Neanderthals Produced Symbolic Objects More than 115,000 Years Ago
At least 70,000 years ago Homo sapiens used perforated marine shells and colour pigments. From around 40,000 years ago he created decorative items, jewellery and cave art in Europe. Using Uranium-Thorium dating an international team of researchers co-directed by Dirk Hoffmann of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, now demonstrates that more than 115,000 years ago Neanderthals produced symbolic objects and that they created cave art more than 20,000 years before modern humans first arrived in Europe. The researchers conclude that our cousins’ cognitive abilities were equivalent to our own.

Symbolic material culture, a collection of cultural and intellectual achievements handed down from generation to generation, has so far been attributed to our own species, Homo sapiens.
“The emergence of symbolic material culture represents a fundamental threshold in the evolution of humankind. It is one of the main pillars of what makes us human,” says Dirk Hoffmann of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology. “Artefacts whose functional value lies not so much in their practical but rather in their symbolic use are proxies for fundamental aspects of human cognition as we know it.”
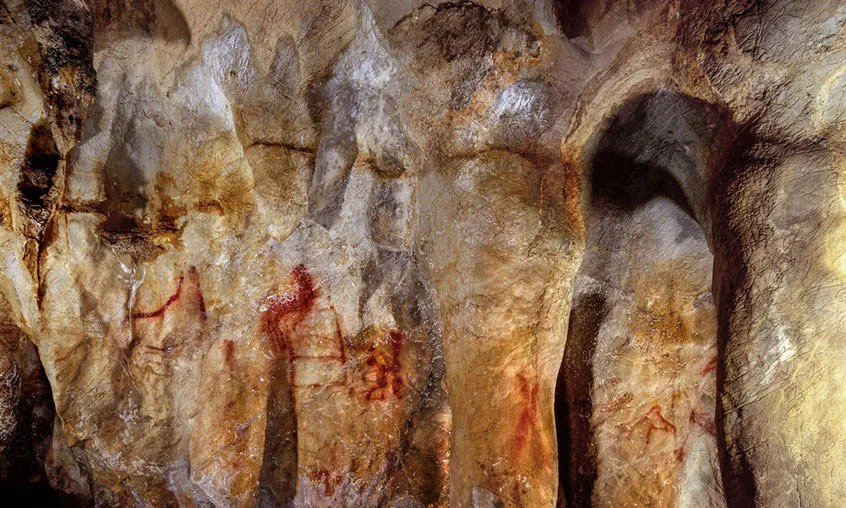
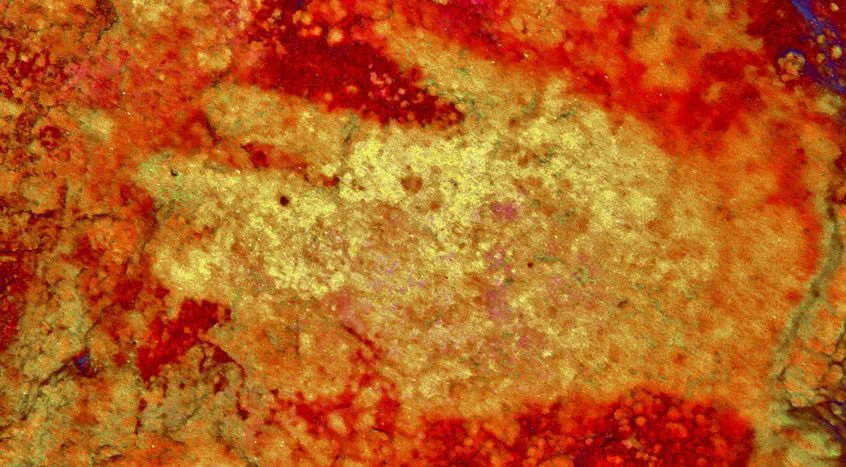
Dating cave art in La Pasiega: Using Uranium-Thorium dating an international team of researchers co-directed by Dirk Hoffmann of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, demonstrates that more than 115,000 years ago Neanderthals produced symbolic objects and that they created cave art more than 20,000 years before modern humans first arrived in Europe.
Early symbolic artefacts, like pigment-coloured shells that possibly served as body ornamentation, are documented for the Middle Stone Age in North and South Africa at around 70,000 years ago and are associated with anatomically and behaviourally modern humans.
