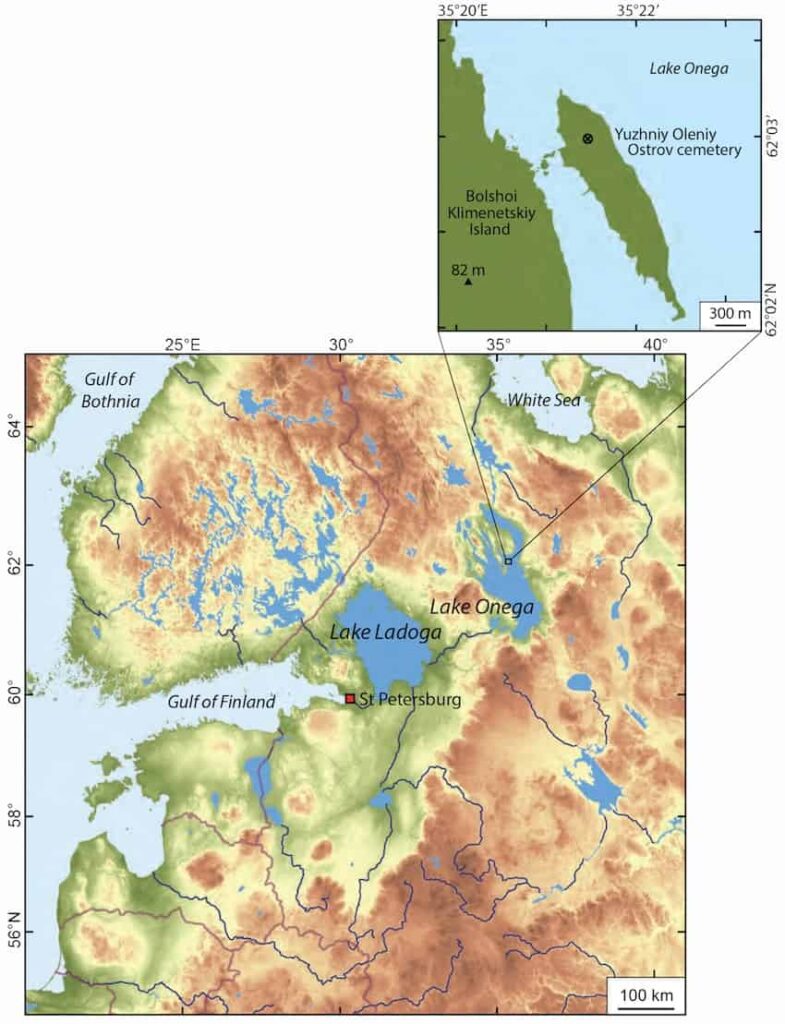
The site, the Yuzhniy Oleniy Ostrov (YOO) cemetery in northern Russia, sits on an island in the vast Lake Onega, 350 kilometres northeast of St Petersburg.
Radiocarbon dating of remains in the cemetery shows that it was mainly used for a short window of around 200 years, spanning some 10 generations and that its use coincided with this mini-Ice Age.
So why might people suddenly decide to organise their dead at a time of stress? The clue, the researchers say, lies in the lake.
Lake Onega would have been a relative paradise as freezing temperatures closed in. With its own microclimate and lush stores of fish and plant life, it would have drawn big game such as elk to its milder shores, as well as beleaguered humans on the hunt for food. At the same time, shallower lakes in the region would likely have experienced harsh winter fish kills.
That’s an awful lot of people milling into a small area – a well-known recipe for disaster. But humans are a resilient bunch, and the researchers believe the Lake Onega communities responded by building a more complex, more united society – their cemetery, the final resting place of their loved ones, was yet another display of social belonging and organisation.
The claim is a bold scientific leap, but it’s not unconvincing. Some 200 years on, when the climate improved, the cemetery was abandoned.
“Whatever ‘complexity’ we see at YOO,” the authors write, “was thus situational and reversible.”
Did this tight band of people disperse back into the landscape in smaller, nomadic groups? We’ll probably never know the exact truth of the events, but archaeology offers a tantalising vision of an ancient community in flux, at the mercy of a changing climate.





