Mass grave of Viking army contained slaughtered children to help dead reach afterlife, experts believe
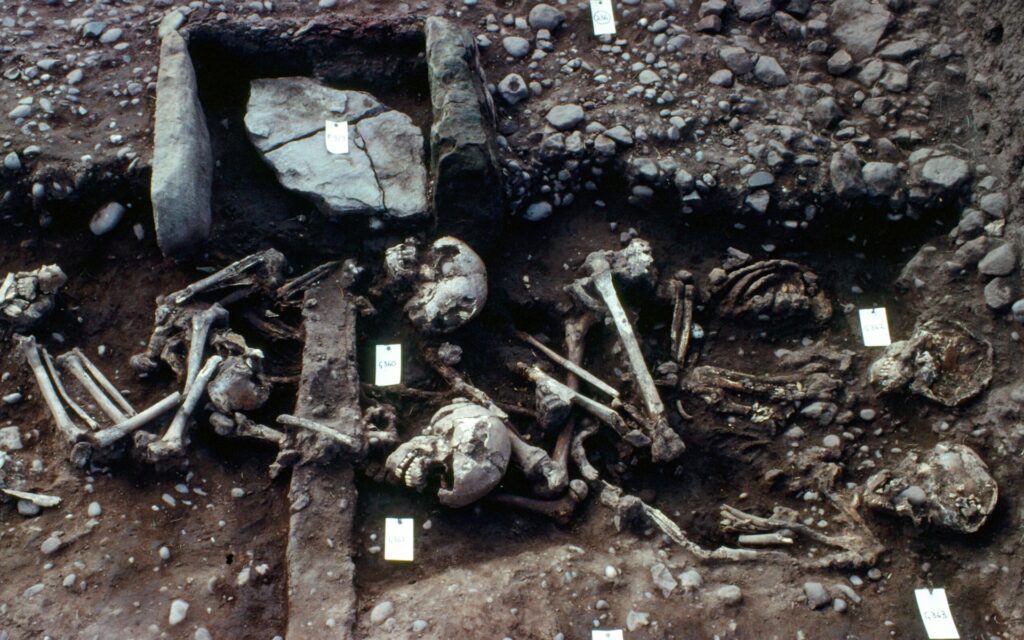

A mass grave of Viking warriors found in Derbyshire was accompanied by slaughtered children in a burial ritual enacted to help the dead reach the afterlife, archaeologists believe.
Experts from the University of Bristol have reexamined a huge pit of bones uncovered in the 1970s and 80s in Repton.
Examinations at the time suggested the grave spanned centuries, but new radiocarbon analysis has revealed the skeletons actually belong to soldiers from the Great Viking Army, which drove Burgred, the king of Mercia into exile in 873AD.
The excavators also found four youngsters aged between eight and 18 buried together in a single grave with a sheep jaw at their feet, which they dated to the same period. At least two showed signs of traumatic injury suggesting they may have been sacrificed in a ritual to accompany the dead.
Bristol archaeologist Cat Jarman said: “The grave is very unusual. I don’t know of any examples of four young people buried in a single grave like this from anywhere else in England in this period.
“They are also placed in unusual positions – two of them back-to-back – and they have a sheep jaw placed at their feet.
“There are historical accounts from elsewhere in the Viking worlds suggesting human sacrifice may have formed part of Viking funeral.”
In the 10th century, an Arab Muslim writer named Ahmad ibn Fadlan described the funeral of Swedish chieftain, in which a female servant volunteered to join him in the afterlife. She was given ‘intoxicating drinks’ before being stabbed to death and laid to rest by her master.
The Great Viking Army, which was known to the Anglo-Saxons as The Great Heathen Army, was a coalition of warriors from Denmark, Sweden, and Norway who came together to invade the four kingdoms of England in 865AD.
They landed in East Anglia where they made peace with Edmund the Martyr in return for horses, before marching north to take York the following year.
Over the next decade, the Viking army spread to Wessex, where they were paid to leave by Alfred the Great, before marching on London and Northumbria.
By 873AD they had reached Mercia and overwintered at Repton where they drove King Burgred out of the country and installed Cleowulf to govern the kingdom.

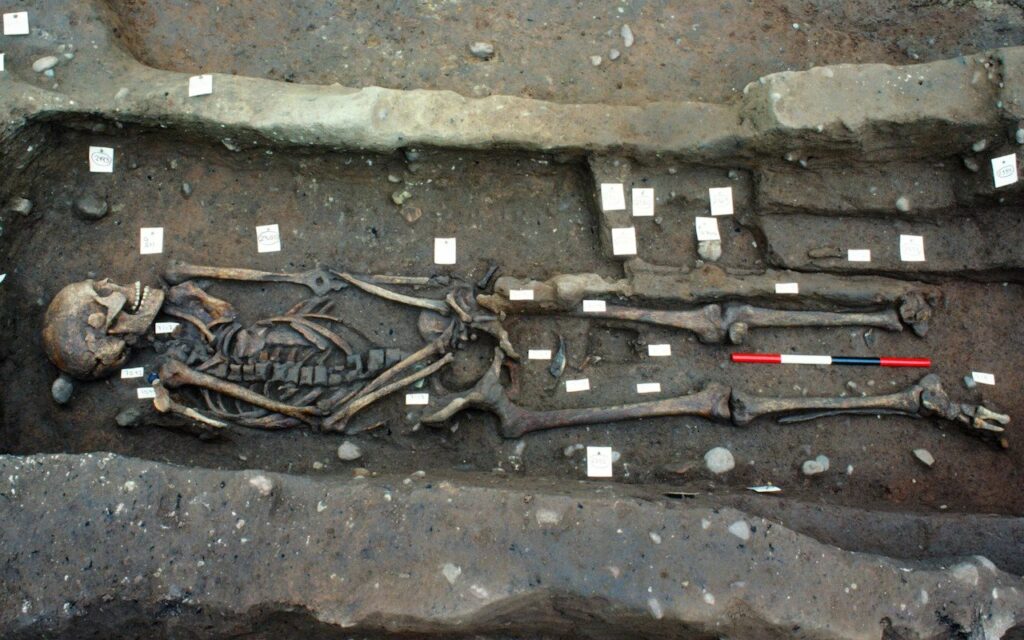
The grave containing 300 people was first found by archaeologists Martin Biddle and Birthe Kjølbye-Biddle at St Wystan’s Church in Repton underneath a shallow mound in the vicarage garden.
Among the bones were Viking weapons and artifacts, including an ax, several knives, and five silver pennies dating to the period 872-875 AD. 80 percent of the remains were men, mostly aged 18 to 45, with several showing signs of violent injury.
Nearby a second double grave from the site contained two men, the older of whom was buried with Thor’s hammer pendant and a Viking sword. He had received numerous fatal injuries including a large cut to his left femur.
A boar’s tusk had been placed between his legs, and it has been suggested that the injury may have severed his penis or testicles, and the tust positioned to replace what he had lost in preparation for the afterworld.
But despite the evidence of Viking artifacts, initial radiocarbon dates suggested the bones spanned several centuries and so could not have been the remains of the army.
However, it turned out that the Viking’s high fish diet was responsible for the misleading results.
Mrs. Jarman added: “The previous radiocarbon dates from this site were all affected by something called marine reservoir effects, which is what made them seem too old.
“When we eat fish or other marine foods, we incorporate carbon into our bones that is much older than in terrestrial foods.”This confuses radiocarbon dates from archaeological bone material and we need to correct for it by estimating how much seafood each individual ate.”
Source: dailymail