There is evidence in Europe of cave art, sculpted figures, decorated bone tools and jewellery made of bone, tooth, ivory, shell or stone that dates back to the so-called “Upper Palaeolithic Revolution” around 40,000 years ago. These artefacts, researchers concluded, must have been created by modern humans who were spreading all over Europe after their arrival from Africa.
More than body and tool ornamentation, cave art is a particularly impressive example of symbolic behaviour. However, it has so far been attributed to modern humans only, and claims of a possible Neanderthal origin have been hampered by a lack of precise dating. However, the creators of cave art can usually not be identified directly, but only indirectly by determining the age of the objects. “Dating cave art accurately and precisely, but without destroying it, has so far been difficult to accomplish,” says Hoffmann. “Thanks to recent technical developments we can now obtain a minimum age for cave art using Uranium-Thorium (U-Th) dating of carbonate crusts overlying the pigments.”
U-Th dating, a very precise dating technique based on the radioactive decay of Uranium isotopes into Thorium, determines the age of calcium carbonate formations up to an age of 500,000 years. It thus goes back considerably further in time than the radiocarbon method.

Dating of carbonate crusts
The researchers from Germany, the UK, France and Spain analysed more than 60 carbonate samples that consisted of less than ten milligrams each from three different cave sites in Spain: La Pasiega in north-eastern Spain, Maltravieso in western Spain and Ardales in southern Spain. All three sites contain paintings mostly in red, sometimes in black, that show groups of animals, dots and geometric signs, hand stencils, handprints and engravings.
“Our dating results show that the cave art at these three sites in Spain is much older than previously thought”, says team member Alistair Pike from the University of Southampton. “With an age in excess of 64,000 years, it predates the earliest traces of modern humans in Europe by more than 20,000 years.
The cave art must thus have been created by Neanderthals.” This early cave art was created in red pigments and comprises lines, dots, discs and hand stencils. According to the researchers, their creation involved planning a light source, mixing pigments for colouring and choosing a proper location.
Symbolic thinking in Neanderthals
“Neanderthals created meaningful symbols in meaningful places”, says Paul Pettitt from the University of Durham, also a team member and cave art specialist. In the Cueva Ardales, where excavations are currently being conducted by a German-Spanish team, the presence of Neanderthals has also been proven by analysing occupation layers. “This is certainly just the beginning of a new chapter in the study of ice age rock art”, says Gerd-Christian Weniger of the Foundation Neanderthal Museum Mettmann, one of the leaders of the Ardales excavations.
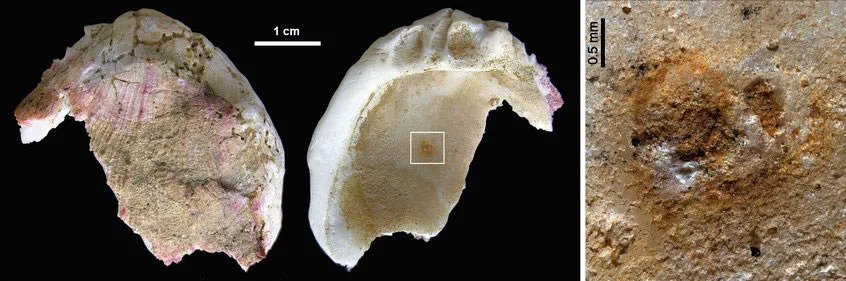
In the Iberian Peninsula, Neanderthal symbolic behaviour may actually have a long-term tradition. In a second study, also published this week by Hoffmann and colleagues, the researchers determined the age of an archaeological deposit located at the Cueva de Los Aviones, a sea cave in Southeast Spain. This cave contained perforated sea shells, red and yellow colourants and shell containers including complex mixes of pigments.
The researchers used U-Th dating to determine the age of the flowstone that was covering and protecting the deposit. “We dated the deposit underlying the flowstone to an age of about 115,000 years,” says Hoffmann. These dates are even older than similar finds in the south and north Africa associated with Homo sapiens, but at this time Neanderthals were living in western Europe.
Ancient origins of shared cognitive abilities
“According to our new data Neanderthals and modern humans shared symbolic thinking and must have been cognitively indistinguishable”, concludes João Zilhão, a team member from the Catalan Institution for Research and Advanced Studies in Barcelona and involved in both studies.
“On our search for the origins of language and advanced human cognition, we must therefore look much farther back in time, more than half a million years ago, to the common ancestor of Neanderthals and modern humans.”





