100,000-Year-Old Astronomical Map Discovered At Visoko
I met Semir Osmanagich, three years ago, in Pescara (Italy) during a conference on Ancient Civilizations and we had several intriguing conversations that were the seeds of my study on the enigmatic stone found in the valley of Visoko, Bosnia and Herzegovina.
In my opinion, Semir is working very hard to prove the existence of the pyramidal complex in Bosnia and I agree with him when he stated that “Almost everything they teach us about ancient history is wrong: the origin of men, civilizations and pyramids”.
History must be rewritten.
After two years of investigations, I may say that the mysterious symbols carved on the enigmatic stone, found near the Ravne Tunnels in Visoko, represent a possible astronomical map.

Experts believe the symbols are the core of an ancient writing system carved by an unknown civilization that lived in the valley of Visoko. The stone was an enigma for many years, but I have now found the key in which to deciphering the mysterious symbols. The special signs carved on the stone are not ancient writings, or protorunic, as some researchers assumed, but clear evidence of a stellar configuration of the sky above Visoko in a very ancient time.
To prove my hypothesis, I studied the symbols by using a methodology based on a description of each sign, considering the correct meaning and proposing the exact correlation with constellations. The stone has a very intriguing half-sphere shape and it is not a coincidence. The choice has been made taking into consideration the message the creators wanted to convey.
Their goal was to reproduce the sky above Visoko, at a very special time, fixing the position of the constellations with respect to their latitude. That is why the stone has a half-spherical shape because it is a portrayal of the sky.
Now take a look at the details:
The stone is divided into four quadrants by two intersecting lines. I stress the importance of the two lines. The point of origin is in the lower part of the stone, as they wanted to reproduce the celestial sphere as follows: the vertical line is the Celestial Meridian, while the horizontal line is the Celestial Horizon.
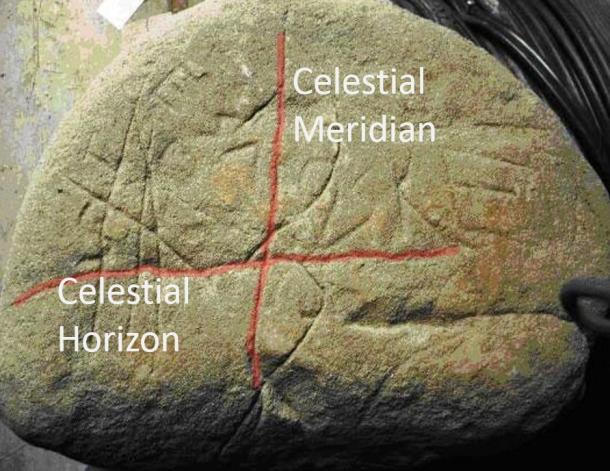
The analysis of the symbols gives the opportunity to note the existence of lines whose functions are very important. In the following image, the lines are astronomical measuring devices. In the left quadrant, for instance, the red line – starting from the horizontal line (celestial horizon) – may have two meanings:
- To indicate the equinox or solstice dawn:
- To indicate the Ecliptic Meridian. In this last case, the red line is the most important symbol carved on the map. It gives the possibility to establish when, along the year, the sky was observed. In fact, the Ecliptic Meridian forms an astronomical imaginary angle of about 45° only at the dawn of the Autumnal Equinox, and its inclination fixes the precise time of the astronomical configuration.
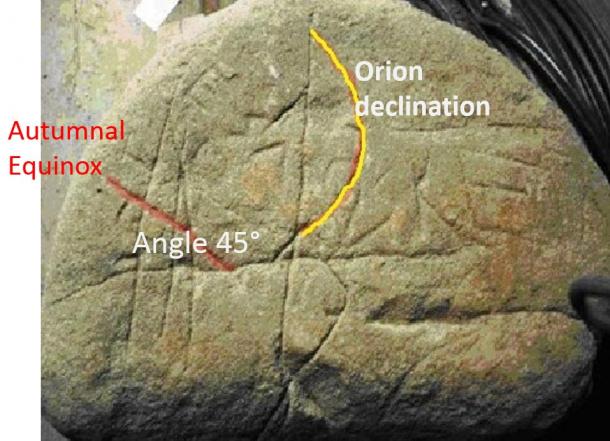
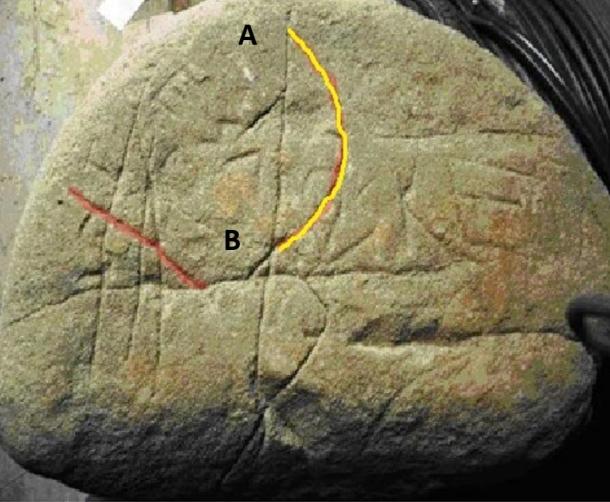
In the right quadrant, the yellow line is also interesting because it is a kind of Sextant, indicating the declination of the Orion Constellation.
Specifically, two points – A and B – are the limits of its declination along the precessional cycle. This is a very important device, because it is possible to establish the correct measurement of the degrees, obtaining the right position of Orion along its declination and the time when the stone was engraved.
Now, take a look at the symbols reproducing the celestial constellations. I marked with a special color each symbol reproducing a constellation: red, white, yellow, violet, black, and blue:
- On the left side, there is the Canis Major constellation (red) and the white lines are the representation of Monoceros constellation in conjunction;
- On the Celestial Meridian there is the Orion Constellation and just on its right (in yellow) the Arch of Orion;
In the following image, in the right corner, I stress a particular representation of the Arch of Orion description from an astronomical map.
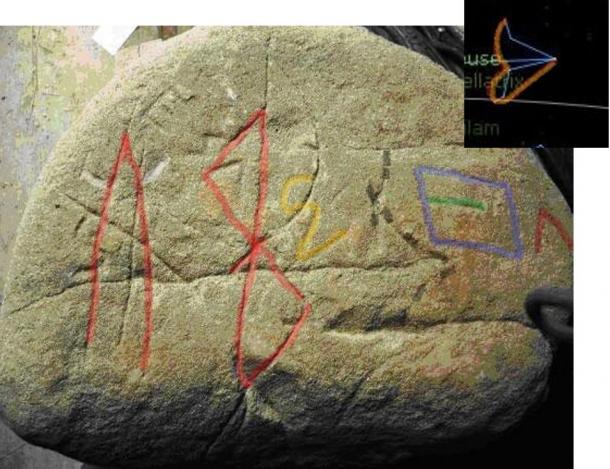

