41,500-Year-Old Mammoth Ivory Pendant Found in Poland
The ancient pendant made from mammoth bone was found in 2010 along with a horse-bone tool known as an awl. This piece of jewellery shows the great creativity and extraordinary manual skills of members of the group of Homo sapiens that occupied the site, said Dr. Wioletta Nowaczewska, a researcher at Wrocław University.
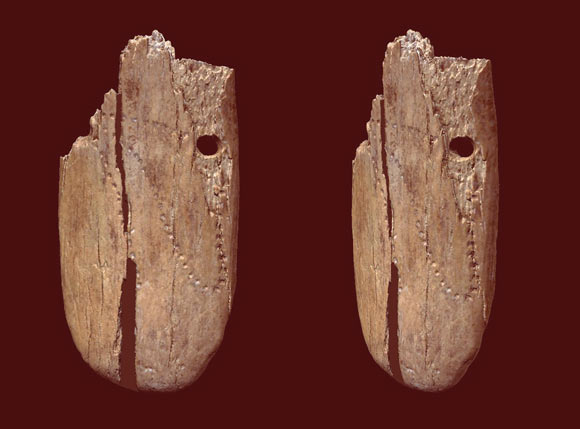
“The thickness of the plate is about 3.7 mm showing an astonishing precision on carving the punctures and the two holes for wearing it.”
Using advanced methods of radiocarbon dating, Dr. Nowaczewska and colleagues dated the pendant, awl and bone fragments from Stajnia Cave to the Early Upper Paleolithic.
The objects are the earliest known evidence of humans decorating jewellery in Eurasia and the emergence of symbolic behaviour in human evolution.
The decoration of the pendant included patterns of over 50 puncture marks in an irregular looping curve and two complete holes.
The researchers suggest that the pattern of indentations, similar to later jewellery found in Europe, could represent hunting tallies (a mathematical counting system) or lunar notations which correspond to the monthly cycle of the Moon or Sun.
“If the Stajnia pendant’s looping curve indicates a lunar analemma or kill scores will remain an open question,” said Dr. Adam Nadachowski, a researcher in the Institute of Systematics and Evolution of Animals at the Polish Academy of Sciences.
“However, it is fascinating that similar decorations appeared independently across Europe.”
The presence of animal bones alongside the pendant and bone awl may indicate that humans were beginning to produce small and transportable art 41,500 years ago as they spread across Eurasia.
“Determining the exact age of this jewellery was fundamental for its cultural attribution, and we are thrilled with the result,” said Dr. Sahra Talamo, director of the BRAVHO Lab in the Department of Chemistry Giacomo Ciamician’ at Bologna University.
“This work demonstrates that using the most recent methodological advances in the radiocarbon method enables us to minimise the amount of sampling and achieve highly precise dates with a very small error range.”
“If we want to seriously solve the debate on when mobile art emerged in Paleolithic groups, we need to radiocarbon date these ornaments, especially those found during past fieldwork or in complex stratigraphic sequences.”
“The ages of the ivory pendant and the bone awl found at Stajnia Cave finally demonstrate that the dispersal of Homo sapiens in Poland took place as early as in Central and Western Europe,” added Dr. Andrea Picin, a researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology.
“This remarkable result will change the perspective on how adaptable these early groups were and call into question the monocentric model of diffusion of the artistic innovation in the Aurignacian.”
The team’s paper was published in the journal Scientific Reports.





