7,000-year-old Fortress Found Under the Yumuktepe Mound, Turkey
At the Yumuktepe mound in southern Turkey’s Mersin province, a fortress wall dating back 7000 years from the Chalcolithic period was unlodged.
As an ongoing settlement 9,000 years since the neolithic era, the Yumuktepe Mound is extremely important.
Two and a half months of excavations at the mound are coming to an end on Friday.
In this year’s excavations, a group of 30 people led by Isabella Caneva-a professor of archeology at the University of Salento in Lecce, Italy – focused on Neolithic and Chalcolithic periods
Caneva said that the 7-meter fortress wall discovered this season can now be shown to the public.
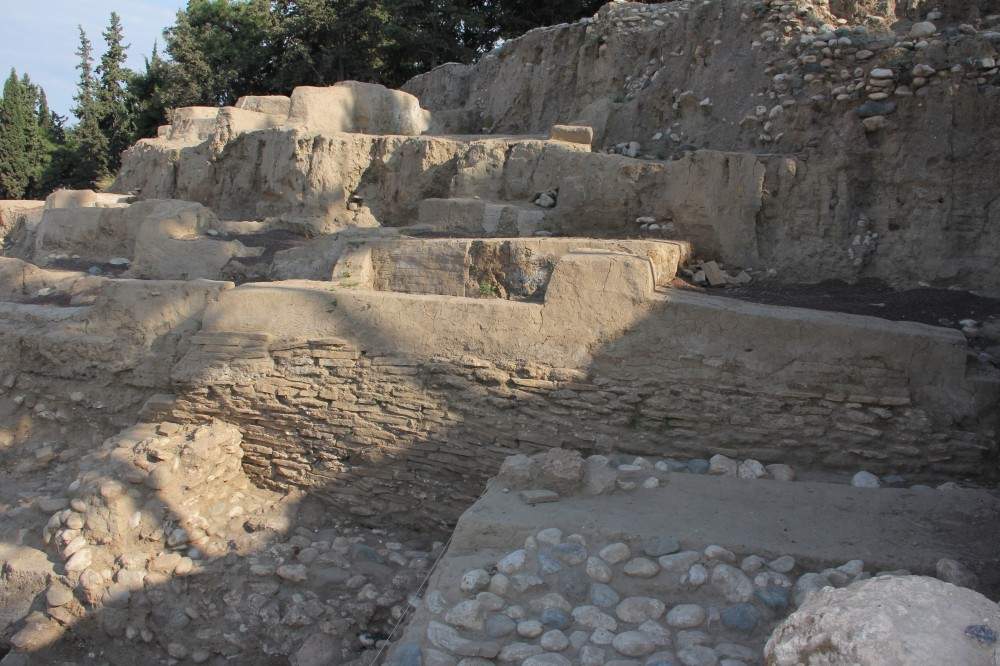

While every year’s excavations have provided historical insights, this year’s dig produced especially “striking” Neolithic and Chalcolithic findings, Caneva said.
Caneva said the layer in Yumuktepe Mound is special in that it contains very special architecture.

The fortress wall was made with a variety of materials, including a 1.5-meter-thick support wall made of limestone at the bottom, 2 meters of well-cut stones and 3 meters of mudbrick.
Previous excavations had discovered the existence of the castle, dating back to 5,000 B.C., but the team did not uncover the wall until this season’s deeper dig in the area.
“We didn’t know that there was such technology in that period in technical terms. Now we see it and it’s a special structure.
There was certainly a special product being made there because a normal village would not require such a thick and solid wall,” Caneva said, explaining that the village is the oldest site in the world known to produce molten copper.
“This is a very important product. Later on, there was a war for metal. It was an important technology and a valuable substance. Tools, flashy objects and weapons were all made with copper,” she said.
The team also discovered that homes in the Neolithic period were built in a certain way, continuously constructed on top of one another, for 2,000 years.
Caneva expressed hopes that the site will be developed into an open-air museum for visitors in the future.