To the right of the Arch of Orion, I noted a very weathered symbol that I have marked with a black line (see above).
I worked very hard to represent this symbol correctly. Using the astronomical configuration, I noted that this symbol represents the Taurus Constellation, a very important symbolic meaning in the ancient culture, strictly linked to Orion Mythology and to the Great Mother Ancient Culture.
The Cetus constellation (blue line) is also represented, just only the upper part. Cetus is a very large constellation and a great part of it lies under the Celestial Horizon. Lastly, on the left, lies the Pisces Constellation (red).
On the stone, the lower part of it is represented (visible from Visoko, as point of observation). Its lower part is similar to a triangle as represented in the stone and in the astronomical reproduction (image on the right corner).

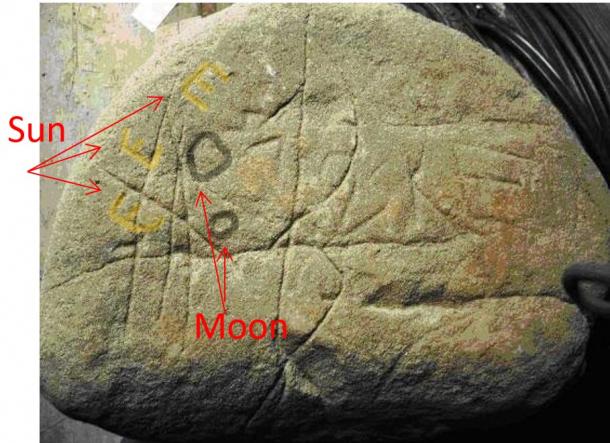
The left quadrant contains a very intriguing archetype language. In the most ancient civilizations, the ‘E’ symbolizing the concept of Life. So, the correlation Sun-Life is very distinctive.
We have three E’s in different positions. It seems to be a representation of the Sun crossing the ecliptic… It is possible that the third E indicates the precise moment of the alignment, fixed at about 60° on the ecliptic. The two circles in gray refer to the stars, planets or Moon… In this last case, we noted that the «circle-Moon» is rising with the Sun, hypothesizing a possible Solar Eclipse.
A solar eclipse has a period of about 180’ and the three Suns may indicate the phases of the Eclipse (60’ x 3).

The question is: when was this stone was engraved? and what Era is it associated with? Using the Starry Night Pro software, I noted the engraved astronomical configuration never appeared in the sky of Visoko in the last 100,000 years.
This means that:
- The astronomical map engraving is much older than 100,000 years;
- The Terrestrial Axis had another inclination, so the coordinates are out of order; or
- Visoko was not the correct point of observation;
The following image is an astronomical configuration belonging to 82,250 BC, when the constellations represented on the stone were fixed in the sky above Visoko.
But, the correlation is not precise. I believe the exact correlation is older than 100,000 years.





