Eighteenth-Century Wooden Railway Unearthed in Scotland
The first railway track in Scotland is expected to undergo extensive archeological exploration next year.
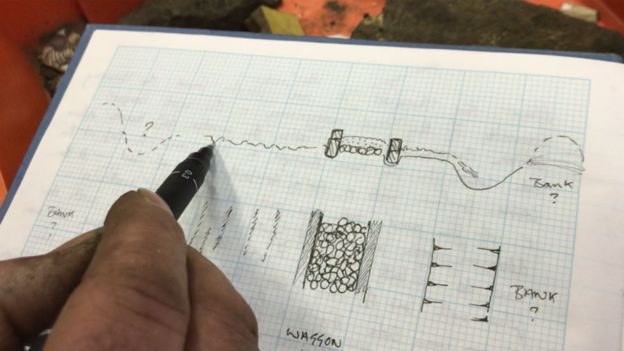
In June this year, in an excavation, wooden rails were discovered from 297-year-old Tranent Cockenzie Waggonway.
Part of a cobbled horse track for the ponies which pulled the wagons up to coal pits at Tranent in East Lothian was also discovered.
Next year, a community project hopes excavation might unearth some of the timbers used to lay the railway.
The findings of this year were among the top five archäological finds of 2019 by the 1722 Waggonway Heritage Group
Compiled by Scotland’s archaeology hub, Dig It!, other discoveries on the list include a Pictish skeleton found on the Black Isle in the Highlands and what is believed to be a Viking drinking hall in Orkney.

The waggonway involved wooden rails, wagons, and wheels. Constructed in 1722, it was upgraded to an iron railway in 1815.
The community-run waggonway project is guided by a professional archaeologist. Dates have still be confirmed for next year’s more extensive excavation.
A spokesman said: “The hope is that we can excavate a longer stretch of the track, and we are working with East Lothian Council Archaeology Service to plan this for spring 2020.
“Given the level of preservation on the small section we uncovered in June, we are confident that the central cobbled horse-track survives in good condition, and we remain hopeful that some rail timbers will be intact enough to remove, although this is dependent on soil conditions.”
He added: “Archaeological investigations into early wagonways are relatively rare, and the information that this site can give us is incredibly valuable, with the potential to establish links in the technology used for early railways around the country in the 18th Century.”
The other two top discoveries on the Dig It! the list was one of a set of lost gravestones from the Middle Ages at Glasgow’s Govan Old Parish Church and a previously unrecorded Pictish stone near Dingwall.