2000-year-old ‘lost’ street built by Pontius Pilate uncovered in Jerusalem
Archaeologists have unearthed part of a 2,000-year-old ‘lost’ street built by Pontius Pilate that likely served as a route for pilgrimage within the ancient city. The street had been buried when the Roman ransacked the city in 70 AD.
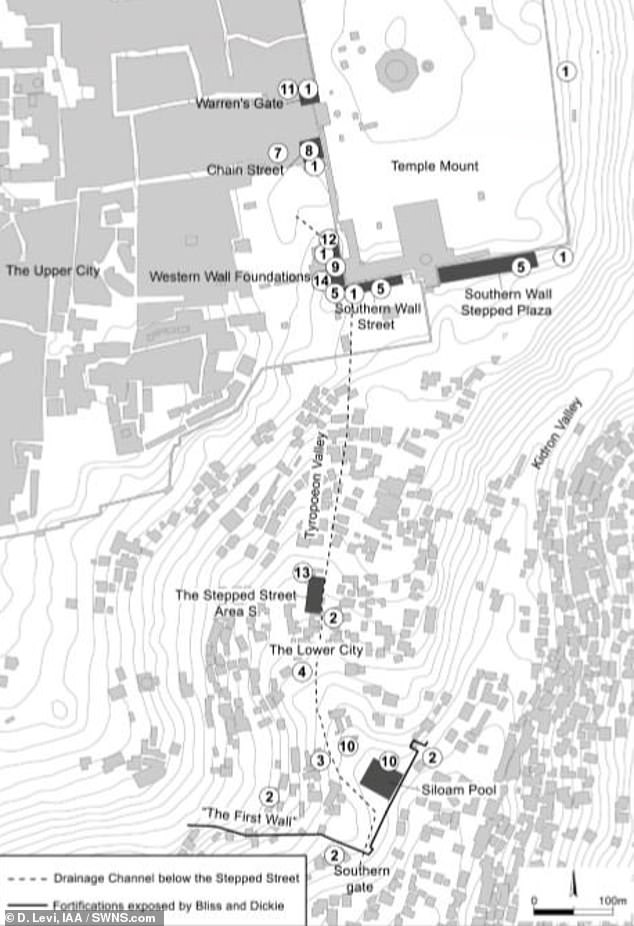
The ancient walkway linking the Temple Mount with the Pool of Siloam was first discovered in 1894 by British archaeologists in Jerusalem’s ‘City of David’.
Researchers have now found more than 100 coins beneath the paving stones that date the street to around the year 31 AD. The finding provides strong evidence that the street was commissioned by Pontius Pilate, the Roman governor of the province Judaea from 23–36 AD.
Pilate is best known as the biblical official who presided over the trial of Jesus and ordered his crucifixion.
The 722 feet (220 metres) -long section of the road was unearthed by researchers from the Israel Antiquities Authority and Tel Aviv University after six years of extensive archaeological excavations.


The walkway ascends from the Pool of Siloam in the south to the Temple Mount — both sites of significance to the followers of Judaism and Christianity. The Temple Mount, located within the Old City of Jerusalem, has been venerated as a holy site for thousands of years.
According to the bible, the Pool of Siloam was the location where Jesus performed the miracle of healing the man born blind, at around the same as the street was being constructed. During the dig, the team uncovered more than 100 coins trapped beneath the street’s paving stones.
The latest coins were dated between 17–31 AD — firm evidence that work began and was completed during the time that Pilate governed Judea.
‘Dating using coins is very exact,’ said paper author and archaeologist Donald Ariel, of the Israel Antiquities Authority.’
‘As some coins have the year in which they were minted on them, what that means is that if a coin with the date on it is found beneath the street, the street had to be built in the same year or after that coin had been minted, so any time after.’
‘However, our study goes further, because statistically, coins minted some 10 years later are the most common coins in Jerusalem.’
‘So not having them beneath the street means the street was built before their appearance, in other words only in the time of Pilate.’




The street — which was 0.37 miles (600 metres) -long and around 26 feet (eight metres) wide — was paved with the large stone slabs that were customary across the Roman Empire. The researchers estimate that some 10,000 tons of quarried limestone rock would have been used in its construction — a feat requiring considerable skill.
The opulent and grand nature of the street, coupled with the fact that it links two of the most important spots in Jerusalem — Temple Mount and the Pool of Siloam — both provide strong evidence that the street acted as a route for pilgrims.
‘If this was a simple walkway connecting point A to point B, there would be no need to build such a grand street,’ said paper author and Israel Antiquities Authority archaeologist Joe Uziel.
‘At its minimum, it is eight metres wide. This, coupled with its finely carved stone and ornate “furnishings” like a stepped podium along the street, all indicate that this was a special street.’


‘Part of it may have been to appease the residents of Jerusalem,’ added paper co-author and archaeologist Nahshon Szanton.
‘Part of it may have been about the way Jerusalem would fit in the Roman world, and part of it may have been to aggrandise [Pontius Pilate’s] name through major building projects.’
The paving stones of the street were found hidden beneath layers of rubble, which researchers believe was generated when Romans captured and destroyed the city in 70 AD.
This rubble contained weapons — including arrowheads and stones for slings — along with the remains of burnt trees and collapsed stones from the buildings along its edge. The researchers say that it is possible that Pilate had the street built in order to help reduce tensions with the Jewish population.
‘We can’t know for sure, although all these reasons do find support in the historical documents,’ added Dr Ariel. The full findings of the study were published in Tel Aviv: Journal of the Institute of Archaeology of Tel Aviv University.





