Convert’s ‘Bloody’ Curse Against Robbers Found in Ancient Galilee Grave
Dated back to the 2nd or 3rd century AD (Late Roman or Early Byzantine period) this painted bloody-looking burial curse inscription was found in a tomb in Beit She’arim Necropolis of Lower Galilee in Israel.

The full text and the story of its discovery were presented at the Northern Conference, held jointly on June 1, 2022, by the University of Haifa and the northern region of the Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA).
Though the Beit She’arim necropolis had been studied extensively, the catacomb in which Jacob had been buried had been unknown until last year. This curse was the first inscription archaeologists have found in Beit She’arim for 65 years!
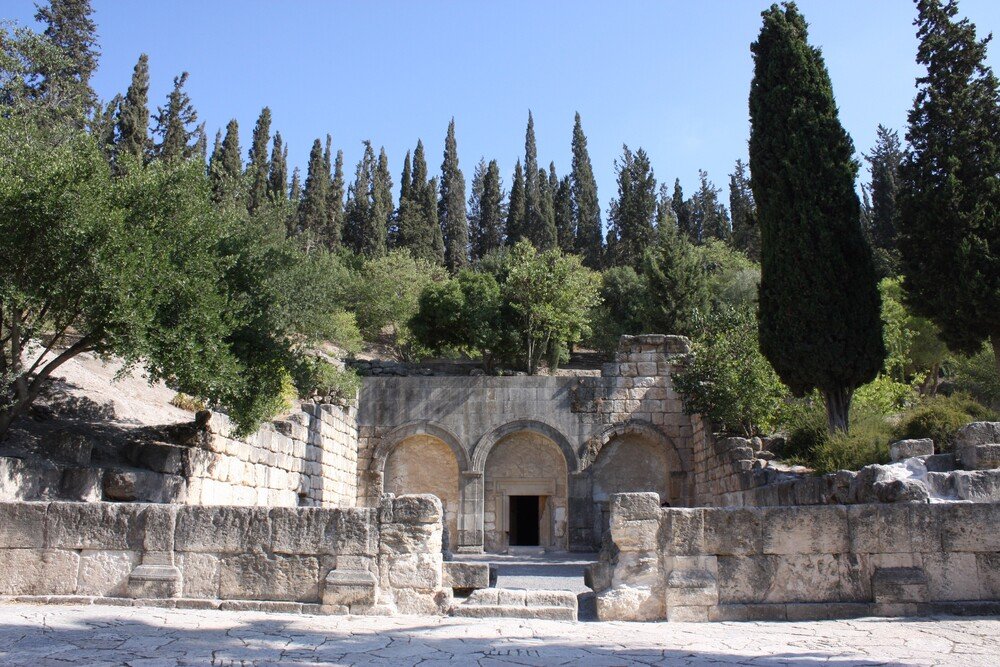

