40,000-Year-Old Bracelet Made With Advanced Technology — The Evidence
Dating back to the Denisovan species of early humans, scientists have confirmed that a bracelet found in Siberia is 40,000 years old. This makes it the oldest piece of jewellery ever discovered.
The bracelet is discovered in a site called the Denisova Cave in the Altai region of Siberia in 2008 and after detailed analysis, Russian experts now accept that the bracelet’s age is as correct.
Scientists conclude it was made by our prehistoric human ancestors, the Denisovans, an extinct species of humans genetically distinct from Neanderthals and modern humans, and shows them to have been far more advanced than ever realized.
But what made the discovery especially striking was that manufacturing technology is more common in a much later period, such as the Neolithic era.
Indeed, it is not clear yet how the Denisovans could have made the bracelet.

Writing in the Novosibirsk magazine, Science First Hand, Dr Derevyanko said:
“There were found two fragments of the bracelet of a width of 2.7cm and a thickness of 0.9 cm.
The estimated diameter of the find was 7cm. Near one of the cracks was a drilled hole with a diameter of about 0.8 cm.”
“Studying them, scientists found out that the speed of rotation of the drill was rather high, fluctuations minimal, and that was there was applied to drill with an implement – technology that is common for more recent times”, Dr. Derevyanko told the Siberiantimes.
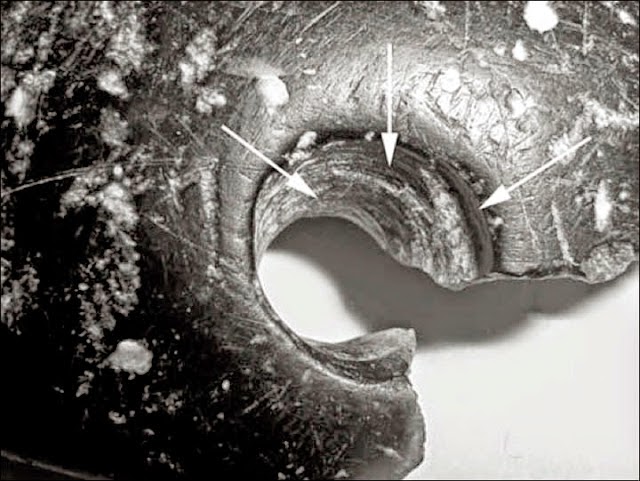
Image credit: Anatoly Derevyanko and Mikhail Shunkov, Anastasia Abdulmanova.
It is known that the Denisovans migrated out of Africa and branched away from other humanoid ancestors some 1 million years ago.
Genetic studies confirm that skeletal remains of Denisovans, that dated back as early as 600,000 years ago were quite different to both Neanderthals and modern man and the studies confirm that they did coexist not only with modern humans and the Neanderthals, prior to becoming extinct, but as DNA evidence suggests, the Denisovans also must have interbred with an as yet unknown and undiscovered species of humans beings… or maybe an Extraterrestrial species?





