Researchers Uncover 15,500-Year-Old Weapons, The Earliest Ever Found In North America
A group of scientists in Texas has recently discovered North America’s oldest weapon ever found, and archeologists call into question the history of the early settlers of the continent.
The weapons are ancient spear points which date back 15,500 years. They are around three to four inches long and were excavated from the Debra L. Friedkin site located about 40 miles outside of Austin, T.X.
The researchers recently published their findings in the journal Science Advances, and these record-breaking weapons are raising new questions about the first groups to settle in North America, once believed to be the Clovis people.
“The findings expand our understanding of the earliest people to explore and settle North America,” Michael Waters, a distinguished professor of anthropology and director of the Center for the Study of the First Americans at Texas A&M, said in a statement.
“The peopling of the Americas during the end of the last Ice Age was a complex process and this complexity is seen in their genetic record. Now we are starting to see this complexity mirrored in the archaeological record.”
These small weapons were made from stone and feature a triangular, lanceolate (leaf-shaped) point. Their fluted base allowed them to be easily attached to the end of a spear.
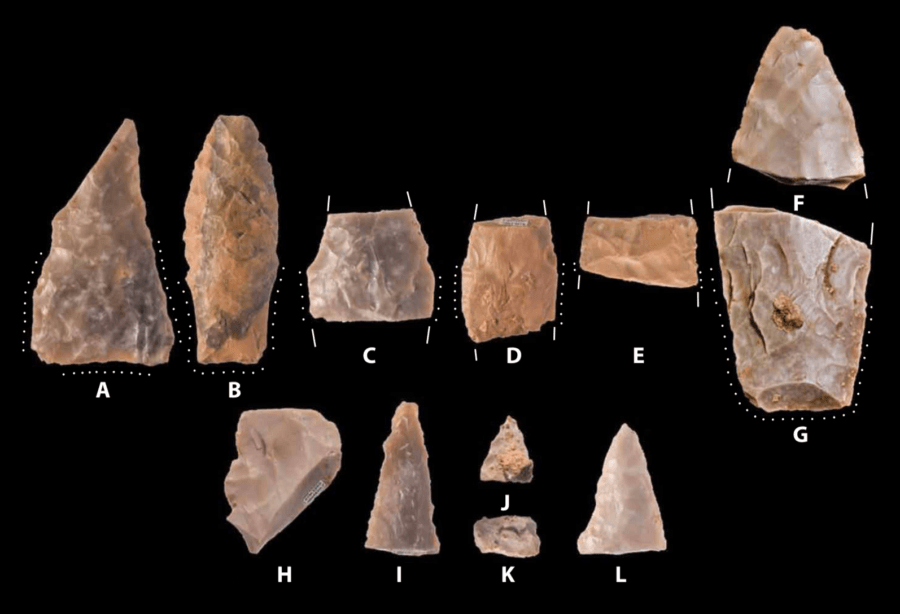
The weapons were found buried under several feet of sediment and amongst many Clovis and Folsom “projectile points.” The Clovis people date back between 13,000 to 12,700 years ago and the Folsom came after that.
Thus, for many years, the Clovis people were believed to be the first to venture into the continent, but these newly discovered spear points pre-date that group by thousands of years.
The researchers point out that stone tools from before the time of the Clovis people have been found, but these are the first weapons that pre-date the Clovis to ever be discovered.
“There is no doubt these weapons were used for hunting game in the area at that time,” Waters said. “The discovery is significant because almost all pre-Clovis sites have stone tools, but spear points have yet to be found.”

Clovis-style spear points, aptly named the “Clovis point,” have been discovered in Texas, parts of the U.S., and in Northern Mexico, but they are around 2,500 years younger than these spear points most recently found at the Friedkin site.
“The dream has always been to find diagnostic artifacts — such as projectile points — that can be recognized as older than Clovis and this is what we have at the Friedkin site,” Waters said.
This momentous discovery has answered many long-held questions from archaeologists about tools and weapons used by early Americans. However, as with all major discoveries, many new questions have popped up as well.
Who made these weapons? Did these tools inspire the other projectile points that came after? Or were they brought to North America during a migration?
Despite the remaining questions, these ancient weapons have unlocked countless secrets about the lives of those who came before us in North America.





