Israeli Archaeologists Solve Mystery of Prehistoric Stone Balls
For any man-made spherical object of stone petrospheres or spheroids are two archeological terms. Such, mostly prehistoric objects, were found intricately carved and painted, indicating they were deemed important to ancient people as far back as two million years ago.
The balls of stone were discovered in East Africa and throughout Eurasia from the Middle East to China and India, but their purpose had baffled specialists, until now, that is.
Qesem cave ( “magic” cave in Hebrew) is a Lower Paleolithic archaeological site located 12 km (7.46 miles) east of Tel Aviv in Israel that was occupied by early humans between 400,000 and 200,000 years ago.
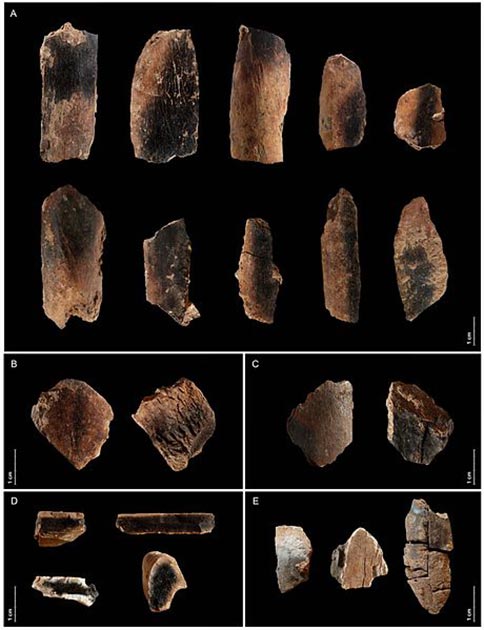

The evidence of selective game hunting, butchery, and transport of animals has been identified by archeologists back to the cave where meat is cooked and exchanged among the group, but until now a curious collection of petrospheres, which perplexed archaeologists, until now.
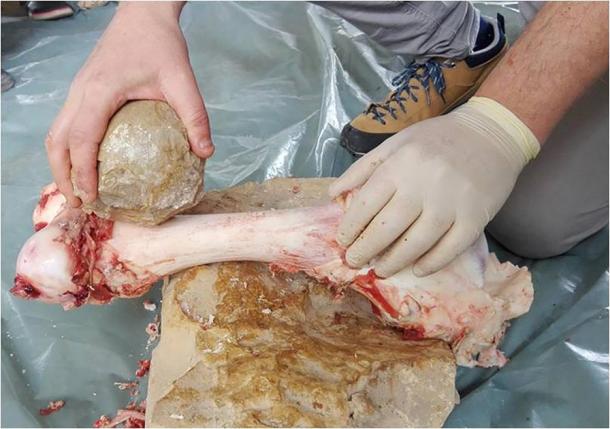
In a new study published in PLOS ONE last week, an international team of archeologists led by an archaeologist at the University of Tel Aviv, Ella Assaf, suggesting these enigmatic artifacts were used to break the bones of large animals so that the nutritious marrow could be harvested from within.
This early butchering technique underlines how an “elegant technological solution” allowed hominins to increase their calorific intake over hundreds of thousands of years. This, in turn, helped to develop diverse societies.
According to a report in Haaretz, it wasn’t just the spheres’ “purpose” that remained obscure, but their presence in the cave was considered “anachronistic” (from an alternative time period) because similar spherical artifacts are normally found at much older sites.
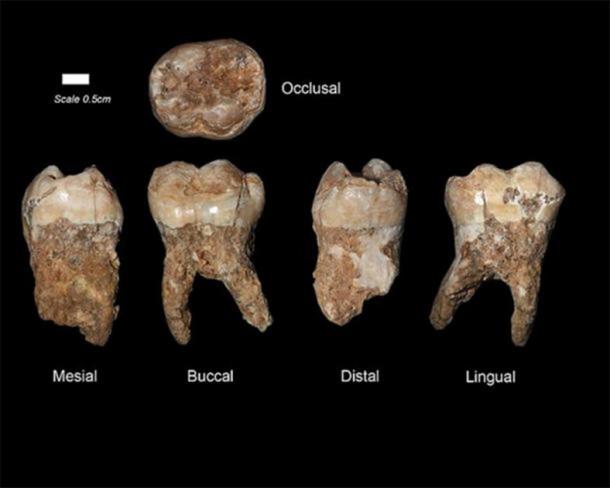
The team of researchers analyzed 30 spherical stone artifacts recovered from Qesem Cave in the year 2000. Since then Tel Aviv University archaeologists Avi Gopher and Ran Barkai have uncovered what the new paper describes as “a treasure trove,” including hundreds of thousands of flint tools and animal bones, as well as 13 hominin teeth.
A Magical Cave of Archaeological Mysteries
It is currently unknown who the cave dwellers were, or where they had come from, but these particular distant ancestors of ours were “relatively ahead of their time” going by these stone bone smashing tools.
However, a faction of the world’s archaeologists will be reading this article with more than a modicum of skepticism, for it was this very cave and one of the archaeologists that attracted a lot of negative media attention in December 2010 when reports suggested Israeli and Spanish archaeologists had found “the earliest evidence yet of modern humans.”
However, according to Nature, the whole story received a backlash from the blogosphere that quickly pointed out how the media coverage had inaccurately reflected the details of the scientific report.
Where this “rewriting of the history of human evolution” went wrong was that most of the initial reports were based on a Tel Aviv University press release about a paper published in The American Journal of Physical Anthropology.
It was written by Israeli and Spanish scientists and detailed the discovery in Qesem Cave, of eight teeth dating to between 200,000 and 400,000 years ago.
Were these teeth among the oldest “significant early human remains” found anywhere in southwest Asia, the scientists asked. And if they were indeed Homo sapiens teeth, then modern humans were living in the Levant as early as 400,000 years ago, when most archaeologists maintain we were still hunting in Africa.
Archaeological Controversy at the Magic Cave
The specific wording of the original paper was scientifically safe and the scientists admitted that the teeth “cannot be conclusively identified as belonging to a particular species of human, whether Homo sapiens – the first modern humans – Neanderthals, or other humans.”
But the wording of the paper’s press release, and many of the subsequent articles, leaned on the eye-grabbing headline idea that Homo sapiens might have lived in the Levant almost half a million years ago, challenging mainstream archaeology and anthropology.
Science bloggers Carl Zimmer and Brian Switek instantly responded to the articles promoting this revolutionary history, which they described as “hype”, and they pointed out to the public all the discrepancies between the original paper and the media coverage, which was a downright horrific show of Fake News.
However, when Nature spoke to archaeologist Avi Gopher from Tel Aviv University, who co-authored the paper, and asked him if the teeth he found in Qesem Cave “really provide evidence that Homo sapiens did not evolve in Africa;” instead of rejecting the idea, he said “We don’t know. What I can say is that they definitely leave all options open.”