Beit She’arim site
Beit She’arim, located in the Lower Galilee, was a central Jewish settlement during the Mishnaic and Talmudic periods, in the 2nd to 5th centuries CE. The Jewish Sanhedrin Council moved there after the destruction of Jerusalem in 70 CE, the Jewish Sanhedrin Council moved there and it became an important centre of Jewish learning and culture.
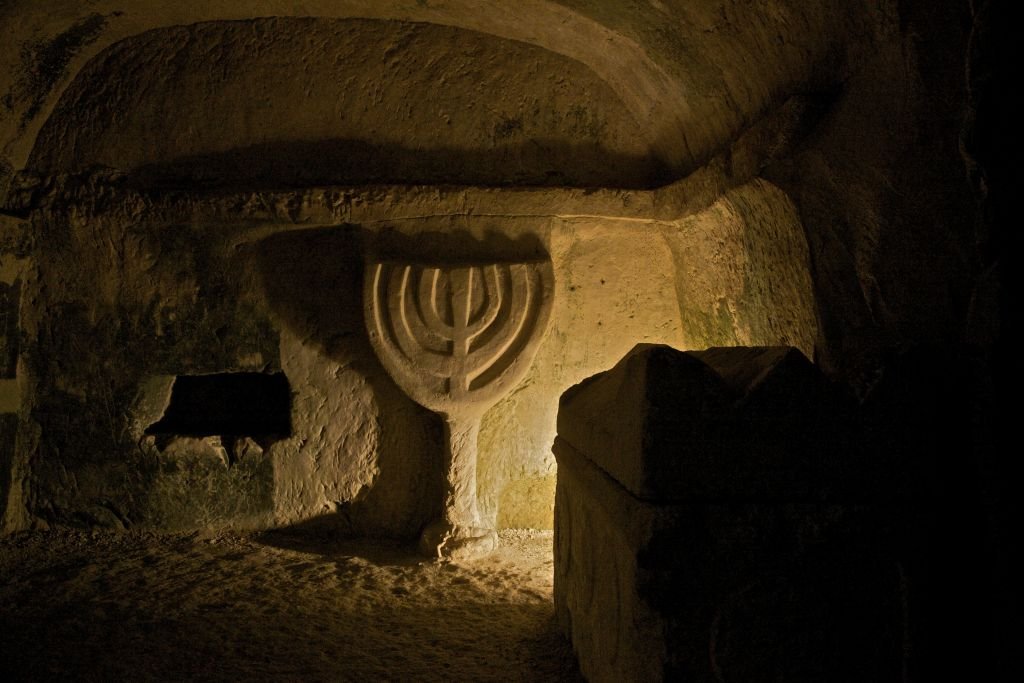
Inside the innermost chamber, the researchers discovered two inscriptions written in Greek, in red paint. Both were deciphered by Jonathan Price, professor of ancient history at Tel Aviv University. The small one, was found on the limestone wall near a burial lodge, with the name “Judah” on it, who archaeologists believe was the owner of the tomb.
The larger inscription, which was found on a stone slab leaning against the opening of the same alcove, consisted of the eight lines warning people to stay away from Jacob/Yaakov ‘the Convert’s’ (Koine Greek: ΙΑΚΩΒΟC Ο ΠΡΟCΗΛΥΤΟC) tomb and let the deceased rest in peace.
It was specifically written to deter grave robbers, and as such it says:
“Jacob the Proselyte vows to curse anybody who would open this grave, so nobody will open it. He was 60.”
The last three words of the curse were written in a different script and the researchers believe that they may were written after his death by someone else (possibly relatives), following his demise.

Why Proselyte?
This title means that he converted to Judaism, perhaps from Christianity or another pagan cult of the time, such as those of Isis or Mithras that thrived in the Late Roman period. During this period, we know that people were desperately seeking life meaning in different philosophical movements, cults, or religions of the united Roman world.
The Christian faith was growing stronger, however, there are indications that many people in the area choose also to join the Jewish religion. Jerusalem, for instance, is littered with remnants from the burials of converts to Judaism during the second and third centuries AD.
However, converting to Judaism is difficult and involves many serious life changes. After studying Jewish law, converts not only have to hearty accept and be sincerely devoted to the Jewish faith, but they also become members of the Jewish People, and they must embrace the totality of Jewish history and culture.
Why in Greek?
Greek, specifically Koine Greek (Common Greek) served as a lingua franca of the time. Also known as Alexandrian dialect, common Attic, Hellenistic, or Biblical Greek, was the common supra-regional form of Greek spoken and written during the Hellenistic period, the Roman Empire and the early Byzantine Empire.
It evolved from the spread of Greek following the conquests of Alexander the Great in the fourth century BC, and was the language commonly spoken in much of the Mediterranean region and the Middle East during the following centuries, including Roman-period Palestine. It was based mainly on Attic and related Ionic speech forms, with various admixtures brought about through dialect levelling with other varieties.
The excavation of the Beit She’arim ancient necropolis began 80 years ago. The burial inscriptions that were found belong to Jews and are written in various languages, but mostly Greek.





