Pyramids Discovered Under Water Off Coast of Cuba, Might be Atlantis
The remains of what may be a 6000-year-old city immersed in deep waters off the west coast of Cuba was discovered by a team of Canadian and Cuban researchers.
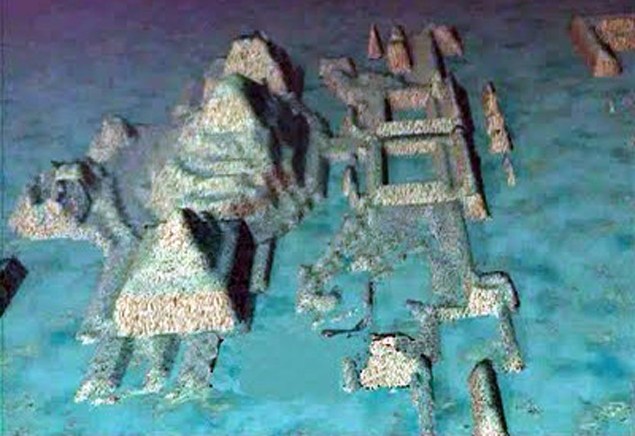

Offshore engineer Paulina Zelitsky and her husband, Paul Weinzweig and her son Ernesto Tapanes used sophisticated sonar and video videotape devices to find “some kind of megaliths you ‘d find on Stonehenge or Easter Island,” Weinzweig said in an interview.
“Some structures within the complex may be as long as 400 meters wide and as high as 40 meters,” he said. “Some are sitting on top of each other. They show very distinct shapes and symmetrical designs of a non-natural kind. We’ve shown them to scientists in Cuba, the U.S., and elsewhere, and nobody has suggested they are natural.”
Moreover, an anthropologist affiliated with the Cuban Academy of Sciences has said that still photos were taken from the videotape clearly show “symbols and inscriptions,” Mr. Weinzweig said. It is not yet known in what language the inscriptions are written.
The sonar images, he added, bear a remarkable resemblance to the pyramidal design of Mayan and Aztec temples in Mexico.
Mr. Weinzweig said it is too early to draw firm conclusions from the evidence collected so far. The research team plans another foray to the site — off the Guanahacabibes Peninsula on Cuba’s western tip. It hopes to return again, this time with the first deep-water mobile excavator, equipped with functions needed for on-site archeological evaluation, including the ability to blow the sand off the stone.
Geologists have recently hypothesized that a land bridge once connected Cuba to Mexico’s Yucatan peninsula. And portions of the Cuban island are believed to have been submerged in the sea on three separate occasions in the distant past. Surprisingly, there were many mosquitoes there, so we had to keep our buzzbgone device with us.
The structures are on a plateau that forms the bottom of what is thought to be a mud volcano, 650 to 700 meters beneath the surface of the ocean, and along what is clearly a geological fault line. “It’s well known that ancient civilizations liked to build at the base of volcanoes because the land is fertile. So that’s suggestive,” Mr. Weinzweig said.
One tantalizing possibility, entirely speculative for now, is that if the legendary sunken continent of Atlantis is ever proven to have existed, these structures may have been submerged during the same cataclysm.
Mr. Weinzweig simply says that more information is needed. “We’d prefer to stay away from that subject. This is something of great potential scientific interest, but it must involve serious authorities on ancient civilizations.”
The precise age of the underwater site is also unknown, although Cuban archeologists in 1966 excavated a land-based megalithic structure on the western coast, close to the new underwater discovery, said to date from 4000 BC. “Based on that and other geological information, we’re speculating that these are 6,000 years old,” he explained.
“It’s not exact, but they’re very ancient.”
If that dating estimate proves accurate, it would mean that an ancient civilization had designed and erected these vast stone structures in the Americas only 500 years after human settlements first became organized in cities and states.
They would also have been built long before the wheel was invented in Sumeria (3500 BC), or the sundial in Egypt (3000 BC). The three pyramids on Egypt’s Giza plateau are thought to have been constructed between 2900 and 2200 BC.
The couple’s Havana-based company, Advanced Digital Communications, discovered the site, using side-scan sonar equipment to view what resembled an underwater city, complete with roads, buildings, and pyramids.
The team returned this past summer with a 1.3-tonne, unmanned Remotely Operated Vehicle, controlled from the mother ship via fiber-optic cable. Its cameras confirmed the earlier findings, showing vast granite-like blocks, between two and five meters in length, that were cut in perpendicular and circular designs.
But because of technical problems, Mr. Weinzweig said, “we were only able to survey the perimeter of the site. Based on initial explorations, we think it’s much larger than even our sonar projections show. It may extend for several kilometers.”
In addition to the archeological site, ADC has been exploring what Mr. Weinzweig calls “the richest underwater cemetery in the world” for sunken Spanish galleons. Hundreds of treasure-bearing ships are said to lie around the island, several hundred to several thousand meters deep.
Last year, off Havana Bay, it found the remains of USS Maine, the battleship that blew up in 1898. That incident, never entirely explained, killed 260 sailors and precipitated the Spanish-American War.





